AI Stream
Last Updated on : 2025-09-22 06:32:30download
Prerequisites
Set up development environment
Before integrating the AI stream, read and implement the Preparation.
After the integration is completed, import the AI stream into your project:
// Available for versions 6.7.0 and later
implementation 'com.thingclips.smart:thingsmart:6.7.6'
// Audio recording component
implementation 'com.thingclips.smart:thingsmart-audio-engine-sdk:6.7.0+'
implementation 'com.thingclips.smart:thingsmart-avlogger-sdk:6.7.0+'
Set up the agent
To enable the AI agent in your app, perform the following steps:
-
Create an agent. For more information, see AI Agent Dev Platform.
-
Publish and deploy the agent to the specified app. After configuring the agent, click Publish at the top of the page.
Record the agent ID to create a session in the SDK.

-
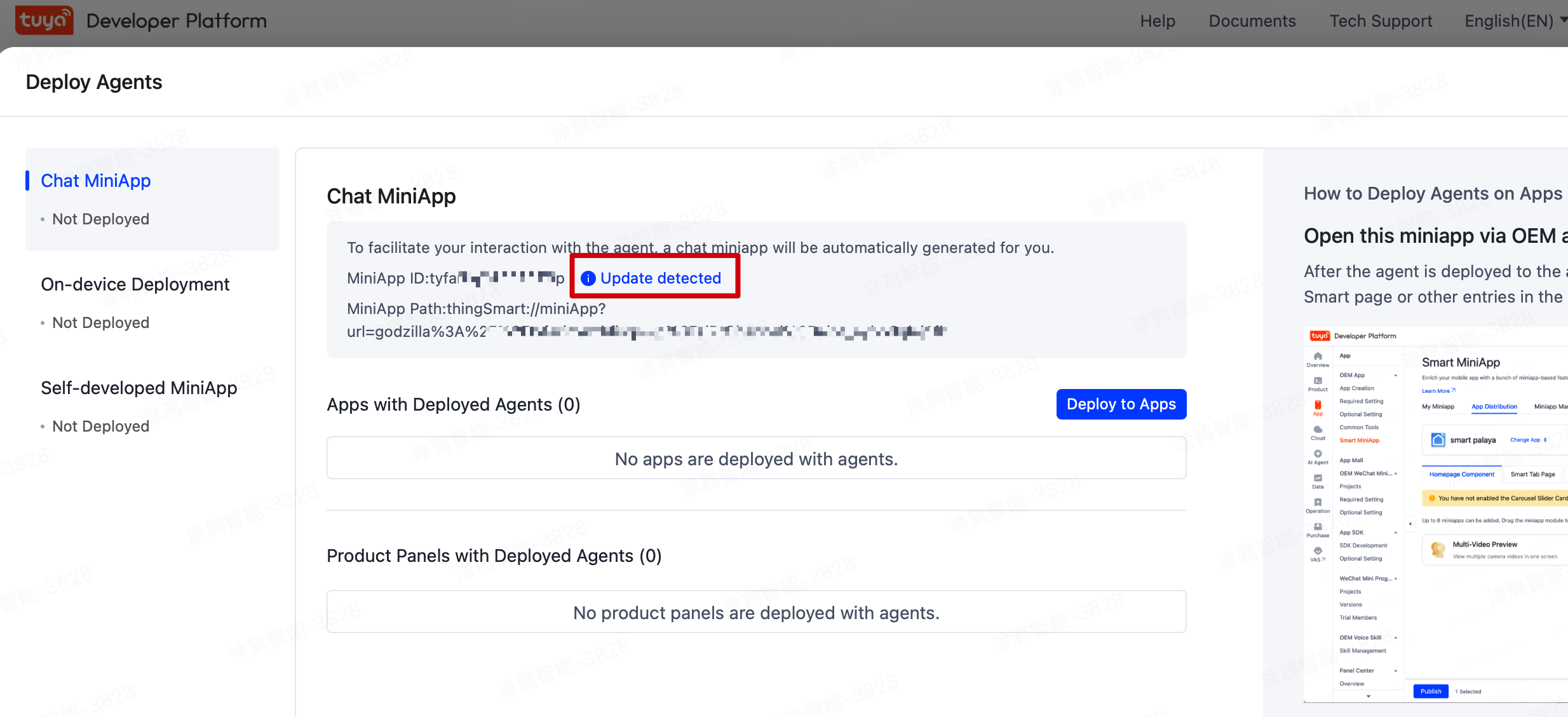
On the Deploy Agents page, click Deploy to Apps to assign the agent to your target app. Confirm and then click Confirm Info and Publish.
Record the MiniApp ID to create a session in the SDK.

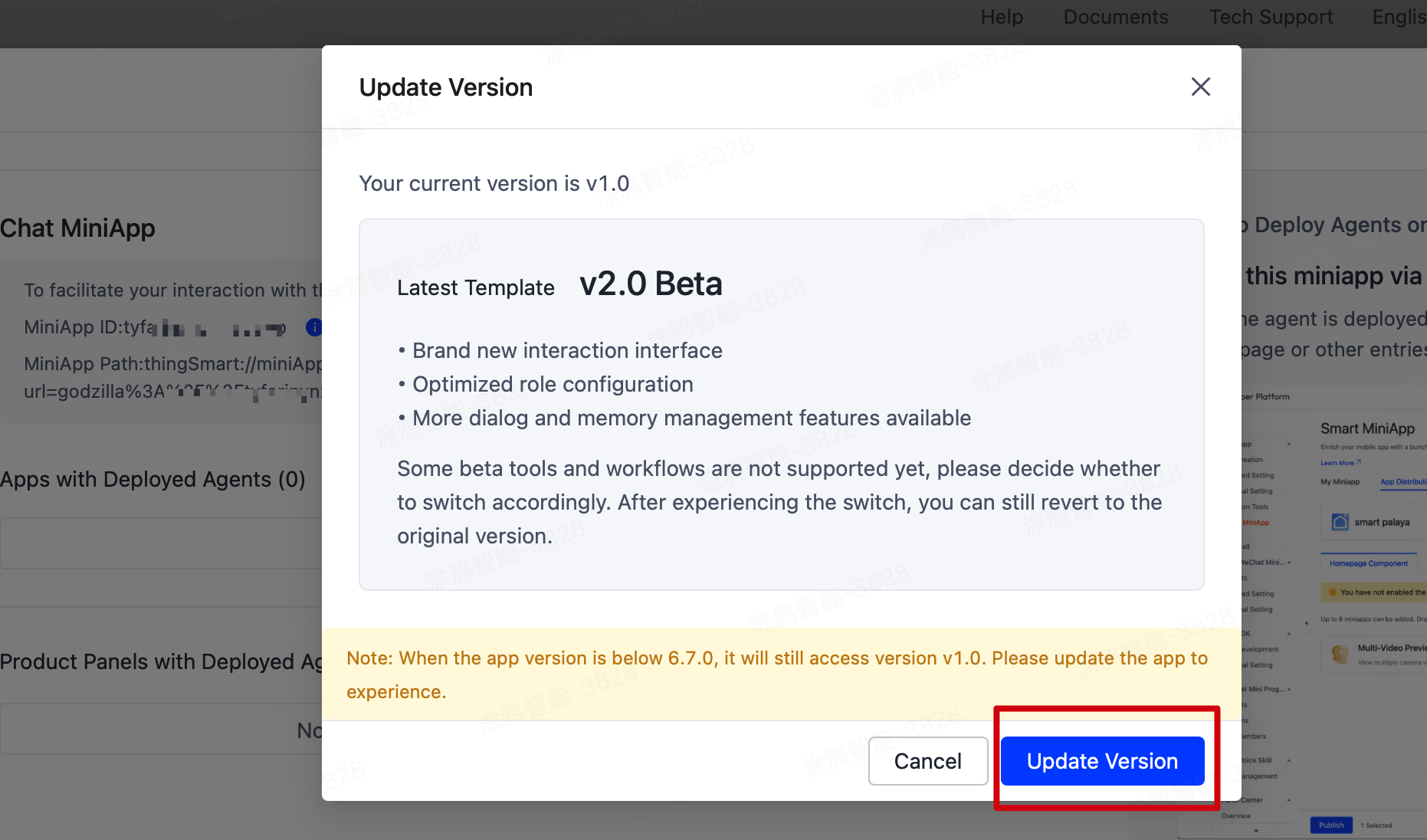
To enable the new version of the agent, you must use the miniapp v2.0 Beta or later. Click Update detected and update the miniapp to v2.0 Beta or later.
Data flow
Connection management
The channel currently supports two connection types: app and proxy device.
- App channel: Authenticate as the logged-in user. One app has only one channel, supporting multi-device login and concurrent usage.
- Proxy device: Authenticate and connect as a device. It is usually designed for devices that cannot connect to the cloud independently, such as Bluetooth devices. It does not support concurrent multi-device connections to the same proxy device.
Session management
Sessions are established on top of channels. A single channel can host multiple sessions, which are required for data stream transmission.
When using different AI agents or configurations, you must request an agent token using the relevant information and create a session.
Data stream transmission
Before transmitting data streams, make sure a session has been created.
Key concepts:
EventDataChannelReuseDataChannelStreamFlag
Event
An event can be sent from the app to the server, or delivered from the server to the app.
When sending data, it mainly includes the following events:
| Event | Description |
|---|---|
EventStart |
Marks the start of an event. It must be sent before data stream transmission. An EventId is required, which must remain consistent until EventEnd or ChatBreak is sent. |
EventPayloadEnd |
Indicates completion of a single data transmission within an event. DataChannel data is required. |
EventEnd |
Marks the end of an event. This event is sent after all data streams are transmitted. After receiving this event, the server will deliver all data to the agent for processing. |
ChatBreak |
Interrupts an event. It can be triggered during data stream transmission or reception. |
When receiving data, it mainly includes the following events:
| Event | Description |
|---|---|
EventStart |
Marks the start of an event, indicating the cloud is about to deliver data to the app. It includes an EventId corresponding to the one sent by the app. |
EventPayloadEnd |
Indicates completion of a single data transmission within an event. |
EventEnd |
Marks the end of an event. This event is sent after all data streams are transmitted. |
ChatBreak |
Interrupts an event. The cloud is interrupting the app, and the app should stop sending or receiving data for this EventId (requires configuration). |
ServerVAD |
Cloud-based voice activity detection (VAD). The cloud has detected the end of an audio segment from the app. Upon receiving this event, the app must stop sending audio data for this EventId. Even if the data is sent, the cloud will ignore it. Requires configuration. |
The channel supports multimodal data transmission, allowing delivery of multiple data types within a single event cycle. Refer to the agent’s configuration for specific compatible data types.
DataChannel
During session creation, the AgentToken response includes bizConfig with two key properties: sendData and revData to indicate the data types.
Based on bizConfig.sendData and bizConfig.revData, the SDK automatically generates sendDataChannels and recvDataChannels.
Scenarios:
- Single-stream data of the same type: Methods like
sendAudioDataandsendVideoDatarequire no explicit data channel. - Multi-stream data of the same type (such as dual-lens cameras with two video streams): Channel order must match physical inputs. The
dataChannelvalue must be passed in the data stream sending method. This scenario is not currently available. sendEventPayloadsEndalways requiresdataChannel, regardless of stream count.
ReuseDataChannel
The session creation interface includes a reuseDataChannel parameter, which defaults to false (meaning it is disabled).
It is designed for real-time streaming scenarios (such as live audio/video streams), where two or more sessions require different processing of the same real-time data. It optimizes data timeliness and reduces transmission overhead.
Scenarios:
Two sessions are required to process audio translation and audio summarization, respectively. Real-time audio data must be captured and shared between both sessions for parallel processing.StreamFlag
Mark the start/end of specific data streams, with four types:
OnlyOne(0): Single packet only. It is used for text or small-sized images.StreamStart(1): Start of data stream to send or receive. The first packet should include metadata, such as sample rate, bit depth, and format for audio data. Packet data can be empty.Streaming(2): Data transmission is in progress.StreamEnd(3): End of data stream. Packet data can be empty.
AI chat flow example
API description
Create AI stream object
var aiStream: IThingAiStream = ThingAiStream.newInstance()
Listen for events
Add or remove a listener
/**
* Set stream listener
*
* @param listener stream listener
*/
fun setStreamListener(listener: ThingAiStreamListener)
/**
* Remove stream listener
*/
fun unsetStreamListener()
Before establishing a connection or receiving data, you must set up a listener to receive messages.
// Set up a listener before connecting and creating a session
aiStream.setStreamListener(streamListener)
Connection and session state change messages
interface ThingAiStreamListener {
/**
* Monitors channel connection state changes
*
* @param connectionId The connection identifier
* @param state The current connection state
* @param errorCode Error code, if any
*/
fun onConnectStateChanged(connectionId: String, state: Int, errorCode: Int)
/**
* Monitors session state changes
*
* @param sessionId The session identifier
* @param state The current session state
* @param errorCode Error code, if any
*/
fun onSessionStateChanged(sessionId: String, state: Int, errorCode: Int)
}
Receive events and data stream messages
/**
* Interface for AI Stream event callbacks.
* Used to monitor and handle various stream data types and connection states.
*/
interface ThingAiStreamListener {
/**
* Monitors event data reception
*
* @param event The received event data
*/
fun onEventReceived(event: StreamEvent)
/**
* Monitors audio data reception
* (When flag == start, the audio will be played automatically by the plugin)
*
* @param data The received audio data
*/
fun onAudioReceived(data: StreamAudio)
/**
* Monitors video data reception
* (When flag == start, video playback will begin until completion)
*
* @param data The received video data
*/
fun onVideoReceived(data: StreamVideo)
/**
* Monitors image data reception
*
* @param data The received image data
*/
fun onImageReceived(data: StreamImage)
/**
* Monitors text data reception
*
* @param data The received text data
*/
fun onTextReceived(data: StreamText)
/**
* Monitors file data reception
* (Currently not supported by the cloud)
*
* @param data The received file data
*/
fun onFileReceived(data: StreamFile)
}
Connection management
How it works:
APIs
/**
* Check if connected to stream service
*
* @param clientType client type: 1-as device agent, 2-as App
* @return true if connected, false otherwise
* @see com.thingclips.smart.android.aistream.Constants.ClientType
*/
fun isConnected(
@ClientType clientType: Int,
deviceId: String? = null
): Boolean
/**
* Connect to stream service as App
*
* @param callback result callback
*/
fun connectWithApp(callback: ConnectCallback?)
/**
* Connect to stream service as Device
*
* @param deviceId device ID
* @param callback result callback
*/
fun connectWithDevice(deviceId: String, callback: ConnectCallback?)
/**
* Connect to stream service
*
* @param clientType client type: 1-as device agent, 2-as App
* @param deviceId device ID, required if acting as device agent, otherwise can be empty string
* @param connectInfo connection info in JSON format
* @param callback result callback
*/
fun connect(
clientType: Int,
deviceId: String?,
connectInfo: String?,
callback: ConnectCallback?
)
/**
* Disconnect from stream service
*
* @return operation result code
*/
fun disconnect(): Int
Session management
A single connection can maintain up to 20 concurrent sessions. Properly create or close sessions as needed.
Create session
There are two session creation methods.
-
Method 1: Normal method. First, get the
agent token infoand use it to create a session.Since getting the
agent token infoinvolves some latency, this method allows pre-fetching. Typically, it is valid for 24 hours./** * Request agent token * * @param requestParams request parameters, you can see [AgentTokenRequestParams] for details, use [AgentTokenRequestParams.Builder] to build * @param listener result listener * @see AgentTokenRequestParams */ fun requestAgentToken( requestParams: AgentTokenRequestParams, listener: ResultListener<ThingAgentTokenInfo> ) /** * Create session with agent token info * * @param bizTag business tag, 0 for default * @param agentToken Agent token, @see [ThingAgentTokenInfo.agentToken] * @param bizConfig business config, @see [ThingAgentTokenInfo.BizConfig] * @param userDataAttributes user data attributes list * @param callback result callback * @see requestAgentToken */ fun createSession( bizTag: Long = 0, agentToken: ThingAgentTokenInfo, userDataAttributes: List<UserDataAttribute>?, reuseDataChannel: Boolean = false, callback: SessionCallback? ) -
Method 2: Convenient method. Get the
agent token infoand automatically create a session./** * Create a session with the requested agent token, it combines requestAgentToken and createSession * * @param ownerId owner ID * @param aiSolutionCode AI solution code * @param userDataAttributes user data attributes list * @param callback result callback */ fun createSession( requestParams: AgentTokenRequestParams, userDataAttributes: List<UserDataAttribute>?, callback: SessionCallback? )
Proactively close sessions
A single connection can maintain up to 20 concurrent sessions. Close unnecessary sessions when appropriate.
/**
* Close session
*
* @param sessionId session ID
* @param callback result callback
*/
fun closeSession(sessionId: String, callback: StreamResultCallback?)
Example of creating a session
To create a session, you must pass the APIs and relevant parameters. Here is an example of invoking the APIs, as well as a parameter description.
aiSolutionCode: Corresponds to theAgent IDin the Agent preparation process.miniProgramId: Corresponds to theMiniApp IDin the Agent preparation process.
String api = "m.life.ai.token.get"; // API name
String apiVersion = "1.0"; // API version
String ownerId = "your_home_id"; // Home ID
String aiSolutionCode = "your_agent_id"; // Agent ID
AgentTokenRequestParams params = new AgentTokenRequestParams.Builder()
.api(api)
.apiVersion(apiVersion)
.ownerId(ownerId) // Home ID
.aiSolutionCode(aiSolutionCode) // Agent ID
.addExtParam("miniProgramId", "your_mini_app_id") // Miniapp ID
.addExtParam("needTts", "false") // Enable tts, default value is false
.addExtParam("onlyAsr", "false") // Only ASR or not, default value is false
.build();
aiStream.createSession(params, null, new SessionCallback() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(@NonNull String sessionId, @NonNull Map<String, Integer> sendDataCodes, @NonNull Map<String, Integer> revDataCodes) {
Log.i(TAG, "createSession onSuccess: " + sessionId);
}
@Override
public void onError(int code, String message) {
Log.e(TAG, "createSession onError: " + code + ", message: " + message);
runOnUiThread(() -> Toast.makeText(AiChatActivity.this, "Session creation failed: " + message, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show());
}
});
Send events
The following events can be sent:
EventStart: Marks the start of a dialogue round. You can either specify an event ID or let the SDK auto-generate one.EventPayloadEnd: Notifies the cloud that one data stream transmission in this dialogue is completed.EventEnd: Ends the dialogue round. After this event is sent, the AI will process all transmitted data and generate a response.ChatBreak: Interrupts a dialogue. This event can be triggered during sending or receiving.
/**
* Send event start signal with VAD and interrupt options
*
* @param options event start options
* @param callback result callback
* @see EventStartOptions
*/
fun sendEventStart(
options: EventStartOptions,
callback: EventStartCallback
)
/**
* Send event payloads end signal
*
* @param eventId event ID
* @param sessionId session ID
* @param dataChannel data channel
* @param userDataAttributes user data attributes list
* @param callback result callback
*/
fun sendEventPayloadsEnd(
eventId: String, sessionId: String, dataChannel: String,
userDataAttributes: List<UserDataAttribute>?,
callback: StreamResultCallback?
)
/**
* Send event end signal
*
* @param eventId event ID
* @param sessionId session ID
* @param userDataAttributes user data attributes list
* @param callback result callback
*/
fun sendEventEnd(
eventId: String, sessionId: String, userDataAttributes: List<UserDataAttribute>?,
callback: StreamResultCallback?
)
fun sendEventChatBreak(
eventId: String, sessionId: String, userDataAttributes: List<UserDataAttribute>?,
callback: StreamResultCallback?
)
Send data stream
/**
* Send audio data
*
* @param data audio data
* @param callback result callback
*/
fun sendAudioData(sessionId: String, data: StreamAudio, callback: StreamResultCallback?)
/**
* Send video data
*
* @param data video data
* @param callback result callback
*/
fun sendVideoData(sessionId: String, data: StreamVideo, callback: StreamResultCallback?)
/**
* Send text data
*
* @param data text data
* @param dataChannel customized data channel (optional), using default "text" if not specified
* @param callback result callback
*/
fun sendTextData(sessionId: String, data: StreamText, callback: StreamResultCallback?)
/**
* Send image data
*
* @param data image data
* @param callback result callback
*/
fun sendImageData(sessionId: String, data: StreamImage, callback: StreamResultCallback?)
/**
* Send file data
*
* @param data file data
* @param dataChannel customized data channel (optional), using default "file" if not specified
* @param callback result callback
*/
fun sendFileData(sessionId: String, data: StreamFile, callback: StreamResultCallback?)
Real-time audio recording and playback
For audio data on Android, real-time recorded audio streams are supported. You can use Tuya’s encapsulated methods for audio stream recording and sending.
/**
* Initializes the audio recorder.
*
* This method is optional and not required before starting recording. It should be called only when
* you want to prepare the recorder in advance before actual recording starts.
* Initializing the audio recorder is a relatively time-consuming operation (about 300ms).
* Calling this method in advance can eliminate the delay when starting to record.
* You can call this method while showing a loading state, so that when the user actually starts
* recording, it can respond immediately.
* If not called in advance, the startRecordAndSendAudioData method will automatically complete
* the initialization internally, but this will cause a noticeable delay before recording actually begins.
*
* @param callback Operation result callback, reporting initialization success or failure
*/
fun initAudioRecorder(callback: StreamResultCallback?)
/**
* Starts recording audio and sending data, without triggering events.
*
* This method will start recording and transmitting audio data. If initAudioRecorder has not been
* called for initialization previously, this method will first complete the initialization of the
* recorder (about 300ms) before starting to record.
* For better user experience, it is recommended to call initAudioRecorder to complete
* initialization before displaying the recording button in the UI.
*
* @param sessionId Session ID, used to identify the session to which the current audio transmission belongs
* @param dataChannel Custom data channel (optional), if not specified, the default "audio" channel will be used
* @param userDataAttributes List of user data attributes, which may contain metadata related to the audio
* @param callback Operation result callback, reporting whether recording started successfully or failed
*/
fun startRecordAndSendAudioData(
sessionId: String,
dataChannel: String? = null,
userDataAttributes: List<UserDataAttribute>?,
callback: StreamResultCallback?
)
/**
* Stop recording audio and sending data, without ending event
*
* @param dataChannel customized data channel (optional), using default "audio" if not specified
* @param userData user data attributes list
* @param callback result callback
*/
fun stopRecordAndSendAudioData(
sessionId: String,
dataChannel: String? = null,
userData: List<UserDataAttribute>?,
callback: StreamResultCallback?
)
Example of sending data
The following code snippet shows how to send a complete text message:
/**
* Send a text message to the AI service
* @param textMessage The text to be sent
*/
fun sendTextMessage(textMessage: String) {
// Check if session is valid
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(currentSessionId) || !aiStream.isConnected(Constants.ClientType.APP, null)) {
Log.e(TAG, "Cannot send message: session not initialized or connection lost")
return
}
// Step 1: Start the event
val eventStartOptions = EventStartOptions.Builder(currentSessionId).build()
aiStream.sendEventStart(eventStartOptions, object : EventStartCallback {
override fun onSuccess(eventId: String) {
Log.i(TAG, "Event started successfully: $eventId")
// Step 2: Send text data
val streamText = StreamText().apply {
text = textMessage
}
aiStream.sendTextData(currentSessionId, streamText, object : StreamResultCallback {
override fun onSuccess() {
Log.i(TAG, "Text data sent successfully")
// Step 3: End text payload
aiStream.sendEventPayloadsEnd(eventId, currentSessionId,
ThingAiStream.DATA_CHANNEL_TEXT, null, object : StreamResultCallback {
override fun onSuccess() {
Log.i(TAG, "Text payload ended successfully")
// Step 4: End the event
aiStream.sendEventEnd(eventId, currentSessionId, null, object : StreamResultCallback {
override fun onSuccess() {
Log.i(TAG, "Event ended successfully: $eventId")
}
override fun onError(errorCode: Int, errorMessage: String) {
Log.e(TAG, "Failed to end event: $errorMessage, code: $errorCode")
}
})
}
override fun onError(errorCode: Int, errorMessage: String) {
Log.e(TAG, "Failed to end text payload: $errorMessage, code: $errorCode")
// Still try to end the event even if payload end fails
aiStream.sendEventEnd(eventId, currentSessionId, null, object : StreamResultCallback {
override fun onSuccess() {
Log.i(TAG, "Event ended successfully after payload error: $eventId")
}
override fun onError(code: Int, message: String) {
Log.e(TAG, "Failed to end event after payload error: $message, code: $code")
}
})
}
})
}
override fun onError(errorCode: Int, errorMessage: String) {
Log.e(TAG, "Failed to send text data: $errorMessage, code: $errorCode")
// End the event if text data sending fails
aiStream.sendEventEnd(eventId, currentSessionId, null, object : StreamResultCallback {
override fun onSuccess() {
Log.i(TAG, "Event ended successfully after text send error: $eventId")
}
override fun onError(code: Int, message: String) {
Log.e(TAG, "Failed to end event after text send error: $message, code: $code")
}
})
}
})
}
override fun onError(errorCode: Int, errorMessage: String) {
Log.e(TAG, "Failed to start event: $errorMessage, code: $errorCode")
}
})
}
The following diagram shows how to send multiple types of data:
Demo
You can visit homesdk_sample to obtain a demo.
How-to
-
Read the sections above and complete the Prerequisites.
-
After the project is opened in Android Studio, a
local.propertiesfile will be generated. Add the following configurations to thelocal.propertiesfile:appKey=your_app_key appSecret=your_app_secret aiSolutionCode=your_agent_id miniProgramId=your_mini_program_id -
Run the demo. After logging in, navigate to the AI Assistant page to use the features.
Error codes
| code | msg | Description | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| 39001 | / | A common error has occurred. | Applies to miscellaneous error cases. |
| 39002 |
|
Invalid parameter. |
|
| 39003 | Cloud error messages | HTTP request failed. | Failed to get the agent token. The request for an agent token from the cloud interface failed. |
| 39004 | not connect | Connection is not established. | This error occurs when creating/closing a session, sending data, or sending an event. |
| 39005 | session is invalid | The sessionId does not exist. |
This error occurs when closing a session, sending data, or sending an event. |
| 39006 | eventId is invalid | The eventId is empty. |
This error occurs when sending an event. |
| 39007 | dataChannel is invalid | Invalid dataChannel. |
This error occurs when sending data and payloadEnd. |
| 39008 | packet is invalid | Invalid data packet. | This error occurs when sending data. For example, the first or only one packet of data requires fixed parameters, and the text content is empty. |
| 39009 |
|
An exception occurred while reading file data. |
|
| 39010 |
|
Failed to send the data. | Failed to send data via socket, containing socket error details. |
| 39012 |
|
The connection was closed by the remote end. |
|
Receive text data
This section details the JSON formats and their processing logic in the AI chat component.
Automatic speech recognition (ASR)
When the user sends a voice input, the system returns the ASR result in the following format:
{
"bizId": "asr-1754380053514",
"bizType": "ASR",
"eof": 0,
"data": {
"text": "What's the weather like today?"
}
}
Field description
| Field | Description | Field type | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| bizId | The business ID used to identify an interaction. | String | asr-1754380053514 |
| bizType | The business type. ASR indicates speech recognition results. | String | ASR |
| eof | The end flag. Valid values: 0 means not ended, and 1 means ended. |
Int | 0 or 1 |
| data | The returned ASR result object. | Object | - |
| text | The recognized text content. | String | What’s the weather like today? |
Treatment
- When the value of
eofis0, save the temporary result and display the intermediate recognition result. - When the value of
eofis1, the final recognition result is displayed and added to the chat list.
Responses from the NLG large model
After the AI model responds to a user query, the data returned is in the following format:
{
"bizId": "nlg-1754380053514",
"bizType": "NLG",
"eof": 0,
"data": {
"appendMode": "append",
"reasoningContent": "Reasoning content",
"content": "Text content returned by the model",
"images": [
{
"url": "https://www.tuya.com/image1.jpg"
}
]
}
}
Field description
| Field | Description | Field type | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| bizId | The business ID, used to associate messages from the same interaction. | string | nlg-1754380053514 |
| bizType | The business type. NLG stands for Natural Language Generation. | string | NLG |
| eof | The end flag. Valid values: 0 means streaming is in progress, and 1 means it is finished. |
int | 0 or 1 |
| data | The data object returned. | object | - |
| appendMode | The text append mode. | string | Append or others |
| reasoningContent | The LLM reasoning process (chain-of-thought). | string | The step-by-step thinking content. |
| content | The actual response content generated by the LLM. | string | Text response from the LLM. |
| images | The image data array returned by the LLM. | array | - |
| url | The URL of the specified image. | string | https://www.tuya.com/image1.jpg |
Treatment
- When the value of
appendModeisappend, the new content is appended to the existing message. Otherwise, a new message is created. - Extract
urlfrom theimagesarray, and render each URL as a rich-media image message. - When the value of
eofis1, it marks the end of NLG streaming.
Skill response format
AI can invoke various skills. For example, display emojis.
This section only illustrates emoji-type skills. Other skills might vary depending on the data definition of the agent.
Emoji skill (llm_emo)
{
"bizId": "skill-1754380053514",
"bizType": "SKILL",
"eof": 0,
"data": {
"code": "llm_emo",
"skillContent": {
"text": "😀",
"startTime": 1000,
"endTime": 2000,
"sequence": 1
}
}
}
Field description
| Field | Description | Field type | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| bizId | The business ID. | string | skill-1754380053514 |
| bizType | The business type. SKILL means to invoke skills. |
string | SKILL |
| eof | The end flag. | int | 0 or 1 |
| data | The returned data. | object | - |
| code | The code of a skill. | string | llm_emo |
| skillContent | The content of a skill. | object | - |
| text | The emoji. | string | 😀 |
| startTime | The start time to display an emoji, in milliseconds. | long | 1000 |
| endTime | The end time to stop displaying an emoji, in milliseconds. | long | 2000 |
| sequence | The sequence number, starting with 1. |
int | 1 |
Treatment
- When the value of the
sequenceis1, the existing emoji step list is cleared. - A new emoji step is added to the list.
- When the value of
eofis1, the emojis begin to be displayed in chronological order.
Supported emojis
The following emoji types are supported:
| Emotion type | Unicode | Display effect |
|---|---|---|
| SAD | \uD83D\uDE22 | 😢 |
| ANGRY | \uD83D\uDE20 | 😠 |
| NEUTRAL | \uD83D\uDE10 | 😐 |
| FEARFUL | \uD83D\uDE28 | 😨 |
| SURPRISE | \uD83D\uDE32 | 😲 |
| CONFUSED | \uD83D\uDE15 | 😕 |
| DISAPPOINTED | \uD83D\uDE1E | 😞 |
| ANNOYED | \uD83D\uDE21 | 😡 |
| THINKING | \uD83E\uDD14 | 🤔 |
| HAPPY | \uD83D\uDE00 | 😀 |
Is this page helpful?
YesFeedbackIs this page helpful?
YesFeedback





