TuyaLink-Based Devices
Last Updated on : 2024-11-18 11:33:13download
TuyaLink is an open solution that enables smart devices, including proprietary network modules and smart devices, to connect to Tuya’s cloud services.
TuyaLink lowers the bar for IoT development by integrating with Tuya’s IoT Core technologies, including things data model, rule engines, data parsing, device management, operations and monitoring, alert management, OTA firmware updates, and application development.
TuyaLink allows you to quickly integrate with the Tuya ecosystem and achieve interconnectivity between devices across different domains. A range of development resources for PaaS, SaaS, and apps helps you implement IoT projects with improved cost efficiency and reduced lead time.
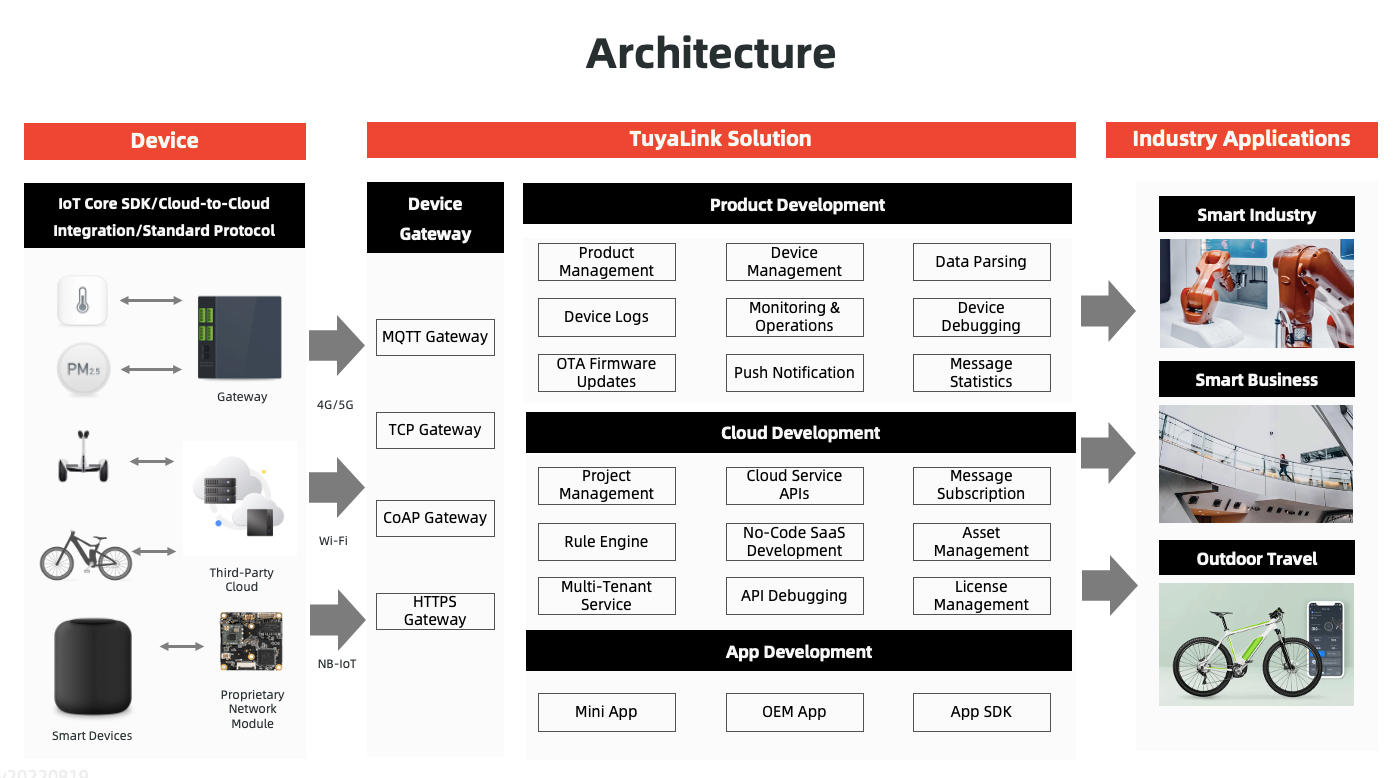
For more information, see TuyaLink.
Identify TuyaLink-based device
API description
boolean isSupportThingModelDevice();
Example:
public void judgeSupportTuyaLink(){
// DeviceBean deviceBean = TuyaOSDevice.getDeviceBean("your_device_id");
boolean isSupport = deviceBean.isSupportThingModelDevice();
Log.i("judgeSupportTuyaLink", isSupport);
}
Things data model
The device model construct describes an abstraction of physical devices. It defines the characteristics and behaviors of a type of device that connects to the Tuya Developer Platform.
A device model defines an abstract representation of a device as a set of properties, actions, and events. This model determines how a connected physical device interacts with the cloud applications.
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Property | The property type is used to define the continuous and queryable states of a device, which can represent one or several feature parameters. A property can be read-write or read-only for data update and query. When a specific feature parameter is updated, the device can update the property accordingly. For example, a light bulb might have properties like power state and brightness. |
| Action | The action type is used to run complex tasks. An action command is not intended to change the device property, but directs the device to return a response. For example, face recognition and picture transmission. |
| Event | The event type is used to define a live notification reported by a device, which requires external sensing and processing. Events work with message subscription or rule engines to respond as per the predefined logic, for example, overheating alerts and fault alerts. |
Currently, things data models are returned on demand from a local cache. To keep the cached data up to date, you need to timely pull the latest things data model and update the cache.
API description
Get things data model
DeviceBean{
// ....
// Locally caches the things data model of the device.
TuyaSmartThingModel thingModel;
}
Example
TuyaSmartThingModel thingModel = TuyaOSDevice.getDeviceBean("your_device_id").getThingModel();
Request and save things data model
ITuyaDeviceOperator.java
/**
* Pulls the latest things data model that matches the specified product ID (PID) from the cloud and updates the cache.
* @param pid
* @param callback Called when the task is finished or interrupted by an error.
*/
void getThingModelWithProductId(String pid,ITuyaDataCallback<TuyaSmartThingModel> callback);
/**
* Pulls the latest thing model from the cloud that matches the specified PID and PID version and updates the cache.
* @param pid
* @param productVersion
* @param callback Called when the task is finished or interrupted by an error.
*/
void getThingModelWithProductId(String pid, String productVersion,ITuyaDataCallback<TuyaSmartThingModel> callback);
Example
TuyaOsDevice.getDeviceOperator().getThingModelWithProductId("pid", new ITuyaDataCallback<TuyaSmartThingModel>() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(TuyaSmartThingModel result) {
}
@Override
public void onError(String errorCode, String errorMessage) {
}
});
}
Data model of TuyaSmartThingModel
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| modelId | String | The ID of the things data model. |
| productId | String | The product ID (PID). |
| productVersion | String | The version of the PID. |
| services | List |
The service model. |
| extensions | Map<String, Object> | The extension information. |
Data model of TuyaSmartThingServiceModel
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| properties | List |
The list of properties. |
| actions | List |
The list of actions. |
| events | List |
The list of events. |
Data model of TuyaSmartThingProperty
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| abilityId | int | The property ID can be regarded as dpId of dps for a generic device. |
| code | String | The property code. |
| accessMode | String | The access mode. Valid values: rw: can be sent and reportedro: only reported wr: only sent |
| typeSpec | Map<String, Object> | The definition of a data type. |
| defaultValue | Object | The default value. |
Description
Currently, typeSpec supports the following data types: value, string, date, bool, enum, fault (bitmap), array, and struct.
The array and struct types are dedicated for TuyaLink. struct is a nested type that encloses other type definitions.
Examples of data types
// type = value
{
"unit" : "°C",
"type" : "value",
"min" : 0,
"max" : 100,
"typeDefaultValue" : 0,
"step" : 1,
"scale" : 1
}
// type = string
{
"type" : "string",
"typeDefaultValue" : "",
"maxlen" : 50
}
// date
{
"type" : "date",
"typeDefaultValue" : 1658482441413
}
// bool
{
"type" : "bool",
"typeDefaultValue" : false
}
// enum
{
"range" : [
"e1",
"e2",
"e3"
],
"typeDefaultValue" : "e1",
"type" : "enum"
}
// fault (bitmap)
{
"label" : [
"f1",
"f2"
],
"typeDefaultValue" : 0,
"type" : "bitmap"
}
// array
{
"maxSize" : 4,
"type" : "array",
"elementTypeSpec" : {
"type" : "value"
}
}
// struct
{
"type" : "struct",
"properties" : {
"struct_value" : {
"name" : "test_value",
"typeSpec" : {
"type" : "value",
"min" : 11,
"typeDefaultValue" : 11,
"max" : 22,
"step" : 2,
"scale" : 1
}
}
}
}
Data model of TuyaSmartThingAction
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| abilityId | int | The action ID. |
| code | String | The action code. |
| inputParams | List | The list of parameters to be sent. |
| outputParams | List | The list of parameters to be reported. |
inputParams and outputParams are arrays of typeSpec and can be empty. Example:
// input
{
"code": "action_input_output_params",
"abilityId" : 108,
"inputParams" : [{
"typeSpec" : {
"unit" : "$",
"type" : "value",
"min" : 0,
"max" : 5,
"typeDefaultValue" : 0,
"step" : 1,
"scale" : 0
},
"code" : "action_value"
},
{
"typeSpec" : {
"type" : "string",
"typeDefaultValue" : "",
"maxlen" : 100
},
"code" : "action_string"
}],
"outputParams" : [{
"typeSpec" : {
"unit" : "$",
"type" : "value",
"min" : 0,
"max" : 100,
"typeDefaultValue" : 0,
"step" : 1,
"scale" : 0
},
"code" : "out_action_value"
}]
}
Data model of TuyaSmartThingEvent
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| abilityId | int | The event ID. |
| code | String | The event code. |
| outputParams | List | The list of parameters to be reported. |
Control devices
Send commands
API description
ITuyaDevice
void publishThingMessageWithType(TuyaSmartThingMessageType thingMessageType,
Object command,
IResultCallback callback);
Parameters
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| thingMessageType | TuyaSmartThingMessageType | PROPERTY, // The property. ACTION, // The action. EVENT; // The event. |
| command | Object | Payload in JsonString format |
| callback | IResultCallback | The success or failure callback. |
-
The content validity is checked to send a command. Therefore, the things data model must be cached in this process. You need to timely check and pull the latest things data model.
-
To support the features of TuyaLink-based devices, they can be controlled over MQTT only.
-
The events in
TuyaSmartThingMessageTypecan only be reported, which means they are read-only and cannot be changed. -
The following examples show the command format.
Rules of sending properties
// Multiple properties can be sent simultaneously. `code` is the property code in a things data model. `value` is subject to the definition of `typeSpec`.
{
"code": value,
"code": value
}
// Example:
{
"color":"green",
"brightness": 50
}
Rules of sending an action
// Only one action can be sent at a time.
{
"actionCode": "code",
"inputParams": {
"paramsCode": value,
"paramsCode": value,
}
}
// Example:
{
"actionCode": "action_input_output_params",
"inputParams": {
"action_value": 5,
"action_string": "test_string"
}
}
Example:
// Pulls the latest things data model at the right time, for example, when users tap a device to go to the device control page.
void fetchThingModel(){
// DeviceBean deviceBean = TuyaOSDevice.getDeviceBean("your_device_id");
if (deviceBean.isSupportThingModelDevice()) {
TuyaOsDevice.getDeviceOperator().getThingModelWithProductId("pid", new ITuyaDataCallback<TuyaSmartThingModel>() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(TuyaSmartThingModel result) {
}
@Override
public void onError(String errorCode, String errorMessage) {
}
});
}
}
// Device control: send properties
// Note: `deviceModel.thingModel` must exist before properties are sent.
void publishProperty(){
// ITuyaDevice device = TuyaOSDevice.newDeviceInstance("your_device_id");
// Sends properties.
JSONObject command = new JSONObject();
command.put("color","green");
command.put("brightness", 50);
device.publishThingMessageWithType(TuyaSmartThingMessageType.PROPERTY, command, new IResultCallback() {
@Override
public void onError(String code, String error) {
Log.i("publish", "error");
}
@Override
public void onSuccess() {
Log.i("publish", "success");
}
});
}
// Device control: send an action
// Note: `deviceModel.thingModel` must exist before an action is sent.
void publishAction(){
// ITuyaDevice device = TuyaOSDevice.newDeviceInstance("your_device_id");
// Sends an action.
JSONObject command = new JSONObject();
command.put("actionCode","action_input_output_params");
JSONObject inputParams = new JSONObject();
inputParams.put("action_value",5);
inputParams.put("action_string", "test_string");
command.put("inputParams", inputParams);
device.publishThingMessageWithType(TuyaSmartThingMessageType.ACTION, command, new IResultCallback() {
@Override
public void onError(String code, String error) {
Log.i("publish", "error");
}
@Override
public void onSuccess() {
Log.i("publish", "success");
}
});
}
Listen for the callback
You can use ITuyaDevice to listen for the callback.
API description
// Registers a listener.
void registerTuyaLinkMessageListener(ITuyaLinkDeviceListener listener);
// Unregisters a listener by using `ITuyaDevice#onDestroy`.
void unRegisterTuyaLinkMessageListener();
Parameters
ITuyaLinkDeviceListener#(TuyaSmartThingMessageType messageType, Map<String, Object> payload)
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| messageType | TuyaSmartThingMessageType | PROPERTY, // The property. ACTION, // The action. EVENT; // The event. |
| payload | Map<String, Object> | The reported content that is received. The format can vary, depending on different values of type. For more information, see the examples below in things to note. |
- The content validity is checked to report status data. Therefore, the things data model must be cached in this process. You need to timely check and pull the latest things data model.
- The property messages will be converted into the
dpsformat, and the callback will be returned byIDevListener#onDpUpdate(String devId,String dpStr)registered withITuyaDevice. - The following examples show the payload format that varies depending on different message types.
Report device properties
// Rules of the format
{
"code": {
"value": value,
"time": 1234567890
},
"code": {
"value": value,
"time": 1234567890
}
}
// Example:
{
"color": {
"value": "green",
"time": 1234567890
},
"brightness": {
"value": 50,
"time": 1234567890
}
}
Report an action
// Rules of the format
{
"actionCode": code,
"outputParams": {
"outputParam1": value,
"outputParam2": value
}
}
// Example:
{
"actionCode": "open_door_action",
"outputParams": {
"status": "open",
"angle": 30
}
}
Report an event
// Rules of the format
{
"eventCode": code,
"outputParams": {
"outputParam1": value,
"outputParam2": value
}
}
// Example:
{
"eventCode": "people_move_event",
"outputParams": {
"count": 2,
"time": "2022-07-22 18:30:00"
}
}
Example
ITuyaDevice
// Listens for the callback at the right time.
ITuyaDevice tuyaDevice = ITuyaOSDevice.newDeviceInstance("your device id");
// Note: `deviceModel.thingModel` must exist before the reported content is received.
tuyaDevice.registerTuyaLinkMessageListener(new ITuyaLinkDeviceListener() {
@Override
public void onReceiveThingMessage(TuyaSmartThingMessageType messageType, Map<String, Object> payload) {
Log.i("TuyaDevice", thingMessageType, payload);
// The payload format can vary, depending on different values of `type`. For more information, see the parameter description.
if (thingMessageType == TuyaSmartThingMessageType.PROPERTY) {
//.. do something
} else if (thingMessageType == TuyaSmartThingMessageType.ACTION) {
//.. do something
} else if (thingMessageType == TuyaSmartThingMessageType.EVENT) {
//.. do something
}
});
Cached payload of property, action, and event
For a things data model, the property represents the continuous and queryable states of a device. The action and event represent the real-time responses of a device.
Therefore, the cache rules for each message payload are described as follows:
- The
propertyis cached.DeviceBean##getDps()can be used to get the cached content. - The
actionis not cached. - The
eventis not cached.
The property is defined in the same way as the data point (DP) of a generic device. Therefore, the property can be cached based on DeviceBean##getDps. Format: dpId = value.
The property is displayed based on the mappings of TuyaSmartThingProperty##abilityId in the property model.
Convert property payload to DP
The properties of a TuyaLink-based device are defined in the same way as the DP of a generic device. The difference is that array and struct are added as new types for TuyaLink.
When reported property messages are received, a callback is returned by ITuyaDevice#registerTuyaLinkMessageListener(ITuyaLinkDeviceListener listener). Meanwhile, the property is converted to dps, and the callback for onDpUpdate is returned by the listener registered in ITuyaDevice#registerDevListener(IDevListener listener). The returned content is cached in the properties DeviceBean##dps and DeviceBean##dpsTime.
You can also convert the property to the DP by using TuyaOsDevice#getDeviceOperator#dpsFromProperties(String deviceId,String propertyPayload).
API description
ITuyaDeviceOperator{
//...
// Converts the property to the DP.
String dpsFromProperties(String deviceId, String properties);
}
Parameters
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| properties | String | The property payload, in the same JsonString format as that of the reported property, as described in the following example. |
Format of the property payload
{
"code": {
"value": value,
"time": time
},
"code": {
"value": value,
"time": time
},
}
Example
void transferPropertiesToDp(){
JSONObject propertiesPayload = new JSONObject();
propertiesPayload.put("color","green");
propertiesPayload.put("brightness", 50);
String dps = dpsFromProperties("deviceId", propertiesPayload.toJSONString());
Log.i("dps:", dps);
/**
In the output, `101` and `105` respectively represent `color` and `brightness` of `TuyaSmartThingProperty::abilityId`.
@{
@"101": @"green",
@"105": @50
}
*/
}
Is this page helpful?
YesFeedbackIs this page helpful?
YesFeedback





