Basic Features
Last Updated on : 2024-07-30 03:01:54download
This topic describes the serial protocol used to interface your MCU with Tuya’s NB-IoT module.
Serial communication
- Baud: 9600/115200
- Data bit: 8
- Parity check: none
- Stop bit: 1
- Data flow control: none
- MCU: microcontroller unit. Your MCU communicates with Tuya’s modules through the serial port. The serial protocol is designed to enable full-duplex communication between the device and the server.
Frame format
-
All data greater than one byte is transmitted in big-endian format.
-
All sample data in the protocol is in hexadecimal format.
-
The NB-IoT module sends packets and waits for a response. If no response is received within one second, the unanswered packets will be retransmitted three times.
-
One command is sent by one party and received by the other party synchronously. That is, one party sends a command and waits for a response from the other party. If the sender does not receive a correct response packet within a specified time period, the transmission times out.
For more information, see Protocol list.
-
The MCU reports status synchronously. Assume that the MCU reports a command
Y. The data transmission is as follows.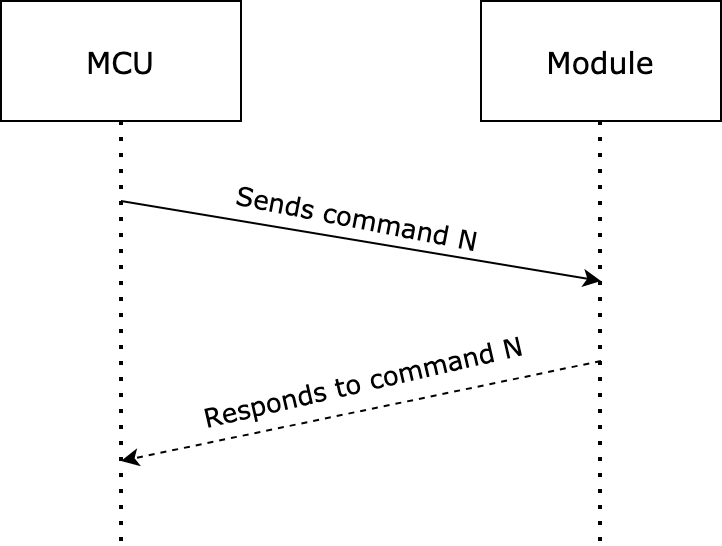
Field Bytes Description Header 2 It is fixed to 0x55aa. Version 1 It is used for updates and extensions. Command 1 The frame type. Data length 2 Big-endian format. Data N The data from the network layer is included, such as the IP address packet. Checksum 1 Start from the header, add up all the bytes, and then divide the sum by 256 to get the remainder.
Basic protocol
Query product information (0x01)
Product information consists of the product ID and the MCU software version number.
- Product ID (PID): A unique identifier assigned to each product created on the Developer Platform for storing product information in the cloud.
- MCU software version number: Expressed in dot-decimal notation. For example,
x.x.x(0 ≤x≤ 99), andxis a decimal digit.
Example:
| Field | Bytes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Header | 2 | 0x55aa |
| Version | 1 | 0x00 |
| Command | 1 | 0x01 |
| Data length | 2 | 0x0000 |
| Data | 0 | None |
| Checksum | 1 | Start from the header, add up all the bytes, and then divide the sum by 256 to get the remainder. |
Example:
55 aa 00 01 00 00 00
The MCU returns the following data.
| Field | Bytes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Header | 2 | 0x55aa |
| Version | 1 | 0x00 |
| Command | 1 | 0x01 |
| Data length | 2 | N |
| Data | N | {"p":"gl9iswyeobu5s93j", "v":"1.0.0", "s":"psm", "c":"isp"}{"p":"gl9iswyeobu5s93j", "v":"1.0.0", "s":"psm", "c":"isp","t":"22092217004703"} |
| Checksum | 1 | Start from the header, add up all the bytes, and then divide the sum by 256 to get the remainder. |
Data
| Parameter | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| p | Required | The PID of the product you create on the Tuya Developer Platform. |
| v | Required | The MCU version number. |
| s | Required | The power consumption mode.
|
| c | Required | Cloud connectivity.
|
| t | Optional | For time-sensitive scenarios, you can instruct the MCU to configure the RTC of the NB-IoT module. For example, create a local schedule in the format 22092217004703.
|
Example:
55 AA 00 01 00 38 7B 22 70 22 3A 22 67 6C 39 69 73 77 79 65 6F 62 75 35 73 39 33 6A 22 2C 22 76 22 3A 22 31 2E 30 2E 30 22 2C 22 73 22 3A 22 70 73 6D 22 2C 22 63 22 3A 22 69 73 70 22 7D 02
Report network status (0x02)
| Network status | Description | Status value |
|---|---|---|
| Status 1 | The module is searching for a carrier to register to. | 0x01 |
| Status 2 | The module is connecting to the carrier’s network. | 0x02 |
| Status 3 | The module is registered to the carrier but not bound. | 0x03 |
| Status 4 | The module is bound and connected to the cloud. | 0x04 |
| Status 5 | The module attempting to attach to the network is rejected. | 0x05 |
Example:
| Field | Bytes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Header | 2 | 0x55aa |
| Version | 1 | 0x00 |
| Command | 1 | 0x02 |
| Data length | 2 | 0x0001 |
| Data | 1 | The network connection status.
|
| Checksum | 1 | Start from the header, add up all the bytes, and then divide the sum by 256 to get the remainder. |
Example:
The module is bound and connected to the cloud.
55 aa 00 02 00 01 04 06
The MCU returns the following data.
| Field | Bytes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Header | 2 | 0x55aa |
| Version | 1 | 0x00 |
| Command | 1 | 0x02 |
| Data length | 2 | 0x0000 |
| Data | 0 | None |
| Checksum | 1 | Start from the header, add up all the bytes, and then divide the sum by 256 to get the remainder. |
Example:
55 aa 00 02 00 00 01
Reset NB-IoT module (0x03)
The module is reset to factory defaults and unbound from the cloud.
The MCU sends the following data.
| Field | Bytes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Header | 2 | 0x55aa |
| Version | 1 | 0x00 |
| Command | 1 | 0x03 |
| Data length | 2 | 0x0000 |
| Data | 0 | None |
| Checksum | 1 | Start from the header, add up all the bytes, and then divide the sum by 256 to get the remainder. |
Example:
55 aa 00 03 00 00 02
The module returns the following data.
| Field | Bytes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Header | 2 | 0x55aa |
| Version | 1 | 0x00 |
| Command | 1 | 0x03 |
| Data length | 2 | 0x0000 |
| Data | 0 | None |
| Checksum | 1 | Start from the header, add up all the bytes, and then divide the sum by 256 to get the remainder. |
Example:
55 aa 00 03 00 00 02
Report real-time status (0x05)
This command can be executed successfully only when the module is connected to the cloud.
The MCU reports the real-time status of DPs to the module.
- This is a synchronous command. The MCU reports DP status and then waits for the result from the module. Ideally, the cloud returns the result within five seconds.
- The MCU can report the status of single or multiple DPs at a time. You can select the appropriate packet transmission option as needed. See the example for data packets.
Scenario
With this command, devices such as smart alarms can send the real-time status of a DP to the cloud for delivering instant alerts to the users.
The MCU sends the following data.
| Field | Bytes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Header | 2 | 0x55aa |
| Version | 1 | 0x00 |
| Command | 1 | 0x05 |
| Data length | 2 | It depends on the protocol version as well as the type and number of data units. |
| Message ID | 2 | It applies to protocol versions 0x01 and later. Protocol version 0x00 does not include this field. |
| Data | N | Single or multiple data units. |
| Checksum | 1 | Start from the header, add up all the bytes, and then divide the sum by 256 to get the remainder. |
The module returns the following data.
| Field | Bytes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Header | 2 | 0x55aa |
| Version | 1 | 0x00 |
| Command | 1 | 0x05 |
| Data length | 2 | The value of this field is 0x0001 for protocol version 0x00, and 0x0003 for versions 0x01 and later. |
| Message ID | 2 | It applies to protocol versions 0x01 and later. Protocol version 0x00 does not include this field. |
| Data | 1 | 0x00: Success. 0x01: Failure. |
| Checksum | 1 | Start from the header, add up all the bytes, and then divide the sum by 256 to get the remainder. |
-
Report a single data unit (protocol version
0x00)Status data: The DP 109 is of Boolean data type, and its value is
1.55 aa 00 05 00 05 6d 01 00 01 01 79 -
Report multiple data units (protocol version
0x00)-
Status data 1: The DP 109 is of Boolean data type, and its value is
1. -
Status data 2: The DP 102 is of string data type, and its value is
201804121507that is transferred in ASCII mode.55 aa 00 05 00 15 6d 01 00 01 01 66 03 00 0c 32 30 31 38 30 34 31 32 31 35 30 37 5d
-
-
Report a single data unit (protocol versions
0x01and later)-
Message ID:
0x00FF -
Status data: The DP 109 is of Boolean data type, and its value is
1.55 AA 01 05 00 07 00 FF 6D 01 00 01 01 7B
-
-
Report multiple data units (protocol versions
0x01and later)-
Message ID:
0x0100 -
Status data 1: The DP 109 is of Boolean data type, and its value is
1. -
Status data 2: The DP 102 is of string data type, and its value is
201804121507that is transferred in ASCII mode.55 AA 01 05 00 17 01 00 6D 01 00 01 01 66 03 00 0C 32 30 31 38 30 34 31 32 31 35 30 37 61
-
Report record-type data (0x08)
A piece of record-type data contains the status of multiple DPs, which should be reported in one packet. If the device is offline when the MCU reports data, the module will retain this data and send it to the cloud on the next reporting operation.
-
Stranded data: Each time the module successfully reports a piece of stranded data to the cloud, it sends
0x01to the MCU through the command0x08. -
Cloud connection: If the network works fine, the module will be connected to the cloud within 30 seconds after the first power on. The MCU needs to wait for the network status from the module before reporting record-type data. However, if the MCU does not receive the status of a successful cloud connection within six seconds, it can report data through this command
0x08and then wait for the result. -
Data length limit: The maximum payload size for each packet is 100 bytes. The actual size varies based on the DP data. When the module is offline, it will return a failure if the MCU reports the data whose length exceeds the limit.
-
Maximum records: The module can retain up to 20 historical records. When the limit is reached, the newest record will overwrite the oldest one.
-
Return result: The module returns the result of a reporting operation to the MCU.
0x00: Reporting succeeded.- The reported data is sent to the cloud and no data is stranded.
- The module is offline and retains the reported data in its flash memory.
0x01: The reported data is sent to the cloud but stranded data exists.0x02: Reporting failed.
-
Timestamp: Carrying a timestamp ensures that the reported data reflects the actual events when the module is offline. If you use the time when the data arrives at the server, the time of the stranded data is not the one when the event actually occurs.
Therefore, when a module is paired for the first time, if the network works fine, the MCU should sync with the server time through the serial protocol. This way, the carried system time will prevail when the server processes the stranded data.
Scenario
For the door lock, its MCU can report record-type data with a system timestamp. In case of transient network failure, the module can retain the received data and send it to the cloud on the next reporting operation.
The MCU sends the following data.
| Field | Bytes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Header | 2 | 0x55aa |
| Version | 1 | 0x00 |
| Command | 1 | 0x08 |
| Data length | 2 | It depends on the protocol version as well as the type and number of data units. |
| Message ID | 2 | It applies to protocol versions 0x01 and later. Protocol version 0x00 does not include this field. |
| Data | 7 | If you use the MCU’s system timestamp, take the following format.
Note: If you use the module’s system timestamp, populate this field with |
| N | Single or multiple data units. | |
| Checksum | 1 | Start from the header, add up all the bytes, and then divide the sum by 256 to get the remainder. |
Example:
-
Report a single data unit (protocol version
0x00)The DP 109 is of Boolean data type, and its value is
1. The RTC time of the module prevails.55 aa 00 08 00 0c 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 6d 01 00 01 01 d1 -
Report multiple data units (protocol version
0x00)-
Status data 1: The DP 109 is of Boolean data type, and its value is
1. -
Status data 2: The DP 102 is of string data type, and its value is
201804121507that is transferred in ASCII mode. The server time prevails.55 aa 00 08 00 1c 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 6d 01 00 01 01 66 03 00 0c 32 30 31 38 30 34 31 32 31 35 30 37 a7
-
-
Report a single data unit (protocol versions
0x01and later)-
Message ID:
0x00FF -
The DP 109 is of Boolean data type, and its value is
1. The RTC time of the module prevails.55 AA 01 08 00 0E 00 FF 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 6D 01 00 01 01 85
-
-
Report multiple data units (protocol versions
0x01and later)-
Message ID:
0x0100 -
Status data 1: The DP 109 is of Boolean data type, and its value is
1. -
Status data 2: The DP 102 is of string data type, and its value is
201804121507that is transferred in ASCII mode. The server time prevails.55 AA 01 08 00 1E 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 6D 01 00 01 01 66 03 00 0C 32 30 31 38 30 34 31 32 31 35 30 37 6B
-
The module returns the following data.
| Field | Bytes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Header | 2 | 0x55aa |
| Version | 1 | 0x00 |
| Command | 1 | 0x08 |
| Data length | 2 | The value of this field is 0x0001 for protocol version 0x00, and 0x0003 for versions 0x01 and later. |
| Message ID | 2 | It applies to protocol versions 0x01 and later. Protocol version 0x00 does not include this field. |
| Data | 1 |
|
| Checksum | 1 | Start from the header, add up all the bytes, and then divide the sum by 256 to get the remainder. |
Send commands (0x09)
The module sends control commands to the MCU asynchronously. The MCU acknowledges receipt of the command and executes a specific operation. Then, it reports the current status of related DPs to the module.
Example:
| Field | Bytes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Header | 2 | 0x55aa |
| Version | 1 | 0x00 |
| Command | 1 | 0x09 |
| Data length | 2 | It depends on the types and the number of data units. |
| Data | N | Data units |
| Checksum | 1 | Start from the header, add up all the bytes, and then divide the sum by 256 to get the remainder. |
Example:
Suppose that DP 3 of Boolean type is used for on/off control, and 1 means to turn on the device. The module sends the following to the MCU.
55 aa 00 09 00 05 03 01 00 01 01 13
The MCU returns the following data.
| Field | Bytes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Header | 2 | 0x55aa |
| Version | 1 | 0x00 |
| Command | 1 | 0x09 |
| Data length | 2 | 0x0000 |
| Data | 0 | None |
| Checksum | 1 | Start from the header, add up all the bytes, and then divide the sum by 256 to get the remainder. |
Example:
55 aa 00 09 00 00 08
Data units
The DP command and status data units are defined as follows:
| Field | Length (byte) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| dpid | 1 | The DP ID. |
| type | 1 | It indicates the data type of a DP defined on the Tuya Developer Platform.
|
| len | 2 | The length is the number of bytes of the value, in big-endian format. |
| value | 1/2/4/N | Represented in hexadecimal format. Data greater than one byte is transmitted in big-endian format. |
All available data types except for the raw type are the object types. The MCU can report the status of multiple DPs.
Get the local time (0x06)
- After the MCU receives the status of a successful cloud connection, it sends this command to request the local time.
- The request might fail due to poor network conditions. For time-critical devices such as door locks, you can set a three-second request interval to handle the situation that the MCU fails to get the time data for its first time-sync.
The MCU sends the following data.
| Field | Bytes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Header | 2 | 0x55aa |
| Version | 1 | 0x00 |
| Command | 1 | 0x06 |
| Data length | 2 | 0x0000 |
| Data | 0 | None |
| Checksum | 1 | Start from the header, add up all the bytes, and then divide the sum by 256 to get the remainder. |
Example:
55 aa 00 06 00 00 05
The module returns the following data.
| Field | Bytes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Header | 2 | 0x55aa |
| Version | 1 | 0x00 |
| Command | 1 | 0x06 |
| Data length | 2 | 0x0008 |
| Data | Data | The data length is eight bytes.
|
| Checksum | 1 | Start from the header, add up all the bytes, and then divide the sum by 256 to get the remainder. |
Example:
The local time is 16:09:05 on September 17, 2018, Monday.
-
If the device is activated in mainland China, the local time is Beijing time (UTC+8).
-
If the device is activated in other countries or regions, the local time is the time zone in which the device is located.
55 aa 00 06 00 08 01 12 09 11 10 09 05 01 59
Get the GMT (0x10)
- GMT is independent of the time zone and DST. For products with the dynamic password function, such as door locks, if they do not support local time display, you only need to implement the GMT feature. When the MCU reports record-type data, the GMT can be carried.
- If your products support local time display, they must request the local time regularly and store the time zone offset. This way, the local time can be calculated by adding the time zone offset to the GMT.
The MCU sends the following data.
| Field | Bytes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Header | 2 | 0x55aa |
| Version | 1 | 0x00 |
| Command | 1 | 0x10 |
| Data length | 2 | 0x0000 |
| Data | 0 | None |
| Checksum | 1 | Start from the header, add up all the bytes, and then divide the sum by 256 to get the remainder. |
Example:
55 aa 00 10 00 00 0F
The module returns the following data.
| Field | Bytes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Header | 2 | 0x55aa |
| Version | 1 | 0x00 |
| Command | 1 | 0x10 |
| Data length | 2 | 0x0008 |
| Data | 8 | The data length is eight bytes.
|
| Checksum | 1 | Start from the header, add up all the bytes, and then divide the sum by 256 to get the remainder. |
Example:
The GMT is 08:21:03 on September 17, 2018, Monday.
55 aa 00 10 00 08 01 12 09 11 08 15 03 01 65
Request signal strength (0x0B)
The MCU can send this command to get the received signal strength.
The MCU sends the following data.
| Field | Bytes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Header | 2 | 0x55aa |
| Version | 1 | 0x00 |
| Command | 1 | 0x0b |
| Data length | 2 | 0x0000 |
| Data | 0 | None |
| Checksum | 1 | Start from the header, add up all the bytes, and then divide the sum by 256 to get the remainder. |
Example:
55 aa 00 0b 00 00 0a
The module returns the following data.
| Field | Bytes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Header | 2 | 0x55aa |
| Version | 1 | 0x00 |
| Command | 1 | 0x0b |
| Data length | 2 | 0x0002 |
| Data | 2 | The value of Data[0] can be:
0x01, Data[1] indicates the received signal strength indication (RSSI).
|
| Checksum | 1 | Start from the header, add up all the bytes, and then divide the sum by 256 to get the remainder. |
Example:
55 aa 00 0b 00 02 01 50 5D
Query module’s memory (0x0F)
The MCU can send this command to the module to query the remaining memory of the module.
The MCU sends the following data.
| Field | Bytes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Header | 2 | 0x55aa |
| Version | 1 | 0x00 |
| Command | 1 | 0x0f |
| Data length | 2 | 0x0000 |
| Data | 0 | None |
| Checksum | 1 | Start from the header, add up all the bytes, and then divide the sum by 256 to get the remainder. |
Example:
55 aa 00 0f 00 00 0e
The module returns the following data.
| Field | Bytes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Header | 2 | 0x55aa |
| Version | 1 | 0x00 |
| Command | 1 | 0x0f |
| Data length | 2 | 0x0004 |
| Data | 2 | Data[0-3]: The RAM available on the module, in bytes. |
| Checksum | 1 | Start from the header, add up all the bytes, and then divide the sum by 256 to get the remainder. |
Example:
55 aa 00 0f 00 04 00 01 F4 00 07
Request the binding state (0xBB)
The MCU can send this command to request whether the module has been bound.
The MCU sends the following data.
| Field | Bytes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Header | 2 | 0x55aa |
| Version | 1 | 0x00 |
| Command | 1 | 0xbb |
| Data length | 2 | 0x0000 |
| Data | 0 | None |
| Checksum | 1 | Start from the header, add up all the bytes, and then divide the sum by 256 to get the remainder. |
Example:
55 aa 00 bb 00 00 0a
The module returns the following data.
| Field | Bytes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Header | 2 | 0x55aa |
| Version | 1 | 0x00 |
| Command | 1 | 0xbb |
| Data length | 2 | 0x0001 |
| Data | 1 | The data length is one byte.
|
| Checksum | 1 | Start from the header, add up all the bytes, and then divide the sum by 256 to get the remainder. |
The module returns the following data.
55 aa 00 bb 00 01 01 bc
Set the power saving lock (0xB2)
If the power saving lock is set to 0x01, the module is not allowed to enter the power saving mode (PSM). If the lock is set to 0x00, the module will automatically enter PSM when it is idle. In PSM, the MCU can pull down PSM-INT to wake up the module.
The MCU sends the following data.
| Field | Bytes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Header | 2 | 0x55aa |
| Version | 1 | 0x00 |
| Command | 1 | 0xb2 |
| Data length | 2 | 0x0001 |
| Data | 1 | The data length is one byte.
|
| Checksum | 1 | Start from the header, add up all the bytes, and then divide the sum by 256 to get the remainder. |
Example:
55 aa 00 b2 00 01 01 00
The module returns the following data.
| Field | Bytes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Header | 2 | 0x55aa |
| Version | 1 | 0x00 |
| Command | 1 | 0xb2 |
| Data length | 2 | 0x0000 |
| Data | 0 | 0 |
| Checksum | 1 | Start from the header, add up all the bytes, and then divide the sum by 256 to get the remainder. |
The module returns the following data.
55 aa 00 b2 00 00 b1
Set the network heartbeat interval (0xB3)
The network heartbeat interval defaults to eight hours. You can set an interval as needed.
The MCU sends the following data.
| Field | Bytes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Header | 2 | 0x55aa |
| Version | 1 | 0x00 |
| Command | 1 | 0xb3 |
| Data length | 2 | 0x0004 |
| Data | 4 | Big-endian unsigned integer in seconds |
| Checksum | 1 | Start from the header, add up all the bytes, and then divide the sum by 256 to get the remainder. |
Example:
Set the heartbeat interval to one hour.
55 aa 00 b3 00 04 00 00 0e 10 da
The module returns the following data.
| Field | Bytes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Header | 2 | 0x55aa |
| Version | 1 | 0x00 |
| Command | 1 | 0xb3 |
| Data length | 2 | 0x0001 |
| Data | 1 |
|
| Checksum | 1 | Start from the header, add up all the bytes, and then divide the sum by 256 to get the remainder. |
The module returns the following data.
55 aa 00 b3 00 01 01 b4
Set the next wake-up interval (0xC1)
- The MCU can send this command to wake up the module if the stranded record-type data failed to be sent to the cloud. After the stranded data is sent, the normal heartbeat interval is resumed.
- The minimum wake-up interval is 120 seconds. If the specified time is less than 120 seconds, 120 seconds will apply.
- You can set the wake-up time to send urgent record-type data.
The MCU sends the following data.
| Field | Bytes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Header | 2 | 0x55aa |
| Version | 1 | 0x00 |
| Command | 1 | 0xc1 |
| Data length | 2 | 0x0004 |
| Data | 4 | Big-endian unsigned integer in seconds |
| Checksum | 1 | Start from the header, add up all the bytes, and then divide the sum by 256 to get the remainder. |
Example:
Set the next wake-up interval to three minutes.
55 aa 00 c1 00 04 00 00 00 b4 78
The module returns the following data.
| Field | Bytes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Header | 2 | 0x55aa |
| Version | 1 | 0x00 |
| Command | 1 | 0xc1 |
| Data length | 2 | 0x0001 |
| Data | 1 |
|
| Checksum | 1 | Start from the header, add up all the bytes, and then divide the sum by 256 to get the remainder. |
The module returns the following data.
55 aa 00 c1 00 01 01 c2
Automate heartbeat transmission (0xB1)
Typically, the module automatically sends heartbeats to the MCU as scheduled. With this command, the MCU can proactively send a heartbeat for DP status reporting. Generally, the command report real-time status can work for the same purpose.
The MCU sends the following data.
| Field | Bytes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Header | 2 | 0x55aa |
| Version | 1 | 0x00 |
| Command | 1 | 0xb1 |
| Data length | 2 | 0x0000 |
| Data | 0 | None |
| Checksum | 1 | Start from the header, add up all the bytes, and then divide the sum by 256 to get the remainder. |
Example:
55 AA 00 B1 00 00 B0
The module returns the following data.
| Field | Bytes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Header | 2 | 0x55aa |
| Version | 1 | 0x00 |
| Command | 1 | 0xb1 |
| Data length | 2 | 0x0001 |
| Data | 1 |
|
| Checksum | 1 | Start from the header, add up all the bytes, and then divide the sum by 256 to get the remainder. |
The module returns the following data.
55 AA 00 B1 00 01 01 B2
Request network status (0x2B)
| Network status | Description | Status value |
|---|---|---|
| Status 1 | The module is searching for a carrier to register to. | 0x01 |
| Status 2 | The module is connecting to the carrier’s network. | 0x02 |
| Status 3 | The module is registered to the carrier but not bound. | 0x03 |
| Status 4 | The module is bound and connected to the cloud. | 0x04 |
The MCU sends the following data.
| Field | Bytes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Header | 2 | 0x55aa |
| Version | 1 | 0x00 |
| Command | 1 | 0x2b |
| Data length | 2 | 0x0000 |
| Data | 0 | None |
| Checksum | 1 | Start from the header, add up all the bytes, and then divide the sum by 256 to get the remainder. |
Example:
55 aa 00 2b 00 00 2c
The module returns the following data.
| Field | Bytes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Header | 2 | 0x55aa |
| Version | 1 | 0x00 |
| Command | 1 | 0x2b |
| Data length | 2 | 0x0001 |
| Data | 1 | The network connection status.
|
| Checksum | 1 | Start from the header, add up all the bytes, and then divide the sum by 256 to get the remainder. |
Example:
The module is bound and connected to the cloud.
55 aa 00 2b 00 01 04 2f
Detect battery level (0xBC)
For battery-powered devices, if the battery is exhausted during a firmware update, the module might not work properly.
The mobile app will request the current battery level after it downloads the updates. You need to set a battery level threshold (usually greater than 50%) for performing a firmware update.
Mains-powered devices can install updates when they are not running at a low battery level.
Example:
| Field | Bytes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Header | 2 | 0x55aa |
| Version | 1 | 0x00 |
| Command | 1 | 0xbc |
| Data length | 2 | 0x0000 |
| Data | 0 | None |
| Checksum | 1 | Start from the header, add up all the bytes, and then divide the sum by 256 to get the remainder. |
Example:
55 AA 00 BC 00 00 BB
The MCU returns the following data.
| Field | Bytes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Header | 2 | 0x55aa |
| Version | 1 | 0x00 |
| Command | 1 | 0xbc |
| Data length | 2 | 0x0001 |
| Data | 1 |
|
| Checksum | 1 | Start from the header, add up all the bytes, and then divide the sum by 256 to get the remainder. |
Example:
55 AA 00 BC 00 01 01 BD
Report the current status (0xBE)
| Status | Description | Status value |
|---|---|---|
| Status 1 | The module is initializing. | 0x00 |
| Status 2 | The module detects a SIM card. | 0x01 |
| Status 3 | The module works properly. | 0x02 |
| Status 4 | The module is bound. | 0x03 |
| Status 5 | The module is unbound. | 0x04 |
| Status 6 | The module successfully downloads the schema. | 0x05 |
| Status 7 | The module is about to sleep. | 0x06 |
| Status 8 | The module is about to restart. | 0x07 |
| Status 9 | Device is being reset. | 0x08 |
| Status 10 | NB-IoT FOTA download is started. | 0x09 |
| Status 11 | NB-IoT FOTA download is finished. | 0x0A |
| Status 12 | NB-IoT FOTA download fails. | 0x0B |
| Status 13 | NB-IoT FOTA update is started. | 0x0C |
| Status 14 | NB-IoT FOTA update succeeds. | 0x0D |
| Status 15 | NB-IoT FOTA update fails. | 0x0E |
| Status 16 | NB-IoT schema download is started. | 0x0F |
| Status 17 | NB-IoT schema download fails. | 0x10 |
Example:
| Field | Bytes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Header | 2 | 0x55aa |
| Version | 1 | 0x00 |
| Command | 1 | 0xbe |
| Data length | 2 | 0x0001 |
| Data | 1 | Indicate the operation status of the NB-IoT module.
|
| Checksum | 1 | Start from the header, add up all the bytes, and then divide the sum by 256 to get the remainder. |
Example:
The module sends the following data when it runs in status 3.
55 aa 00 be 00 01 02 c0
Request the module’s current status (0xBF)
| Status | Description | Status value |
|---|---|---|
| Status 1 | The module is initializing. | 0x00 |
| Status 2 | The module detects a SIM card. | 0x01 |
| Status 3 | The module works properly. | 0x02 |
| Status 4 | The module is bound. | 0x03 |
| Status 5 | The module is unbound. | 0x04 |
| Status 6 | The module successfully downloads the schema. | 0x05 |
| Status 7 | The module is about to sleep. | 0x06 |
| Status 8 | The module is about to restart. | 0x07 |
| Status 9 | Device is being reset. | 0x08 |
| Status 10 | NB-IoT FOTA download is started. | 0x09 |
| Status 11 | NB-IoT FOTA download is finished. | 0x0A |
| Status 12 | NB-IoT FOTA download fails. | 0x0B |
| Status 13 | NB-IoT FOTA update is started. | 0x0C |
| Status 14 | NB-IoT FOTA update succeeds. | 0x0D |
| Status 15 | NB-IoT FOTA update fails. | 0x0E |
| Status 16 | NB-IoT schema download is started. | 0x0F |
| Status 17 | NB-IoT schema download fails. | 0x10 |
The MCU sends the following data.
| Field | Bytes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Header | 2 | 0x55aa |
| Version | 1 | 0x00 |
| Command | 1 | 0xbf |
| Data length | 2 | 0x0000 |
| Data | 0 | None |
| Checksum | 1 | Start from the header, add up all the bytes, and then divide the sum by 256 to get the remainder. |
Example:
55 aa 00 bf 00 00 be
The module returns the following data.
| Field | Bytes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Header | 2 | 0x55aa |
| Version | 1 | 0x00 |
| Command | 1 | 0xbf |
| Data length | 2 | 0x0001 |
| Data | 1 | Indicate the operation status of the NB-IoT module.
|
| Checksum | 1 | Start from the header, add up all the bytes, and then divide the sum by 256 to get the remainder. |
Example:
The module sends the following data when it runs in status 2.
55 aa 00 bf 00 01 01 c0
Enter sleep mode (0xC0)
The MCU can send this command to make the module immediately enter sleep mode.
The MCU sends the following data.
| Field | Bytes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Header | 2 | 0x55aa |
| Version | 1 | 0x00 |
| Command | 1 | 0xc0 |
| Data length | 2 | 0x0000 |
| Data | 0 | None |
| Checksum | 1 | Start from the header, add up all the bytes, and then divide the sum by 256 to get the remainder. |
Example:
55 AA 00 C0 00 00 BF
The module returns the following data.
| Field | Bytes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Header | 2 | 0x55aa |
| Version | 1 | 0x00 |
| Command | 1 | 0xc0 |
| Data length | 2 | 0x0000 |
| Data | 0 | None |
| Checksum | 1 | Start from the header, add up all the bytes, and then divide the sum by 256 to get the remainder. |
Example:
55 AA 00 C0 00 00 BF
Enter PSM mode (0xB4)
The MCU can send this command to unlock the module and make it enter the PSM mode.
The MCU sends the following data.
| Field | Bytes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Header | 2 | 0x55aa |
| Version | 1 | 0x00 |
| Command | 1 | 0xb4 |
| Data length | 2 | 0x0000 |
| Data | 0 | None |
| Checksum | 1 | Start from the header, add up all the bytes, and then divide the sum by 256 to get the remainder. |
Example:
55 AA 00 B4 00 00 B3
The module returns the following data.
| Field | Bytes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Header | 2 | 0x55aa |
| Version | 1 | 0x00 |
| Command | 1 | 0xb4 |
| Data length | 2 | 0x0000 |
| Data | 0 | None |
| Checksum | 1 | Start from the header, add up all the bytes, and then divide the sum by 256 to get the remainder. |
Example:
55 AA 00 B4 00 00 B3
Force restart (0xC4)
The MCU can proactively send this command to the NB-IoT module to restart the device.
The MCU sends the following data.
| Field | Bytes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Header | 2 | 0x55aa |
| Version | 1 | 0x00 |
| Command | 1 | 0xC4 |
| Data length | 2 | 0x0000 |
| Data | 0 | None |
| Checksum | 1 | Start from the header, add up all the bytes, and then divide the sum by 256 to get the remainder. |
Example:
55 AA 00 C4 00 00 C3
The module returns the following data.
| Field | Bytes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Header | 2 | 0x55aa |
| Version | 1 | 0x00 |
| Command | 1 | 0xC4 |
| Data length | 2 | 0x0000 |
| Data | 0 | None |
| Checksum | 1 | Start from the header, add up all the bytes, and then divide the sum by 256 to get the remainder. |
Example:
55 AA 00 C4 00 00 C3
Set the network heartbeat (0xC7)
The MCU can proactively send this command to the NB-IoT module to request the interval of the network heartbeat check.
The MCU sends the following data.
| Field | Bytes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Header | 2 | 0x55aa |
| Version | 1 | 0x00 |
| Command | 1 | 0xC7 |
| Data length | 2 | 0x0000 |
| Data | 0 | None |
| Checksum | 1 | Start from the header, add up all the bytes, and then divide the sum by 256 to get the remainder. |
Example:
55 AA 00 C7 00 00 C6
The module returns the following data.
| Field | Bytes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Header | 2 | 0x55aa |
| Version | 1 | 0x00 |
| Command | 1 | 0xC7 |
| Data length | 2 | 0x0004 |
| Data | 4 | The heartbeat interval. |
| Checksum | 1 | Start from the header, add up all the bytes, and then divide the sum by 256 to get the remainder. |
Example:
55 AA 00 C7 00 04 00 00 70 80 BA
Set the discrete information (0xCB)
The MCU configures the discrete information for the NB-IoT module on the first boot. This feature is only for the first-time network attachment, which can help to reduce network congestion when you onboard a large number of devices at the same time.
Use this feature with caution. Do not apply it to devices with an automatic power-off feature.
The MCU sends the following data.
| Field | Bytes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Header | 2 | 0x55aa |
| Version | 1 | 0x00 |
| Command | 1 | 0xCb |
| Data length | 2 | N |
| Data | N | {"enable": 1,"duration": 360,"step": 1}
|
| Checksum | 1 | Start from the header, add up all the bytes, and then divide the sum by 256 to get the remainder. |
Example:
55 AA 00 CB 00 27 7B 22 65 6E 61 62 6C 65 22 3A 20 31 2C 22 64 75 72 61 74 69 6F 6E 22 3A 20 33 36 30 2C 22 73 74 65 70 22 3A 20 31 7d 9F
The module returns the following data.
| Field | Bytes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Header | 2 | 0x55aa |
| Version | 1 | 0x00 |
| Command | 1 | 0xCb |
| Data length | 2 | 0x0001 |
| Data | 1 |
|
| Checksum | 1 | Start from the header, add up all the bytes, and then divide the sum by 256 to get the remainder. |
Example:
55 AA 00 CB 00 01 00 CB
Protocol version
| Version | Date | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0.6.19 | March 23, 2023 | Added network status 5. Updated the communication protocol version to 0x01, enabling you to report message IDs for both record-type and non-record type data. |
| 0.6.18 | October 18, 2022 | Added the feature to set the RTC and discrete information for the NB-IoT module. |
| 0.6.17 | April 20, 2022 | Added the request for FOTA and schema download status and progress, T3324 active timer, T3412 extended timer, and heartbeat interval. |
| 0.6.16 | January 25, 2022 | Added the commands for download progress query, remaining RAM memory query, and PSM and timer T3412 setting. |
| 0.6.15 | January 21, 2022 | Updated the OTA update services to support the MCU-initiated update download. |
| 0.6.14 | November 13, 2021 | Updated the MCU OTA update service to enable CRC32 result checking and ensure compatibility with the legacy protocol. |
| 0.6.13 | November 2, 2021 | Added resumable download for OTA update. |
| 0.6.12 | April 1, 2021 | Added the description of auto-baud detection for 9600 and 115200. |
| 0.6.11 | November 30, 2020 | Added the feature to allow the record-type data to carry the MCU’s timestamp. |
| 0.6.10 | November 19, 2020 | Added the command to manually set up APN. |
| 0.6.9 | November 16, 2020 | Updated the return value for the heartbeat interval configuration. |
| 0.6.8 | August 17, 2020 | Updated the signal strength representation. |
| 0.6.7 | August 13, 2020 | Added the return values of power mode and cloud connection for the production information request. |
| 0.6.6 | July 27, 2020 | Added wake-up time for resending record-type data. |
| 0.6.5 | May 14, 2020 | Added the types of module’s status, including SIM detection, binding, unbinding, and schema download. |
| 0.6.4 | April 28, 2020 | Added the command to get/send the module’s current status. Added the command to force the module to enter sleep mode. |
| 0.6.3 | April 16, 2020 | Added the command to request the module’s IMEI. |
| 0.6.2 | November 9, 2019 | Added the command to send heartbeats. |
| 0.6.1 | September 5, 2019 | Update the time field for the record-type data reporting. |
| 0.6.0 | June 24, 2019 | Updated the Wi-Fi-related information. |
| 0.5.2 | March 20, 2019 | Updated the description of the power-saving lock. |
| 0.5.1 | March 8, 2019 | Inherited from the Wi-Fi serial protocol for the smart locks. |
Is this page helpful?
YesFeedbackIs this page helpful?
YesFeedback





