Use T5 Peripheral Interfaces
Last Updated on : 2025-07-28 07:23:47download
This topic describes how to use the T5 peripheral interfaces.
GPIOs
The following figure shows the hardware wiring:
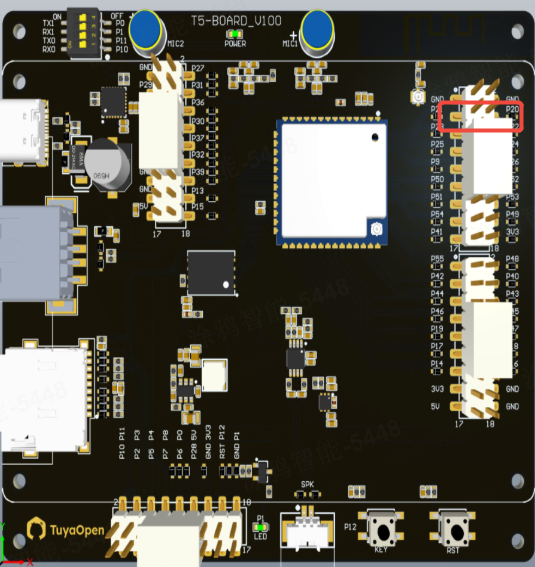
Pin P20 can be used as a general-purpose I/O (GPIO), capable of both outputting logic levels and reading external input levels.
Output level
Initialization
OPERATE_RET tuya_ai_toy_GPIO20_init(void)
{
OPERATE_RET rt = OPRT_OK;
TUYA_GPIO_BASE_CFG_T cfg;
cfg.mode = TUYA_GPIO_PULLDOWN;
cfg.direct = TUYA_GPIO_OUTPUT;
cfg.level = TUYA_GPIO_LEVEL_LOW;
TAL_PR_DEBUG("GPIO %d initialized", TUYA_GPIO_NUM_20);
tkl_gpio_init(TUYA_GPIO_NUM_20, &cfg);
return rt;
}
TUYA_GPIO_NUM_20 output level
The GPIO is used for output. The sample code is as follows:
tkl_gpio_write(TUYA_GPIO_NUM_20, 1); // P20 outputs high level
tkl_gpio_write(TUYA_GPIO_NUM_20, 0); // P20 outputs low level
Input level
The GPIO reads external level. The sample code is as follows:
app_key_init(para.reset_key_pin);
Serial port
The following figure shows the pinout of the development board. uart0 corresponds to P10 and P11.
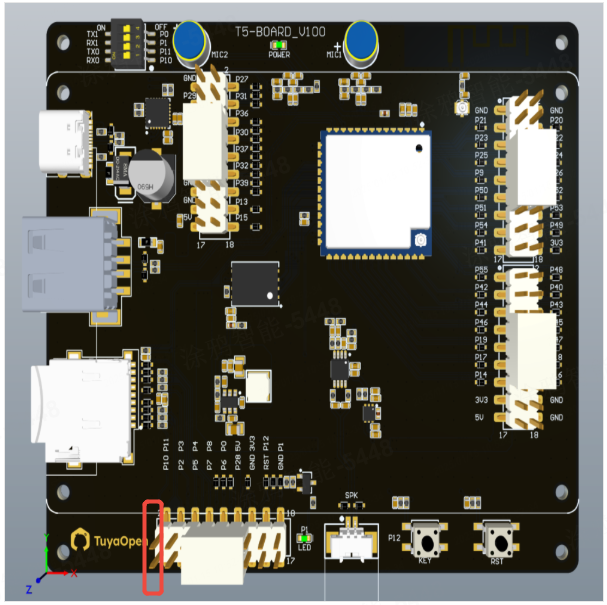
| Pin | Feature |
|---|---|
| GPIO10 | DL_UART_RX |
| GPIO11 | DL_UART_RX |
Sample code
You can refer to the following sample code to implement data transmission/reception via UART.
// Transmit and receive
void my_uart_rx_callback_task(VOID_T *args) {
char buff[256] = {0};
int read_uart_len ;
while(1)
{
read_uart_len = tal_uart_get_rx_data_size(TUYA_UART_NUM_0);
if (read_uart_len > 0 && read_uart_len <= 256)
{
//Receive
tal_uart_read(TUYA_UART_NUM_0, buff,read_uart_len);
//Print
TAL_PR_HEXDUMP_DEBUG("read uart:",buff,read_uart_len);
char str[read_uart_len + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < read_uart_len; i++) {
str[i] = ((char*)buff)[i];
}
str[read_uart_len] = '\0';
tkl_log_output("UART received data: %s\n", str);
// Transmit
char data[] = {0x01,0x02,0x03,0x05,0x08};
int len = sizeof(data) / sizeof(data[0]); //
tal_uart_write(TUYA_UART_NUM_0, (const unsigned char *)data, len);
}
}
}
void user_uart_demo(void)
{
TAL_UART_CFG_T cfg;
memset(&cfg, 0, sizeof(TAL_UART_CFG_T));
cfg.base_cfg.baudrate = 115200;
cfg.base_cfg.databits = TUYA_UART_DATA_LEN_8BIT;
cfg.base_cfg.parity = TUYA_UART_PARITY_TYPE_NONE;
cfg.base_cfg.stopbits = TUYA_UART_STOP_LEN_1BIT;
cfg.rx_buffer_size = 256;
tal_uart_init(TUYA_UART_NUM_0, &cfg);
OPERATE_RET rt = OPRT_OK;
THREAD_HANDLE uart_task_handle;
THREAD_CFG_T thread_cfg = {
.thrdname = "uart_task",
.priority = THREAD_PRIO_5,
.stackDepth = 4096
};
TUYA_CALL_ERR_LOG(tal_thread_create_and_start(&uart_task_handle, NULL, NULL, my_uart_rx_callback_task, NULL, &thread_cfg));
}
Is this page helpful?
YesFeedbackIs this page helpful?
YesFeedback





