Laser Robot Vacuum
Last Updated on : 2024-03-04 08:54:43
The data of a laser robot vacuum is classified into real-time data and historical data. Both types of data include map data and route data, and are stored as files on the Tuya IoT Development Platform.
- The real-time map data is stored in a different file from the real-time route data.
- The historical data of maps and routes are stored in the same file. Map data and route data are divided and read based on specific rules.
We recommend that you use peer-to-peer (P2P) connections to get real-time data. This is an efficient data transfer method. For more information, see P2P Download from Robot Vacuums.
We recommend that all API methods are called after initCloudConfig that initializes cloud storage configurations is called successfully. The configurations are valid for half an hour. If the configurations expire, updateCloudConfig can be called to update the cloud storage configurations.
Get data of a robot vacuum
The real-time data of a laser robot vacuum is processed through the following channels.
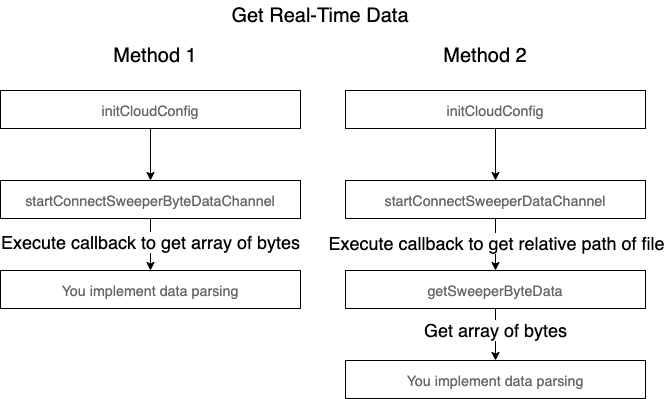
Access robot vacuum features
Access IThingSweeperKit:
IThingSweeperKitSdk iThingSweeperKitSdk = ThingOptimusSdk.getManager(IThingSweeperKitSdk.class);
IThingSweeperKit iThingSweeperKit = iThingSweeperKitSdk.getSweeperInstance()
Initialize cloud storage configurations
Returns the location where files are stored. bucket indicates the location.
/**
*
* @param devId The device ID.
* @param callback
* /
void initCloudConfig(String devId, IThingCloudConfigCallback callback);
Example
ThingOptimusSdk.getManager(IThingSweeperKitSdk.class).getSweeperInstance().initCloudConfig("xxx", new IThingCloudConfigCallback() {
@Override
public void onConfigSuccess(String bucket) {
}
@Override
public void onConfigError(String errorCode, String errorMessage) {
}
});
Update cloud storage configurations
Returns the latest location where files are stored. bucket indicates the location. The bucket location is valid within a limited period. After it expires, call the following API method to update cloud configurations:
/**
*
* @param devId The device ID.
* @param callback
* /
void updateCloudConfig(String devId, IThingCloudConfigCallback callback);
Example
ThingOptimusSdk.getManager(IThingSweeperKitSdk.class).getSweeperInstance().updateCloudConfig("", new IThingCloudConfigCallback() {
@Override
public void onConfigSuccess(String bucket) {
}
@Override
public void onConfigError(String errorCode, String errorMessage) {
}
});
Register or disable real-time data channels
Return relative path of files
We recommend that you use peer-to-peer (P2P) channels to get real-time data. For more information, see P2P Download from Robot Vacuums.
Get the absolute path of the map file on the server. You can manually download the file to parse it.
After cloud configurations are initialized, real-time data channels can be enabled to get real-time data.
/**
* Enables the channel to get data of the robot vacuum and returns the URL where the data is stored.
*
* @param listener
* /
void startConnectSweeperDataChannel(IThingSweeperDataListener listener);
/**
* Disables the real-time data channel.
* /
void stopConnectSweeperDataChannel();
Callback data structure of SweeperDataBean
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| mapType | int | The type of data. Valid values:
|
| mapPath | String | A file path or map path. |
Example
ThingOptimusSdk.getManager(IThingSweeperKitSdk.class).getSweeperInstance().startConnectSweeperDataChannel(new IThingSweeperDataListener() {
@Override
public void onSweeperDataReceived(SweeperDataBean bean) {
}
});
Return an array of bytes
For Sweeper SDK versions later than v3.2.4, this feature will be deprecated. We recommend that you use P2P channels to get real-time data.
After cloud configurations are initialized, real-time data channels can be enabled to get real-time data.
/**
* Enables the channel to get real-time data and returns the array of `byte[]`.
*
* @param listener
* /
void startConnectSweeperByteDataChannel(IThingSweeperByteDataListener listener);
/**
* Disables the real-time data channel.
* /
void stopConnectSweeperByteDataChannel();
Callback data structure of SweeperByteData
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| type | int |
|
| data | byte[] | The data content. |
| devId | String | The device ID. |
Example
ThingOptimusSdk.getManager(IThingSweeperKitSdk.class).getSweeperInstance().startConnectSweeperByteDataChannel(new IThingSweeperByteDataListener() {
@Override
public void onSweeperByteData(SweeperByteData data) {
}
@Override
public void onFailure(int code, String msg) {
}
});
Get the absolute URL
/**
*
* @param bucket The bucket where the file is stored.
* @param path The relative path of the file (`startConnectSweeperDataChannel`).
* /
String getCloudFileUrl(String bucket, String path);
Example
ThingOptimusSdk.getManager(IThingSweeperKitSdk.class).getSweeperInstance().getCloudFileUrl("bucket","path");
Get data content
To get historical data, you can call the following API method to read the file content from the cloud.
/**
* Returns the data content in the format of `byte[]`.
*
* @param bucket
* @param path
* @param listener
* /
void getSweeperByteData(String bucket, String path, IThingByteDataListener listener);
Example
ThingOptimusSdk.getManager(IThingSweeperKitSdk.class).getSweeperInstance().getSweeperByteData("bucket", "path", new IThingByteDataListener() {
@Override
public void onSweeperByteData(byte[] data) {
}
@Override
public void onFailure(int code, String msg) {
}
});
Get data of the current cleaning task
API description
/**
* Returns the path of the map and route that are stored in real time.
* @param devId The device ID.
* @param callback
*/
void getSweeperCurrentPath(String devId,IThingResultCallback<SweeperPathBean> callback);
Fields of SweeperPathBean
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| mapPath | String | The path of a map. |
| routePath | String | The path of a route. |
Example
ThingOptimusSdk.getManager(IThingSweeperKitSdk.class).getSweeperInstance().getSweeperCurrentPath("devId", new IThingResultCallback<SweeperPathBean>() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(SweeperPathBean result) {
}
@Override
public void onError(String errorCode, String errorMessage) {
}
});
Get historical data of cleaning tasks
API description
/**
*
* @param devId The device ID.
* @param limit The number of returned entries in each call. We recommend that you specify a value of up to 100.
* @param offset The offset of returned data to display data on pages.
* @param callback
* /
void getSweeperHistoryData(String devId, int limit, int offset,IThingResultCallback<SweeperHistory> callback);
/**
*
* @param devId The device ID.
* @param limit The number of returned entries in each call. We recommend that you specify a value of up to 100.
* @param offset The offset of returned data to display data on pages.
* @param startTime The start timestamp.
* @param endTime The end timestamp.
* @param callback
* /
void getSweeperHistoryData(String devId, int limit, int offset, long startTime, long endTime,IThingResultCallback<SweeperHistory> callback);
Callback data structure of SweeperHistory
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| datas | List |
The list of historical data. |
| totalCount | int | The total number of returned entries in each call. |
Fields of SweeperHistoryBean
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | String | The map ID. |
| time | long | The timestamp when a file is uploaded. |
| bucket | String | The bucket where a file is stored. |
| file | String | The path of the file. |
| extend | String | The extension field. |
extend is an extension field whose value can be passed through to the device. Example: {"map_id":123, "layout_size":4589, "route_size":1024}.
layout_sizerepresents the data size of the map file.route_sizerepresents the data size of the route file.
When the system reads historical data files, it reads layout_size to get map data and route_size to get route data.
Example
ThingOptimusSdk.getManager(IThingSweeperKitSdk.class).getSweeperInstance().getSweeperHistoryData("devId", 10, 0, new IThingResultCallback<SweeperHistory>() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(SweeperHistory result) {
}
@Override
public void onError(String errorCode, String errorMessage) {
}
});
Delete historical data of cleaning tasks
Deletes historical data and stored data from the cloud. Up to 100 entries can be deleted in each call.
/**
* @param devId The ID of the device.
* @param fileIdList The list of IDs in historical data.
* @param callback
* /
void deleteSweeperHistoryData(String devId, List<String> fileIdList, final IThingDelHistoryCallback callback);
Example
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("10");
list.add("11");
ThingOptimusSdk.getManager(IThingSweeperKitSdk.class).getSweeperInstance().deleteSweeperHistoryData("devId", list, new IThingDelHistoryCallback() {
@Override
public void onSuccess() {
}
@Override
public void onError(String errorCode, String errorMessage) {
}
});
Get multi-floor map data
API description
/**
* Returns historical data of a robot vacuum. Multiple maps are used in this scenario.
* @param devId The device ID.
* @param limit The number of returned entries in each call. We recommend that you specify a value of up to 100.
* @param offset The offset of returned data to display data on pages.
* @param callback
* /
void getSweeperMultiMapHistoryData(String devId, int limit, int offset,
IThingResultCallback<SweeperHistory> callback);
/**
* Returns historical data of a robot vacuum. Multiple maps are used in this scenario.
* @param devId The device ID.
* @param limit The number of returned entries in each call. We recommend that you specify a value of up to 100.
* @param offset The offset of returned data to display data on pages.
* @param startTime The start timestamp.
* @param endTime The end timestamp.
* @param callback
* /
void getSweeperMultiMapHistoryData(String devId, int limit, int offset, long startTime, long endTime,
IThingResultCallback<SweeperHistory> callback);
Example
ThingOptimusSdk.getManager(IThingSweeperKitSdk.class).getSweeperInstance().getSweeperMultiMapHistoryData("devId", 20, 0, new IThingResultCallback<SweeperHistory>() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(SweeperHistory result) {
}
@Override
public void onError(String errorCode, String errorMessage) {
}
});
Name multiple floor maps
When the laser robot vacuum processes multiple maps in a cleaning task, you can call the following API method to name one of the floor maps.
/**
* Names one of the floor maps in a cleaning task.
* @param devId The ID of the device.
* @param id The map ID.
* @param name The map name.
* @param callback The callback.
*/
void sweeperFileNameUpdateWithDevId(String devId, long id, String name,final IThingSweeperNameUpdateCallback callback);
Example
ThingOptimusSdk.getManager(IThingSweeperKitSdk.class).getSweeperInstance().sweeperFileNameUpdateWithDevId("devId",id,"name", new IThingSweeperNameUpdateCallback() {
@Override
public void onNameUpdate(boolean result){
}
@Override
public void void onFailure(String code, String msg){
}
});
Is this page helpful?
YesFeedbackIs this page helpful?
YesFeedback





