Prepare for Integration with Matter Device
Last Updated on : 2024-06-07 02:01:26download
Before the integration of a Matter device into your project, you must configure the project. For the pairing process implemented by Tuya, Matter devices are classified into Tuya-enabled Matter devices and third-party Matter devices. For a third-party Matter device, add an extension target to your Xcode project.
Prerequisites
-
Before you start, the steps in Fast Integration with Cube App SDK must be finished.
-
If you require UI BizBundles, the version of Cube App SDK must be the same as that of the UI BizBundles to ensure stable pairing and control of devices.
Configure and integrate with main project
Configure entitlements
-
Open the project settings in Xcode.
-
Choose the target of the main project > Signing & Capabilities, and click
+ Capability.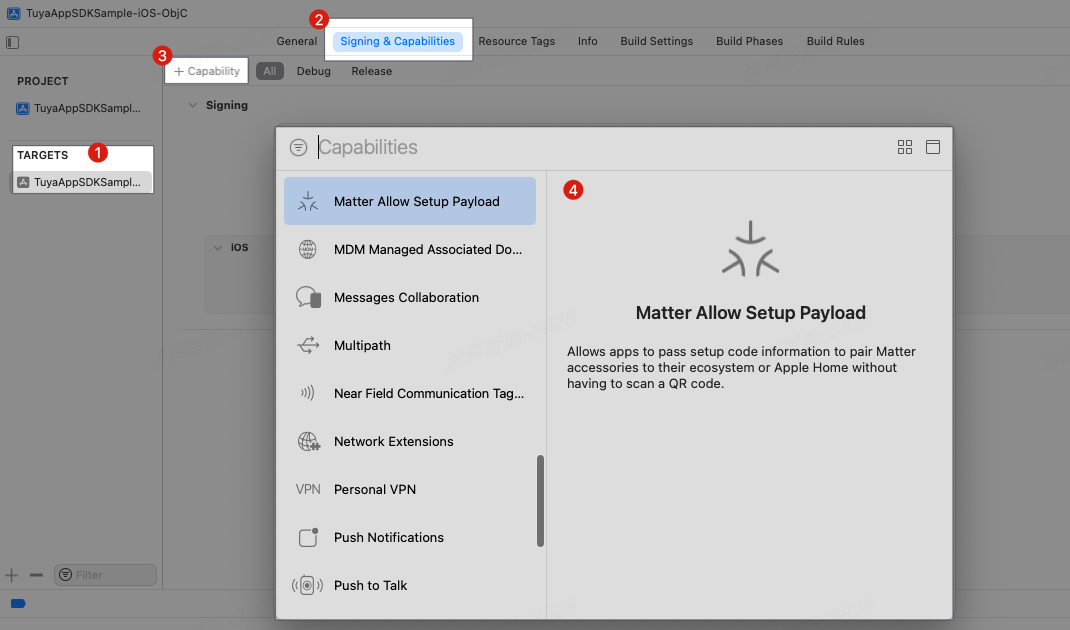
-
Add the entitlement
Matter Allow Setup Payloadthat is used to handle parsing of Matter QR codes. -
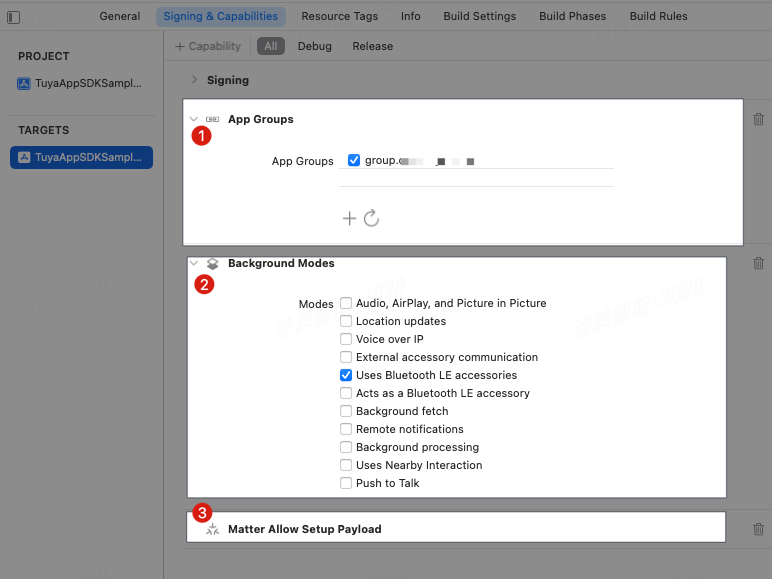
Add the
App Groupsentitlement that is used to share data withMatter Extension Target. SetApp Group IDto the same value asMatter Extension Target. -
Add the
Background Modesentitlement and selectUses Bluetooth LE accessoriesthat is used to ensure stable communication over Bluetooth.The following figure shows these steps.
Configure Info.plist
-
Open the project settings in Xcode.
-
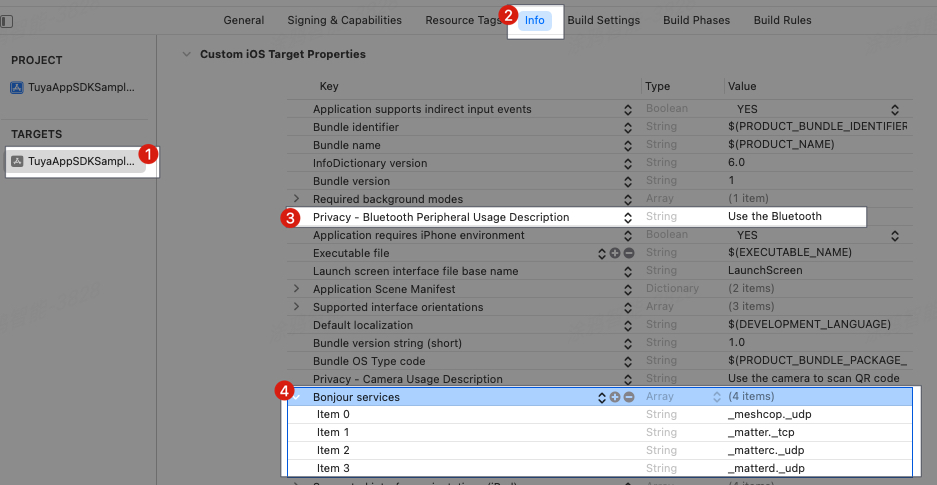
Choose the target of the main project > Info > Custom iOS Target Properties.
-
Privacy - Bluetooth Peripheral Usage Description
Add the entitlement
NSBluetoothPeripheralUsageDescriptionthat is used for privacy and permission purposes and to provide a user-facing description of the reason for requesting access to Bluetooth peripherals. -
Bonjour services
Matter has a strong dependency on communication on a LAN. In light of this, you must configure Bonjour services in the file Info.plist of the main project. Example:
<key>NSBonjourServices</key> <array> <string>_meshcop._udp</string> <string>_matter._tcp</string> <string>_matterc._udp</string> <string>_matterd._udp</string> </array>
-
Use CocoaPods for fast integration
-
We recommend that you update CocoaPods to the latest version.
-
Add the following code block to the
Podfile:platform :ios, '9.0' target 'Your_Project_Name' do pod "ThingSmartMatterKit" end -
In the root directory of your project, run
pod update.For more information about CocoaPods, see CocoaPods Guides.
Initialize module
Follow the instructions in Fast Integration with Cube App SDK for iOS and initialize the SDK. Then, initialize the Matter module.
// Initialize the SDK.
[[ThingSmartSDK sharedInstance] startWithAppKey:<#your_app_key#> secretKey:<#your_secret_key#>];
// Initialize the Matter module.
[ThingSmartMatterActivatorConfig setMatterConfigKey:<#YOUR_APP_GROUP_ID#>];
API description
+ (void)setMatterConfigKey:(NSString *)configKey;
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| configKey | The App Group ID of the project. |
Example
Objective-C:
[ThingSmartMatterActivatorConfig setMatterConfigKey:<#YOUR_APP_GROUP_ID#>];
Swift:
ThingSmartMatterActivatorConfig.setMatterKey("YOUR_APP_GROUP_ID")
Configure and integrate with Extension Target
Things to note
- Xcode 14.1 or later is required.
- iOS 16.1 or later is required.
- Create
Matter Extension Targetand use the default code file to perform the steps described in the following sections. Matter Extension Targetsupports Swift projects only.
Configure entitlements
- Open the project settings in Xcode.
- Choose the target of the main project > Signing & Capabilities, and click
+ Capability. - Add the
App Groupsentitlement that is used to share data with thetarget of the main project. SetApp Group IDto the same value as thetarget of the main project.
Use CocoaPods for fast integration
-
We recommend that you update CocoaPods to the latest version.
-
Add the following code block to the
Podfile:platform :ios, '9.0' target 'Your_Matter_Extension_Target_Name' do pod "ThingSmartMatterExtensionKit" end -
In the root directory of your project, run
pod update.For more information about CocoaPods, see CocoaPods Guides.
Initialize module
Open the file RequestHandler.swift in the ExtensionTarget project and rewrite the init method.
override init()
API description
+ (void)setMatterConfigKey:(NSString *)configKey;
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| configKey | The App Group ID of the project. |
Example
Swift:
override init() {
super.init()
ThingMatterExtensionSupport.shared.setMatterConfigKey(configKey: <#YOUR_APP_GROUP_ID#>)
}
Use ThingSmartMatterExtensionKit
After the Matter Extension Target project is generated, the file RequestHandler.swift appears in the Extension project. Use the API methods provided by the system and call ThingSmartMatterExtensionKit as shown in the following example.
-
Import
ThingSmartMatterExtensionKitinto the project.import ThingSmartMatterExtensionKit -
Make API requests with the methods that are automatically generated by the system, as shown in the following code block.
The callback methods in
RequestHandler.swiftare automatically generated by the system and cannot be modified.override func validateDeviceCredential(_ deviceCredential: MatterAddDeviceExtensionRequestHandler.DeviceCredential) async throws { ThingMatterExtensionSupport.shared.validateDeviceCredential(deviceCredential) } override func selectWi-FiNetwork(from wifiScanResults: [MatterAddDeviceExtensionRequestHandler.Wi-FiScanResult]) async throws -> MatterAddDeviceExtensionRequestHandler.Wi-FiNetworkAssociation { // Use this function to select a Wi-Fi network for the device if your ecosystem has special requirements. // Or, return .defaultSystemNetwork to use the iOS device's current network. return ThingMatterExtensionSupport.shared.selectWi-FiNetwork(from: wifiScanResults) } override func selectThreadNetwork(from threadScanResults: [MatterAddDeviceExtensionRequestHandler.ThreadScanResult]) async throws -> MatterAddDeviceExtensionRequestHandler.ThreadNetworkAssociation { // Use this function to select a Thread network for the device if your ecosystem has special requirements. // Or, return .defaultSystemNetwork to use the default Thread network. return ThingMatterExtensionSupport.shared.selectThreadNetwork(from: threadScanResults) } override func commissionDevice(in home: MatterAddDeviceRequest.Home?, onboardingPayload: String, commissioningID: UUID) async throws { // Use this function to commission the device with your Matter stack. ThingMatterExtensionSupport.shared.commissionDevice(in: home, onboardingPayload: onboardingPayload, commissioningID: commissioningID) } override func rooms(in home: MatterAddDeviceRequest.Home?) async -> [MatterAddDeviceRequest.Room] { // Use this function to return the rooms your ecosystem manages. // If your ecosystem manages multiple homes, ensure you are returning rooms that belong to the provided home. return ThingMatterExtensionSupport.shared.rooms(in: home) } override func configureDevice(named name: String, in room: MatterAddDeviceRequest.Room?) async { // Use this function to configure the (now) commissioned device with the given name and room. ThingMatterExtensionSupport.shared.configureDevice(named: name, in: room) }
Configure Matter capabilities
Due to the characteristics of a Matter device, all its capabilities are implemented based on Matter fabrics. Before a Matter device can be paired, controlled, or managed, you must make API requests to configure basic information about the Matter device. This configuration must be finished before any Matter services are implemented.
A fabric is a group of networked devices (also known as nodes) that share the same security domain. This enables secure communications among these nodes within the fabric. Nodes in the same fabric share the same Certificate Authority’s (CA) top-level certificate (Root of Trust) and within the context of the CA, a unique 64-bit identifier named Fabric ID.
Sequence diagram
The following figure shows the sequence in which basic Matter information is configured.
Prepare information about fabric
Information about Matter is bound with homes. Therefore, at the end of the operation of switching between homes or initially loading a home, call - loadFabricWithSpaceId to get information about the fabric that is bound with the home.
API description
@interface ThingSmartMatterManager : NSObject
+ (instancetype)sharedInstance;
- (void)loadFabricWithSpaceId:(long long)spaceId
success:(ThingSuccessHandler)success
failure:(ThingFailureError)failure;
@end
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| spaceId | The value of HomeID for the current home. |
| success | The success callback. |
| failure | The failure callback. |
Example
Objective-C:
- (void)loadMatterCurrentHomeFabric:(long long)homeId {
// Called at the end of the operation of switching between homes or initially loading a home.
[[ThingSmartMatterManager sharedInstance] loadFabricWithSpaceId:homeId success:^{
NSLog(@"load fabric success");
} failure:^(NSError *error) {
NSLog(@"load fabric fail");
}];
}
Swift:
func loadMatterCurrentHomeFabric(homeId: Int64) {
// Called at the end of the operation of switching between homes or initially loading a home.
ThingSmartMatterManager.sharedInstance().loadFabric(withSpaceId: homeId) {
print("load fabric success")
} failure: { error in
print("load fabric fail")
}
}
Prepare information about devices
Different from other types of Tuya-enabled devices, certain information about Matter devices must be prepared in advance. For this purpose, at the end of loading home information and fabric information, call - getDevicesFabricNodesWithdevIds:callback: to handle Matter devices for the specified home.
API description
@interface ThingSmartMatterShareManager : NSObject
+ (instancetype)sharedInstance;
- (void)getDevicesFabricNodesWithdevIds:(NSArray <NSString *>*)devIds callback:(void(^)(NSArray <ThingSmartMatterDeviceNodeModel *>*result))callback;
@end
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| devIds | The list of device IDs. |
Example
Objective-C:
- (void)loadMatterDeviceInfo {
// Called at the end of - loadFabric and loading devices in the home.
[[ThingSmartMatterShareManager sharedInstance] getDevicesFabricNodesWithdevIds:deviceIdList callback:^(NSArray<ThingSmartMatterDeviceNodeModel *> *result) {
NSLog(@"load matter device node succes");
}];
}
Swift:
func loadMatterDeviceInfo(){
// Called at the end of - loadFabric and loading devices in the home.
ThingSmartMatterShareManager.sharedInstance().getDevicesFabricNodesWithdevIds(deviceIdList) { modelList in
print("load matter device info success")
}
}
Is this page helpful?
YesFeedbackIs this page helpful?
YesFeedback





