GUI System Development
Last Updated on : 2025-10-22 06:49:08download
This topic describes how to develop a GUI system based on the T5 platform, with details of the system framework (communication and application) and interfaces. It also provides reference materials on system resources, along with guidance for system debugging, compilation, and demos.
Communication framework
The system communication framework is used to implement communication between CP0 and CP1.
CP0 and CP1 are the two CPUs of the T5:
- CP0: Handles IoT platform communication.
- CP1: Manages the graphical interface.
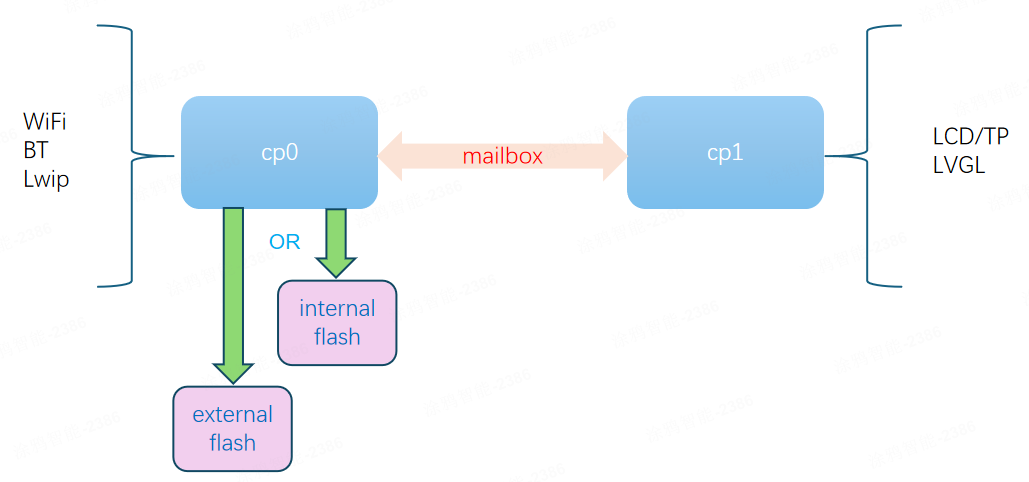
- The resource file system (uniformly using
LittleFSformat) is located in either off-chip or on-chip flash memory and is exclusively managed by CP0. - For SDKs earlier than v3.12.7, start address:
0x600000, length:0x1cb000(1836 KB = 1,880,064 bytes). - For SDKs v3.12.7 or later, start address:
0x6cb000, length:0x100000(1024 KB = 1,048,576 bytes).
Generate a file system in the on-chip flash memory:
- For SDKs earlier than v3.12.7,
#./mklittlefs -c bk/ -b 4096 -p 256 -s 1880064 bk.bin - For SDKs v3.12.7 or later,
#./mklittlefs -c bk/ -b 4096 -p 256 -s 1048576 bk.bin
Application framework
Building upon the system communication framework, the application framework further illustrates the hierarchy of the framework and the interaction between the graphical user interface application (GUI app) and the IoT product application (product app).
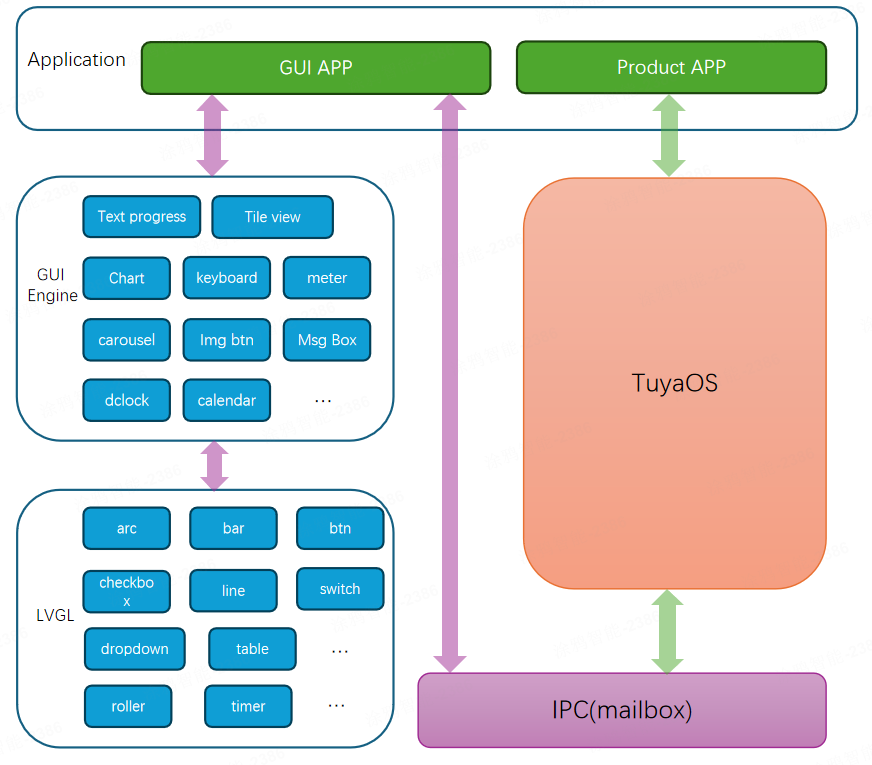
Application interfaces
This section details the following application interfaces:
Inter-process communication data structure
Single message communication
typedef struct
{
char *tag; // The unique identifier of an object
uint32_t obj_type; // The object type (such as switch, slider, and button)
uint32_t event; // The event type (Widget event or system event)
uint32_t param; // The event content
} LV_DISP_EVENT_S;
CP0 (Product application)
Reference header file
#include "tuya_app_gui_gw_core0.h"
#include "tuya_list.h"
#include "app_ipc_command.h"
#include "tkl_display.h"
#include "smart_frame.h"
#include "tal_sw_timer.h"
#include "uni_log.h"
#include "tdd_lcd.h"
#ifdef TUYA_TFTP_SERVER // Upload resource files over LAN via TFTP client tool during debugging
#include "tuya_app_gui_tftp.h"
#endif
Initialization entry point function
Before executing the following functions while the device is activated, make sure all DP data is initialized. Otherwise, screen refresh issues might occur with GUI controls
STATIC VOID tuya_gui_start(BOOL_T is_mf_test)
Request parameter:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
BOOL_T is_mf_test |
Indicates whether the device is in production test mode. |
Features:
Initialize the screen and touch panel (TP) pins
Define the parameters in tuyaos_iot_t5_gui_demo_product_class-T5_gui_demo_quickstart\src\gui\tuya_app_gui_config.h. Here is an example:
| Parameter | Example |
|---|---|
| Screen name | TUYA_LCD_IC_NAME |
| Screen width | TUYA_LCD_WIDTH |
| Screen height | TUYA_LCD_HEIGHT |
Set file system partition (internal or external flash memory)
OPERATE_RET tuya_app_gui_set_lfs_partiton_type(TUYA_GUI_LFS_PARTITION_TYPE_E partition_type)
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
partition_type = TUYA_GUI_LFS_SPI_FLASH |
The on-chip flash file system is used. Due to limited storage space, the on-chip file system does not support dynamic cloud-based resource updates. |
partition_type = TUYA_GUI_LFS_QSPI_FLASH |
The file system is in an external QSPI flash memory. |
Register an event handler callback
Handle requests such as GUI-side crashes, reboots, screen savers, language configuration, and custom private events.
OPERATE_RET tuya_gui_system_event_hdl_register(GUI_SYS_EVENT_CB cb)
Register an event handler callback for GUI controls
Register a callback for GUI control changes that require special processing.
- If this feature is not required in the product application, it can be ignored.
- The component already handles the reporting logic for controls’ corresponding DPs. Registration is unnecessary if no specific processing is needed for control changes.
OPERATE_RET tuya_gui_obj_event_hdl_register(GUI_OBJ_EVENT_CB cb)
Register a callback for manual GUI control state initialization
This registration function allows you to initialize control states during power-on. It is typically used when the device is unactivated and unable to initialize controls automatically via the component’s DP mechanism.
OPERATE_RET tuya_gui_dp2obj_pre_init_hdl_register(GUI_DP2OBJ_PRE_INIT_EVENT_CB cb)
Register a callback for GUI control-to-Tuya DP conversion
Convert GUI-side control event data (LV_DISP_EVENT_S) into Tuya DP data (DP_REPT_CB_DATA) based on actual application requirements.
OPERATE_RET tuya_gui_obj2dp_convert_hdl_register(GUI_OBJ2DP_CONVERT_CB cb)
Initialize core function
VOID tuya_gui_init(BOOL_T is_mf_test, TKL_DISP_INFO_S *info, CHAR_T *weather_code)
-
If you have specific requirements for weather forecast data content, you can customize the
weather_codeparameter. Otherwise, the system’s default weather data will be used. For more information, see Weather Service. -
To output weather data such as temperature, maximum/minimum temperature, humidity, and weather condition codes, set the
weather_codeparameter as the following JSON array string:["w.temp","w.thigh","w.tlow","w.humidity","w.conditionNum","w.date.1"]- The use of numerical weather condition codes here is primarily to accommodate multilingual configurations for different countries.
w.date.1indicates a request for 1-day forecast data. It supports a forecast of 1 to 7 days. This parameter is mandatory — omitting it will cause weather data parsing errors. Forecasts are updated every 30 minutes after successful network connection.
Initialize TFTP service
The application framework supports enabling the macro definition TUYA_TFTP_SERVER to allow local resources (images, language configurations, and font files) to be uploaded to the device via TFTP. For mass production firmware, it is recommended to disable this feature.
tuya_app_gui_tftp_server_init()
CP1 (GUI application)
This section details the following GUI applications and interfaces:
Drawing method
The following drawing methods are currently supported:
NXP GUI-Guider-1.7.2 (LVGL v8.3.10) (Assisted with a tool)
-
Import the tool-generated code directories
custom & generatedintoProject Name\apps\tuyaos_iot_t5_gui_demo_product_class-T5_gui_demo_quickstart\src\gui\. -
Add the following line to
Project Name\apps\tuyaos_iot_t5_gui_demo_product_class-T5_gui_demo_quickstart\src\gui\generated\gui_duider.h.#include "tuya_app_gui.h" -
Enable the macro definition
"NXP_GUI_GUIDER"inProject Name\apps\tuyaos_iot_t5_gui_demo_product_class-T5_gui_demo_quickstart\src\gui\tuya_app_gui_config.hand disable the macro definition"EEZ_STUDIO".
EEZ Studio (0.13.1) (LVGL v8.3/LVGL v8.3 with EEZ Flow) (Assisted with a tool)
-
Import the tool-generated code directory
srcintoProject Name\apps\tuyaos_iot_t5_gui_demo_product_class-T5_gui_demo_quickstart\src\gui\. -
Add the following line to
Project Name\apps\tuyaos_iot_t5_gui_demo_product_class-T5_gui_demo_quickstart\src\gui\src\ui\ui.h.#include "tuya_app_gui.h" -
Enable the macro definition
"EEZ_STUDIO"inProject Name\apps\tuyaos_iot_t5_gui_demo_product_class-T5_gui_demo_quickstart\src\gui\tuya_app_gui_config.hand disable the macro definition"NXP_GUI_GUIDER".
Manual drawing
-
Import the manually written code in C language into
Project Name\apps\tuyaos_iot_t5_gui_demo_product_class-T5_gui_demo_quickstart\src\gui\. -
Disable both the macro definitions
"NXP_GUI_GUIDER"and"EEZ_STUDIO"inProject Name\apps\T5s_gui_demo_quickstart\src\gui\tuya_app_gui_config.h. -
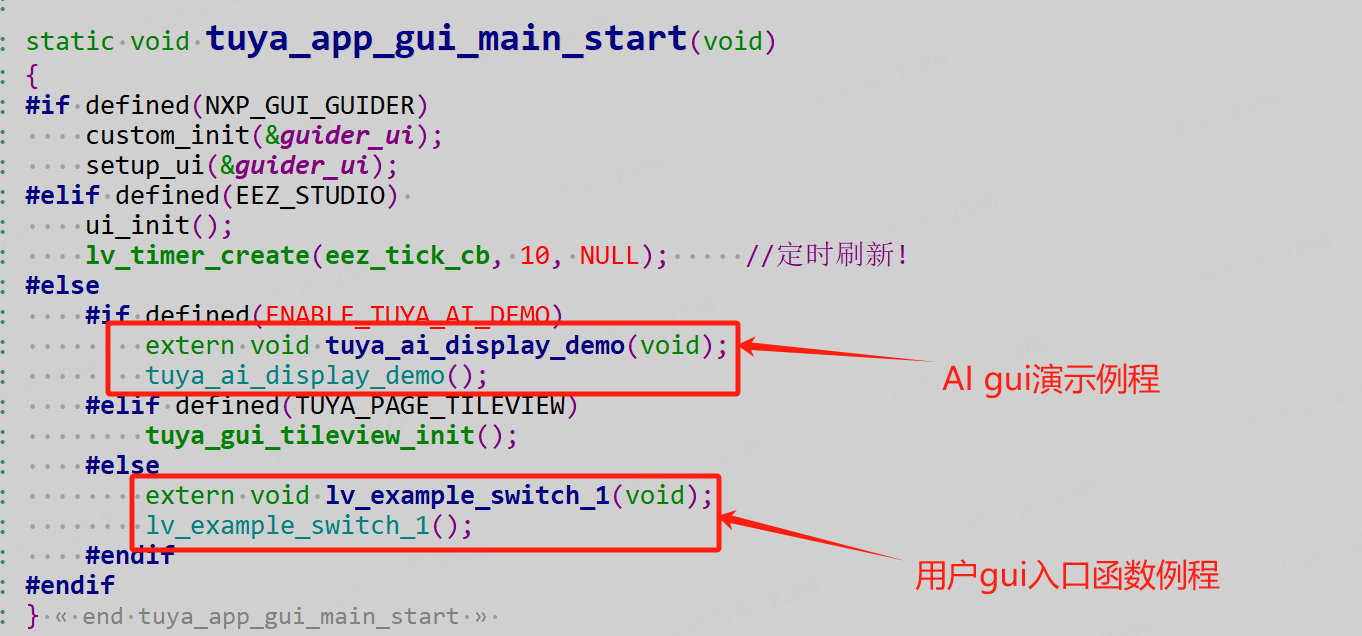
In
Project Name\apps\tuyaos_iot_t5_gui_demo_product_class-T5_gui_demo_quickstart\src\gui\tuya_app_gui_main.c, change the function name in the following red box to your own drawing entry function name. If you do not need to support background image splash screen and image preloading, you can set it toNULL.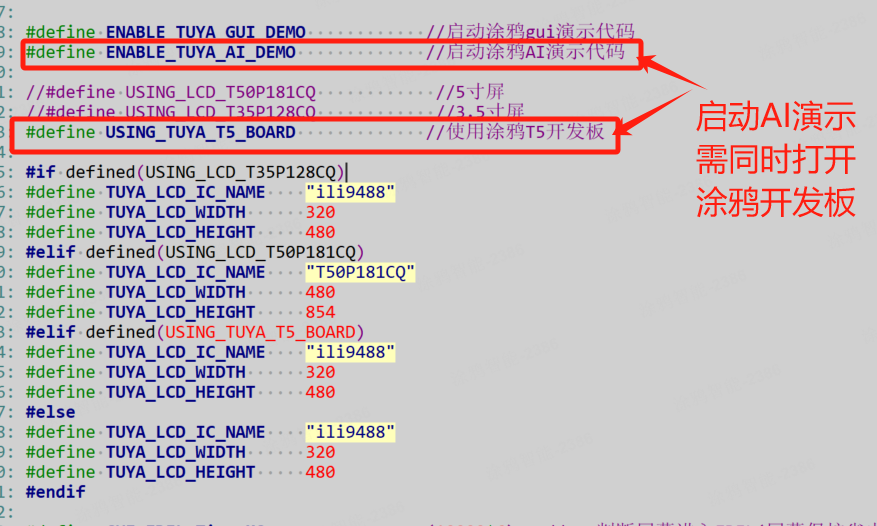

Things to note
-
Object identifier: Since GUI object states are linked to business logic, event callbacks are triggered when either a GUI object changes, or a DP state change from the business logic needs synchronization with the GUI object. Thus, each object requires a unique identifier to facilitate communication between the business logic and GUI layers. For more information, see Inter-process communication data structure.
Before adding an event callback, register the control’s identifier (which must be globally unique within the project) via
lv_obj_set_tag, as highlighted in the red box below: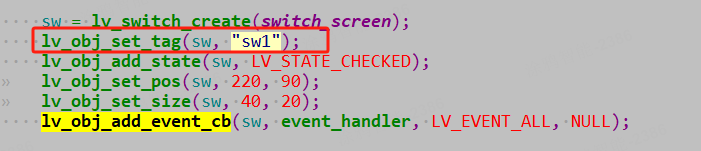
-
Event flag: When sending control change events to CP0 via the
aic_lvgl_msg_event_changeinterface, the presence of theLLV_EVENT_BY_DIRECT_REPORTflag in theeventmember of thelvglMsg_tdata determines the handling logic:- With
LLV_EVENT_BY_DIRECT_REPORT: The DP data corresponding to the control will be reported directly to the cloud, bypassing CP0 business logic processing. - Without
LLV_EVENT_BY_DIRECT_REPORT: The DP data will first be processed by CP0’s business logic before being reported.
- With
-
Page switching: When creating a screen object with a tag set via
lv_obj_set_tag, adhere to the following during page switching:- If using
lv_obj_clean()to clear only child objects of the current page, you must manually calllvMsgEventDelto remove the current page’s tag. - If using
lv_obj_del()to clear both child objects and the parent page object, there is no need to calllvMsgEventDelbecause tags are automatically cleared.
- If using
GUI image pre-decoding
Store images in the resource file system and perform pre-decoding during system startup to accelerate image loading during operation. This may consume significant memory resources. Refer to void tuya_app_gui_img_pre_decode(void) in \apps\tuyaos_iot_t5_gui_demo_product_class-T5_gui_demo_quickstart\src\gui\tuya_basic_demo\lv_example_switch_1.c.
-
When using
jpg_img_loadorpng_img_loadfor pre-decoding, you must usetuya_app_gui_get_picture_full_pathto get the full path of the file.When switching pages, you must call
jpg_img_unload/png_img_unloadto release the specified image data memory. Otherwise, there will be a memory leak. -
When
img_file_load_by_idis used for pre-decoding, the image ID must be specified.When switching pages, you must call
img_file_unloadto release the specified image data memory. Otherwise, there will be a memory leak.
Language and text usage
For applications supporting multilingual interfaces, strictly follow the steps below:
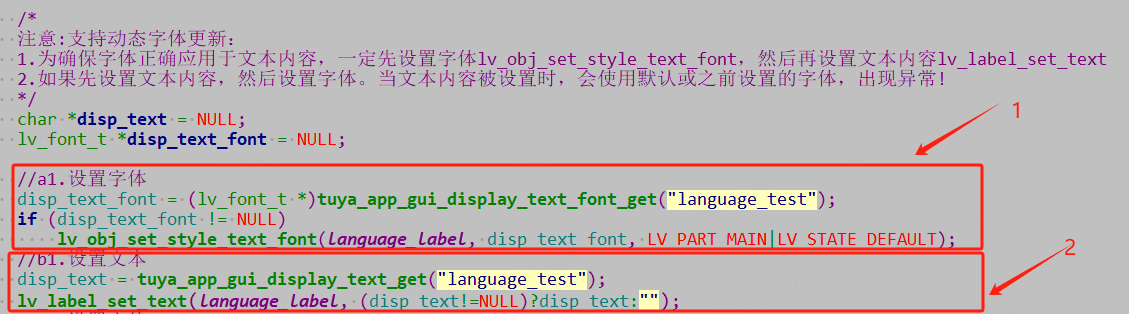
-
Through the interface function
const void *tuya_app_gui_display_text_font_get(char *node_name), input the parameter text label and get the specified font information (mentioned in Language > data.file).If the font information cannot be obtained, do not force the font to be set through the
lv_obj_set_style_text_fontfunction. Otherwise, the system will crash due to invalid font content. -
Through the interface function
const void *tuya_app_gui_display_text_get(char *node_name), input the parameter text label and get the specified text information (mentioned in Language > data.file).If the text information cannot be obtained, do not force the text to be set through the
lv_label_set_textfunction. Otherwise, the system will crash due to invalid text content. -
During language switching, the system purges all previous language resources and initializes the new language environment. In the language-switch callback handler, you must update every text control that uses font resources on the current page.
If you update only some text controls, LVGL retains pointers to deallocated font/text resources from the old language environment. During the next screen refresh cycle, LVGL attempts to render stale pointers, and the system might crash.
GUI interfaces
-
Register a callback for CP0 DP data changes:
Register a callback to handle DP data changes from CP0. The callback must distinguish between standard DP data (
DP_CNTL_S *) and raw data (TY_RAW_DP_REPT_S *) and convert them into corresponding control updates.void tuya_app_gui_dp_update_notify_callback_register (gui_dp_update_cb_t cb) -
CP1 requests DP data (Active device state only)
Get standard DP data (
DP_CNTL_S*) by the specified DPID. Raw data is not currently available, and you need to cache data when it changes.void *tuya_app_gui_get_dp_cntl(unsigned char dpid) -
CP1 requests the current Wi-Fi connection status:
Check whether the Wi-Fi network is connected to the cloud. The output RSSI and SSID are valid only when the Wi-Fi network is connected to the cloud.
bool tuya_app_gui_is_wifi_connected(signed char *out_rssi, char *ssid_buff, int ssid_buff_size) -
CP1 requests the current device activation status:
bool tuya_app_gui_is_dev_activeted(void) -
CP1 requests to unbind from the specified device:
void tuya_app_gui_request_dev_unbind(void) -
CP1 requests the current time:
bool tuya_app_gui_request_local_time(char *time_buff, int time_buff_size) -
CP1 requests the weather forecast data:
Query the current weather information (the weather forecast data format is: LKTLV). For more information, see Weather Service.
bool tuya_app_gui_request_local_weather(char **local_weather, uint32_t *weather_len)The
local_weatherstring (containing weather information) must be manually freed after use to prevent memory leaks. -
CP1 requests resource updates:
Check whether new resources are available for update in the cloud.
void tuya_app_gui_query_resource_update(void) -
Configure read/write interfaces. All write operations below are performed asynchronously. Immediate read-back after writing is not supported.
- KV operations (configuration is saved in the on-chip KV area):
-
Read: The memory pointed to by
valuemust be manually freed by the users after use.bool tuya_app_gui_kv_common_read(char *key, unsigned char **value, uint32_t *p_len) -
Write:
bool tuya_app_gui_kv_common_write(char *key, unsigned char *value, uint32_t len)
-
- KV file operations (configuration is saved in the file system area of flash memory):
-
Read: The memory pointed to by
valuemust be manually freed by the users after use.bool tuya_app_gui_fs_kv_common_read(char *key, unsigned char **value, uint32_t *p_len); -
Write:
bool tuya_app_gui_fs_kv_common_write(char *key, unsigned char *value, uint32_t len)
-
- KV operations (configuration is saved in the on-chip KV area):
Custom private events
If existing event types cannot meet your CP0-CP1 interaction requirements, use the custom private event LLV_EVENT_USER_PRIVATE.
-
Define a handler function in CP1, where
datais a pointer of typelvglMsg_t.void tuya_app_gui_user_private_event_process(void *data) -
Define a private data structure and pass its pointer to the
paramfield inlvglMsg_tduring interaction.
System resources (LittleFS format)
First use of the development board
When the development board is used for the first time, if the onboard external flash memory fails to mount, the screen will remain unresponsive. Manually run the following commands in the log console and restart.
- Run
xqspi fceto erase the external flash memory. - Run
lfs mkfsto format the external flash memory.
Generate the file system
After the screen powers on, since the file system in the flash memory is empty, no images or text will be displayed. Follow the steps below to generate the file system:
There is a system resource sample in Project Name\tuyaos_iot_t5_gui_demo_product_classT5_gui_demo_quickstart\sr\gui\project_resource_sample\littlefs. The bk folder contains the file system content to be packaged. Note: the length of all resource filenames, including extensions, must not exceed 32 characters. Place the content to be packaged inside according to the folder’s directory tree structure, and then use the tool to generate the file system image bk.bin.
-
Generate a file system in the on-chip flash memory:
./mklittlefs -c bk/ -b 4096 -p 256 -s 1880064 bk.binAfter execution, follow the instructions to import
bk.bininto the tool, and set the start address according to the values described in the Communication framework. “File length” refers to the file size. Larger files will result in longer address lengths. The file length is automatically generated and requires no additional action.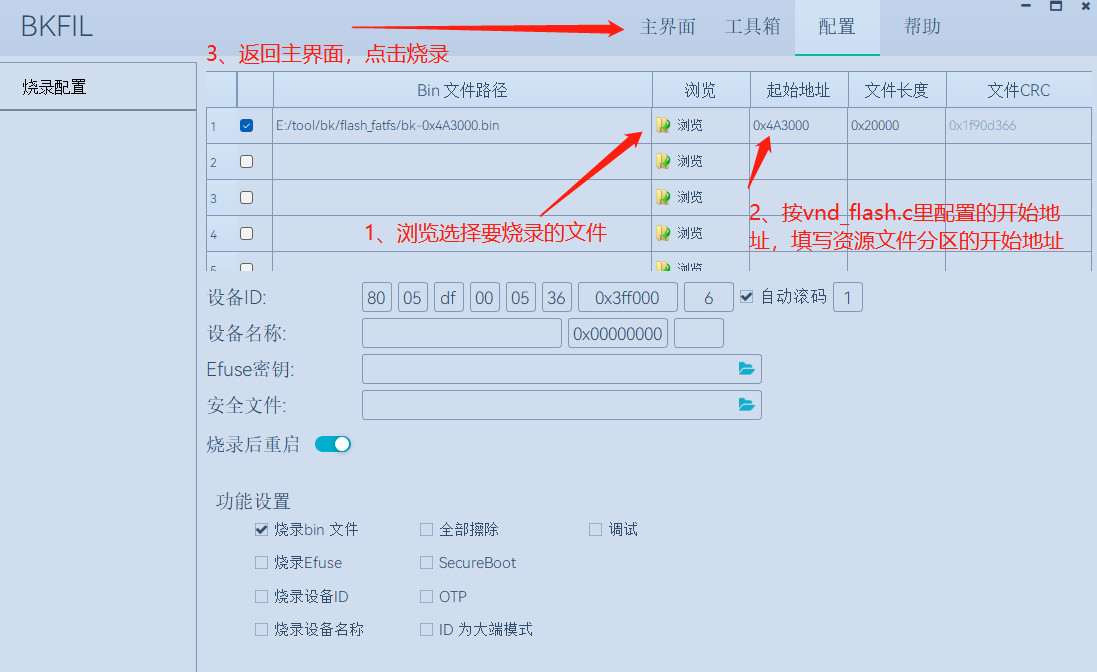
-
Generate a file system in the off-chip flash memory (Configure parameters
-b,-p, and-sbased on your flash memory specifications):./mklittlefs -c bk/ -b xxx -p xxx -s xxx bk.binAfter execution, flash the
bk.binfile to QSPI flash memory. -
Tool parameters
Parameter Description -bThe block size. Default value: 4096. -pThe page size. Default value: 256. -cThe input resource folder. -sThe size of the output image. The value must not be smaller than the actual resource size. For an off-chip flash memory, this equals the flash memory size in bytes. -bk.binThe file name of the output image.
Directory
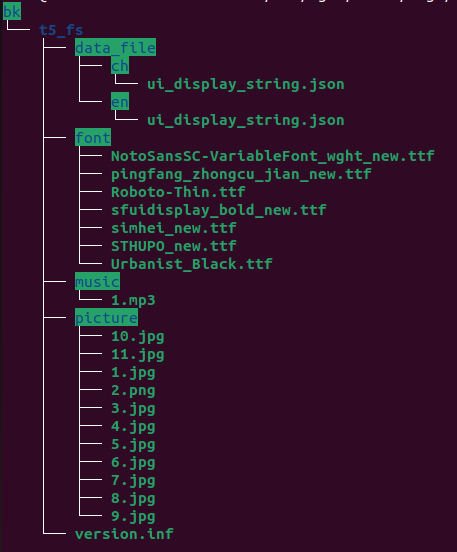
Language
Multilingual configuration consumes significant memory resources. If the product application requires only a single language, it is recommended to avoid the following configuration and instead use a static font library approach.
-
data_file: This folder stores the language text definitions used in the GUI. Strictly adhere to the format specified in the JSON sample when organizing the content.-
Chinese language text definition:
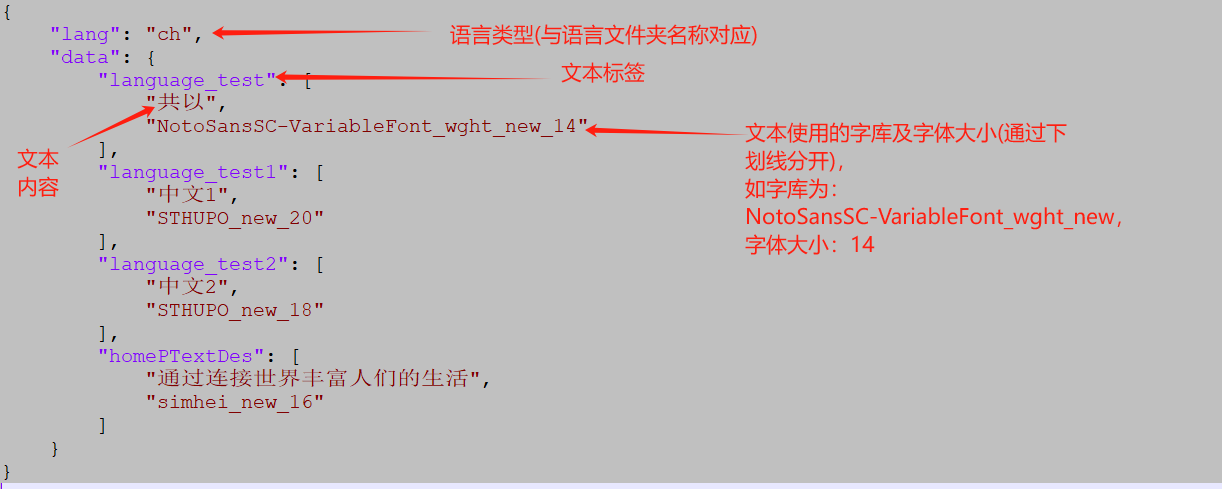
-
English language text definition:
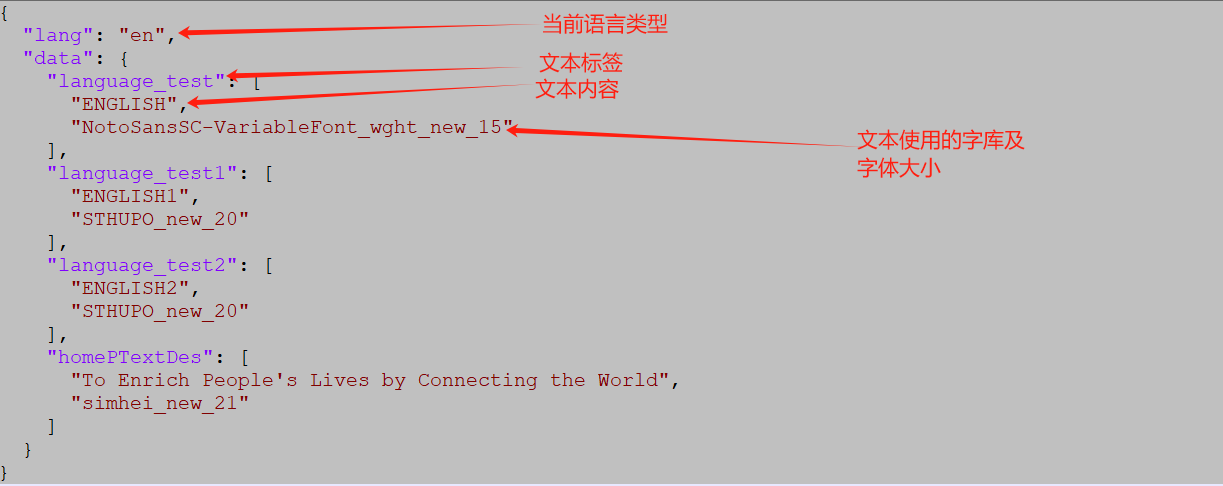
-
The following table shows the definitions of various language folders. (If you need other languages, please get in touch with Tuya’s developers.)
Language Folder Chinese ch English en Korean kr Japanese jp French fr German de Russian ru Indian in
-
-
font: This folder stores font libraries (currently only TTF format is supported). Ensure you use licensed, legitimate font libraries to avoid system font parsing errors. The font library name (excluding the .ttf extension) must exactly match the font library name specified in the specified language folder. -
Usage: For example, in
lv_label_set_text(language_label, tuya_app_gui_display_text_get("language_test")), the objectlanguage_labeldisplays the text corresponding to the label"language_test".- If the current language is set to Chinese, the
language_labelwill display 共以 (demo text, no actual meaning). - If the current language is set to English, it will display ENGLISH.
- If the current language is set to Chinese, the
Image
picture: This folder stores image resources used in the GUI, supporting formats such as JPG, PNG, and GIF. To ensure smooth image display during GUI operation, it is recommended to perform image pre-decoding. Note: Pre-decoded images might consume significant memory. For more information, see Image pre-decoding.
- Image naming rules: Each image must be named with a unique numeric ID (starting from
1.jpg,1.png, or1.gif, with no duplicate IDs, incrementing sequentially). Your programs should reference the corresponding image name where needed. - Image pixel requirements:
When decoding images, the system transfers them as 4 bytes. If you use JPG images, please note:- When the color depth is 16 bits, the pixel width of the image must be an even number (such as
138 × 42). Do not use images with odd pixels (such as135 × 41). Otherwise, you can use image editing tools to convert odd pixels to even pixels. - When the color depth is 24 bits, the pixel width of the image must be a multiple of 4 (such as
192 × 192).
- When the color depth is 16 bits, the pixel width of the image must be an even number (such as
Music
music: The naming rules for music files. Each music file must be named with a unique numeric ID (starting from 1.mp3, with no duplicate IDs, incrementing sequentially). Your programs should reference the corresponding file name where needed.
This row cannot be deleted yet.
Resource version information
version.inf: The version information, such as 0.1.
Tutorial
For a detailed tutorial on how to use the resources, refer to the lv_example_switch_1.c file in the demo.
Use TFTP to download resources to the device (debugging stage)
-
Go to Tftpd64 to download the client.
-
Enable the TFTP server on the device.
Enable the macro definition"TUYA_TFTP_SERVER"inProject Name\apps\tuyaos_iot_t5_gui_demo_product_class-T5_gui_demo_quickstart\src\gui\tuya_app_gui_config.h.During mass production, ensure this macro definition is disabled to prevent security risks.
-
Get the TFTP server IP address and port information from the device log.
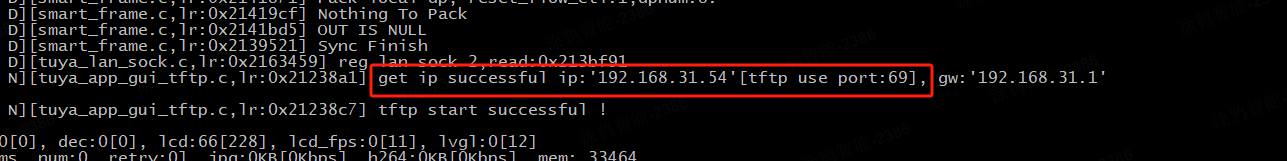
-
Open the TFTP client tool in Windows and configure it.
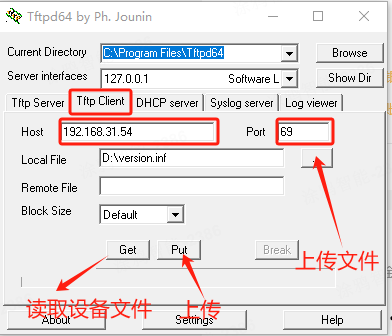
After the configuration is completed:
- Click Put to upload files.
- Click Get to download and read the device file.
-
Currently, only the following file formats are supported:
File Format description Language configuration file .jsonFont library file .ttfAudio file (Currently unsupported) .mp3. For naming rules, see Music.Image file .jpg/.png/.gif. For naming rules, see Image.Resource version information file version.inf. The name is fixed and cannot be changed. -
When uploading language configuration files (for language prefixes, refer to the detailed description in Language), follow the naming rule
language_filename.json. Example:- For a Chinese configuration file
xxx.json, rename it toch_xxx.json. - For an English configuration file
yyy.json, rename it toen_yyy.json. - For a Korean configuration file
jjj.json, rename it tokr_jjj.json.
- For a Chinese configuration file
Debugging
- Logging port:
UART1, baud rate: 460800. - Firmware flashing port:
UART2, baud rate: 2000000.
Compilation
The project with the GUI example is named tuyaos_iot_t5_gui_demo_product_class-T5_gui_demo_quickstart. Run the following code to compile the project.
./build_app.sh apps/tuyaos_iot_t5_gui_demo_product_class-T5_gui_demo_quickstart/ tuyaos_iot_t5_gui_demo_product_class-T5_gui_demo_quickstart 1.0.0
Screen switching
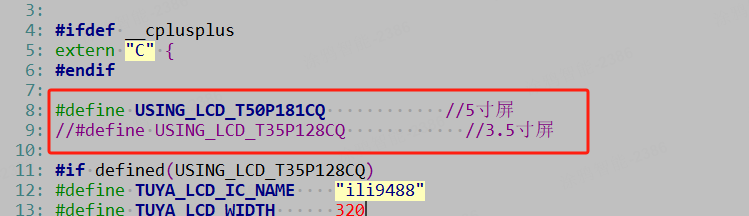
The development kit already supports optional macro definition configurations for two screen sizes:
- 3.5-inch screen manufacturer model:
T35P128CQ - 5-inch screen manufacturer model:
T50P181CQ
Configure it according to the existing development board in the \apps\tuyaos_iot_t5_gui_demo_product_class-T5_gui_demo_quickstart\src\gui\tuya_app_gui_config.h.
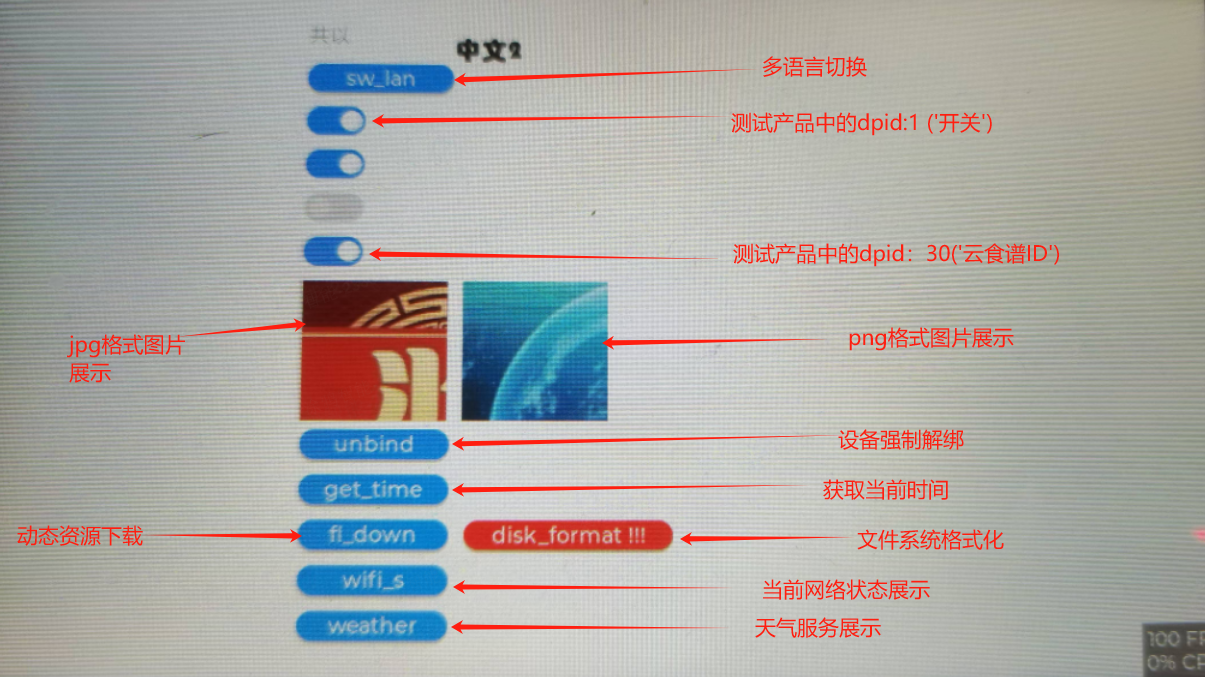
Sample screen
Things to note
Development framework
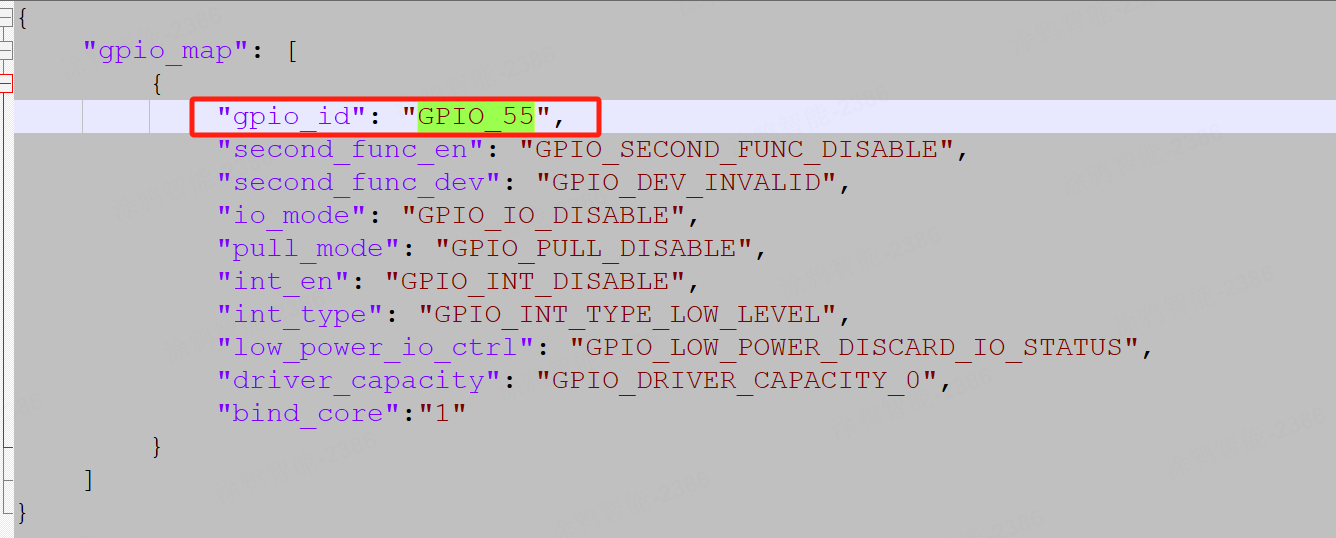
The file tuyaos_iot_t5_gui_demo_product_class\apps\T5_gui_demo_quickstart\default_gpio_config.json is related to the GPIO interrupt configuration used by the current system.
For example, when the interrupt pin tp_intr of the touch panel is configured as TUYA_GPIO_NUM_55, the settings in the file should be synchronized as shown in the figure below:
Is this page helpful?
YesFeedbackIs this page helpful?
YesFeedback





