Bluetooth Basics Demo
Last Updated on : 2025-06-04 03:28:05download
This topic demonstrates how to develop a Tuya-enabled Bluetooth device with TuyaOS, using the popular Bluetooth chip nRF52832 as an example.
The instructions in this topic also apply to other platforms, except for the firmware flashing procedure. Currently, the Bluetooth low energy (LE) chips compatible with TuyaOS include Nordic’s nRF52832, FREQCHIP’s FR801x, Phyplus’s PHY6222, Telink’s TLSR825x, and BEKEN’s BK3431Q and BK32881. The procedure in this topic also applies to the Bluetooth beacon and Bluetooth mesh products.
Hardware
Tuya’s proprietary development board is recommended. You can purchase the development board (part number: 2.03.99.00045) from the Tuya Developer Platform. This board uses Tuya’s Bluetooth LE dongle hardware.

You can also use Nordic’s development boards or other nRF52832 development boards. Prepare an I2C OLED display with a resolution of 128 × 32 pixels. If you do not have a display, you can still debug other features, excluding I2C.
Software
Install the TuyaOS development environment and download the latest version of TuyaOS BLE SDK (nRF52832). For detailed steps, refer to Environment Setup.
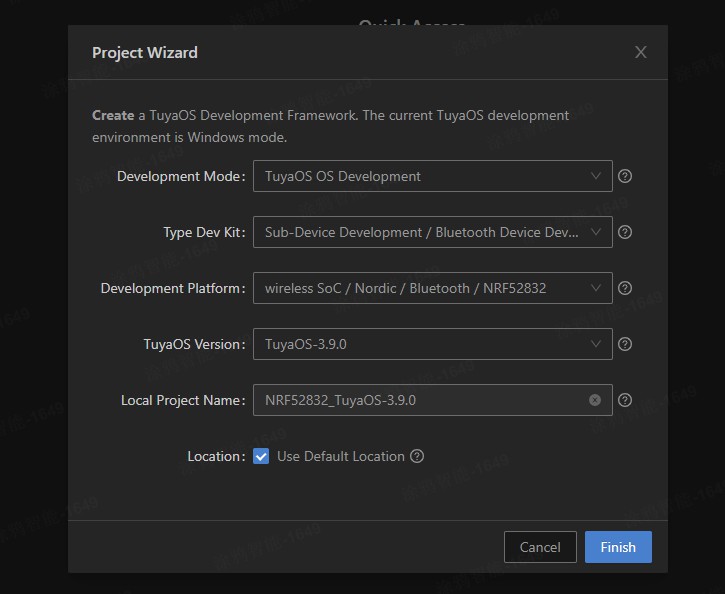
Procedure
Build and flash
-
(Optional) If your project is not intended for production, you can perform temporary authorization by altering the code. This is for debugging purposes only. Before production, make sure to change the code back.
-
Right-click
nRF52832-3.5.3/software/TuyaOS/apps/tuyaos_demo_ble_peripheral. -
Choose Build Project and wait for the building to complete.
-
To flash the full firmware, open the
nRF52832-3.5.3\software\TuyaOS\.log\hexand double-clickload_softdevice_bootloader_app.bat. (You can right-click the directory and select Flash Prod to flash the full firmware later.) See the Development Platform for other approaches to firmware flashing.
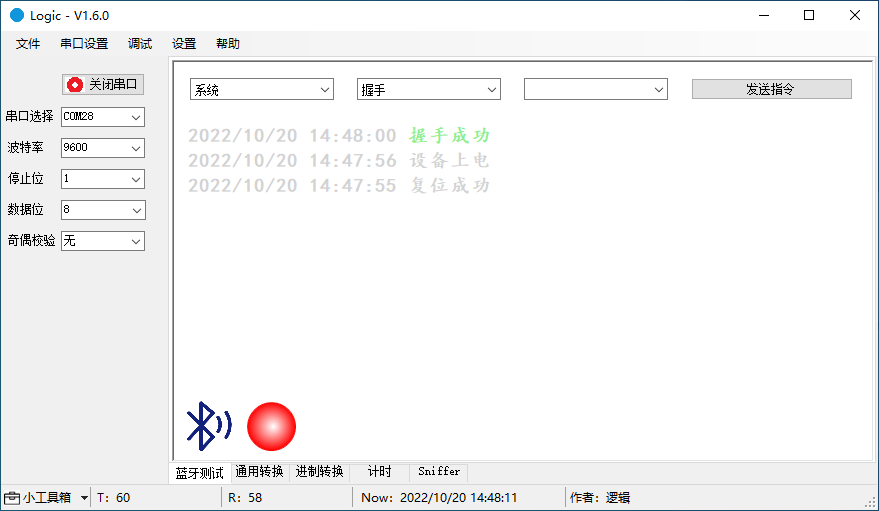
Handshake
-
Connect Tuya’s development board to the computer using a micro-USB cable. The serial port TX is P0.06 and RX is P0.08.
-
Click to download the host software. For more information, see the Host Software User Guide. Open the host software. If you receive a pop-up window, choose More info > Run anyway. Select the correct serial port and set the baud rate 9600.
-
Choose System > Handshake and click Send Command to initiate a handshake with the device.
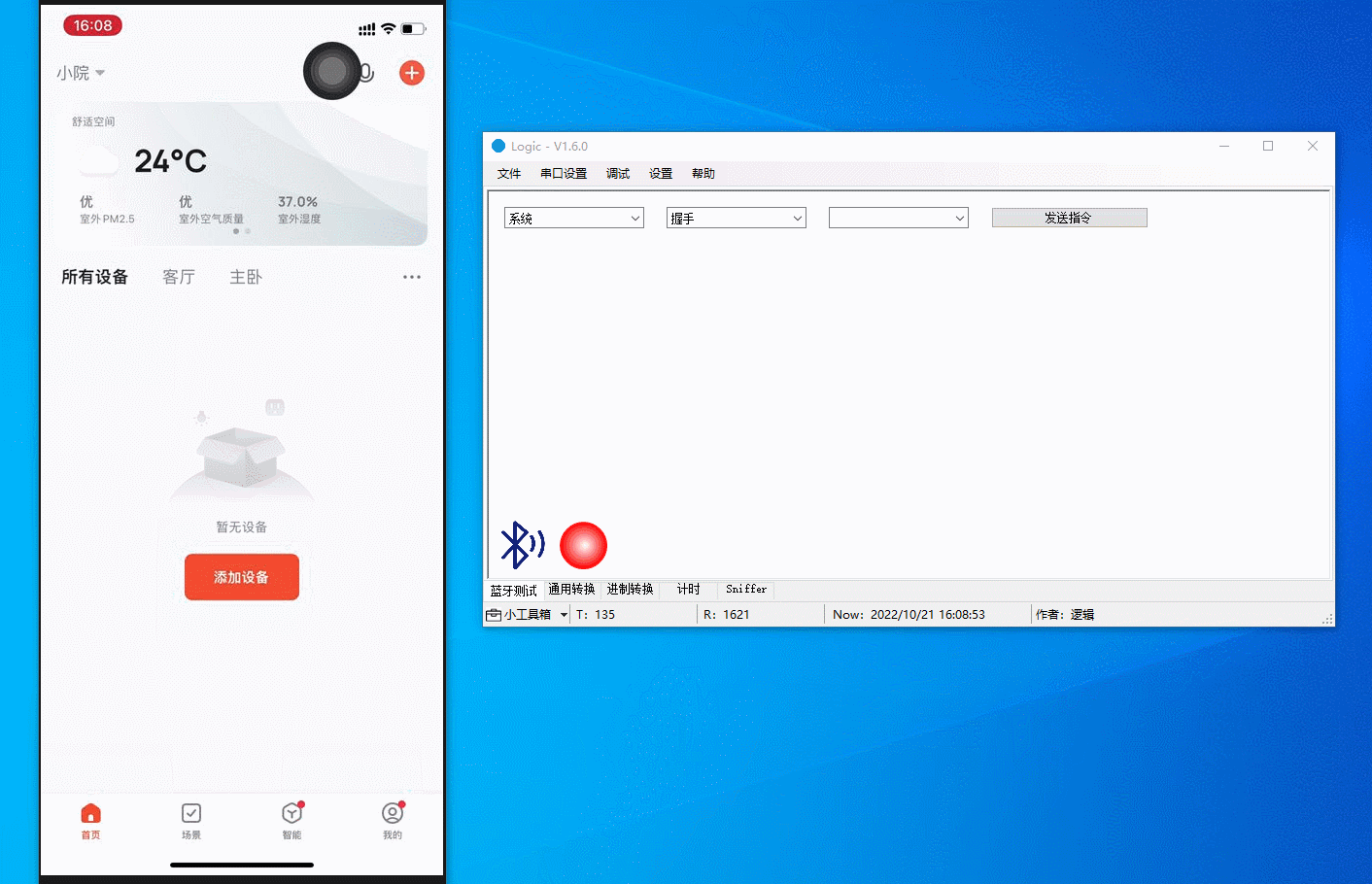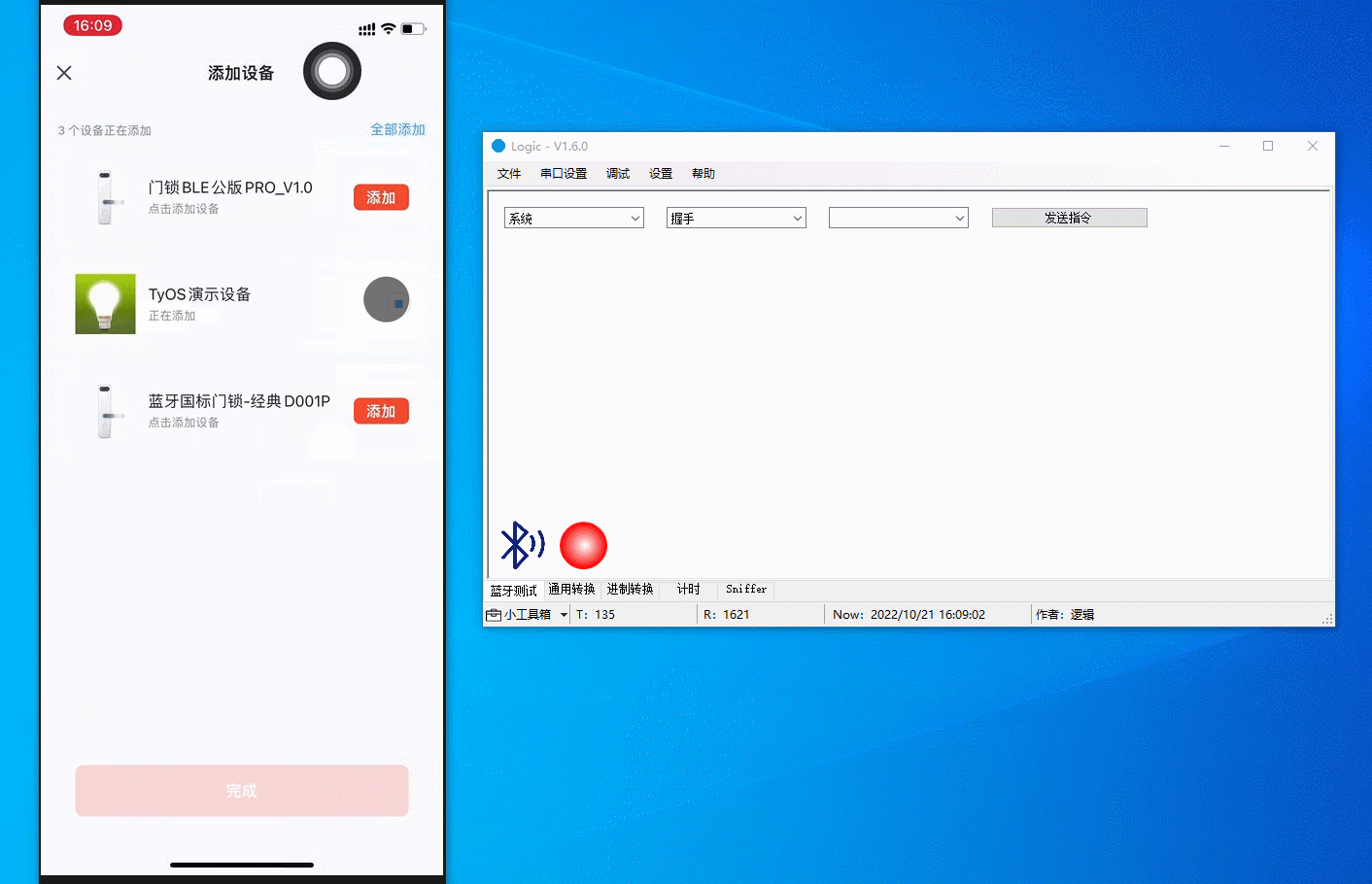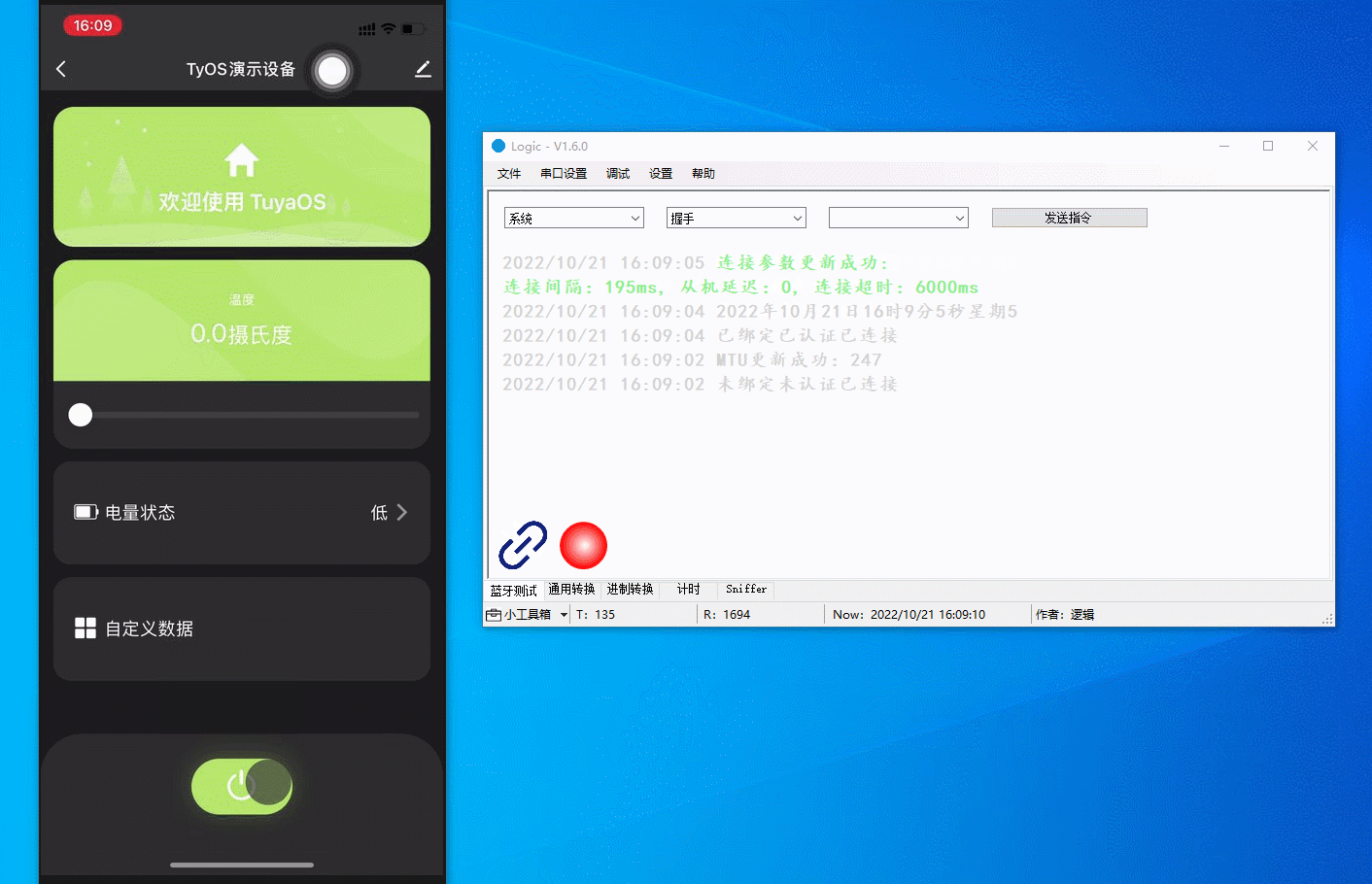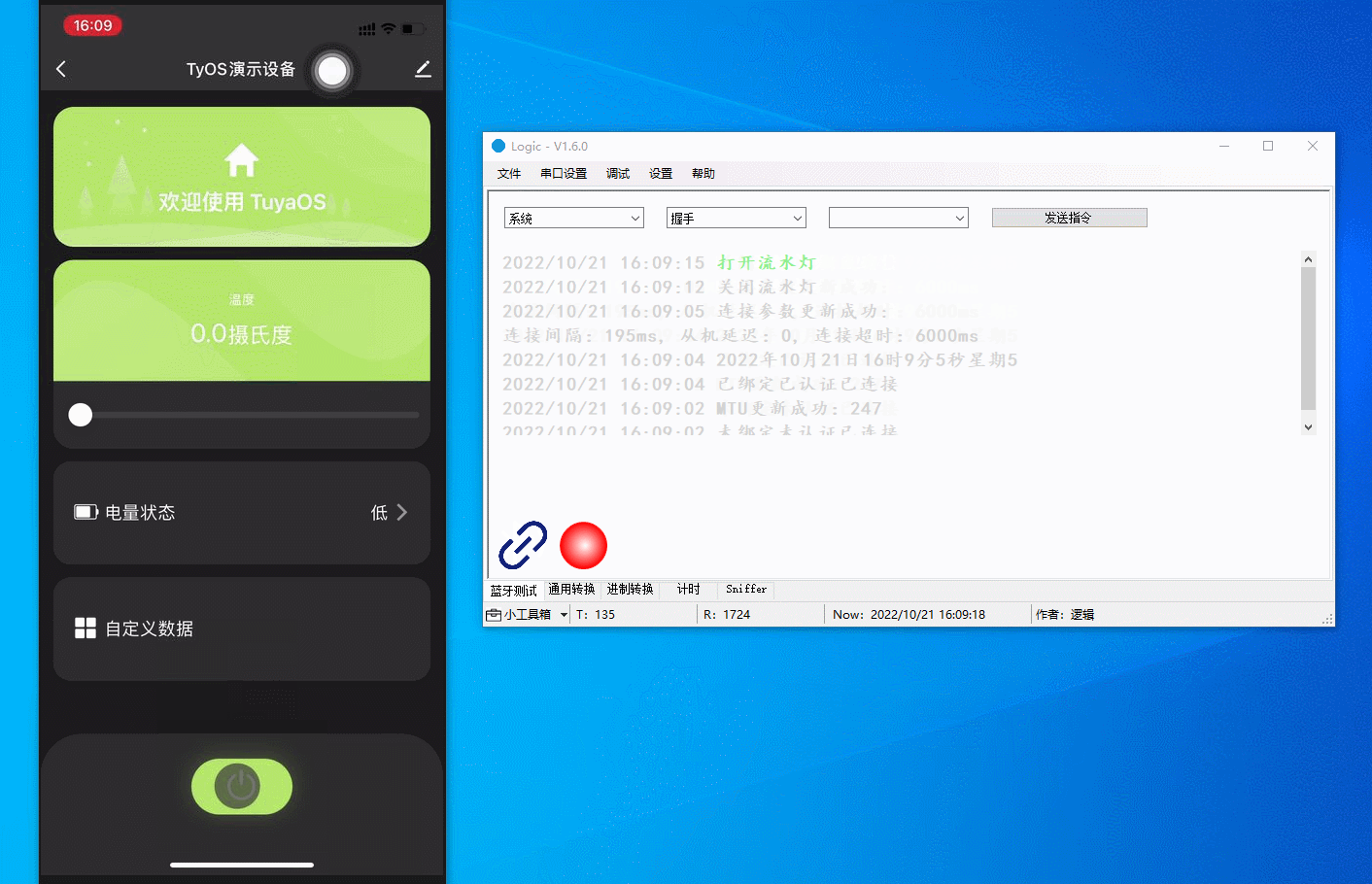
Pairing
Search for the Tuya app on app stores and install it on your mobile phone. Log in to the app and tap Add Device or the + in the top right corner and choose Add Device. The host software displays the updated pairing status, MTU, timestamp, and connection parameters. The figure below demonstrates the process.
Data exchange
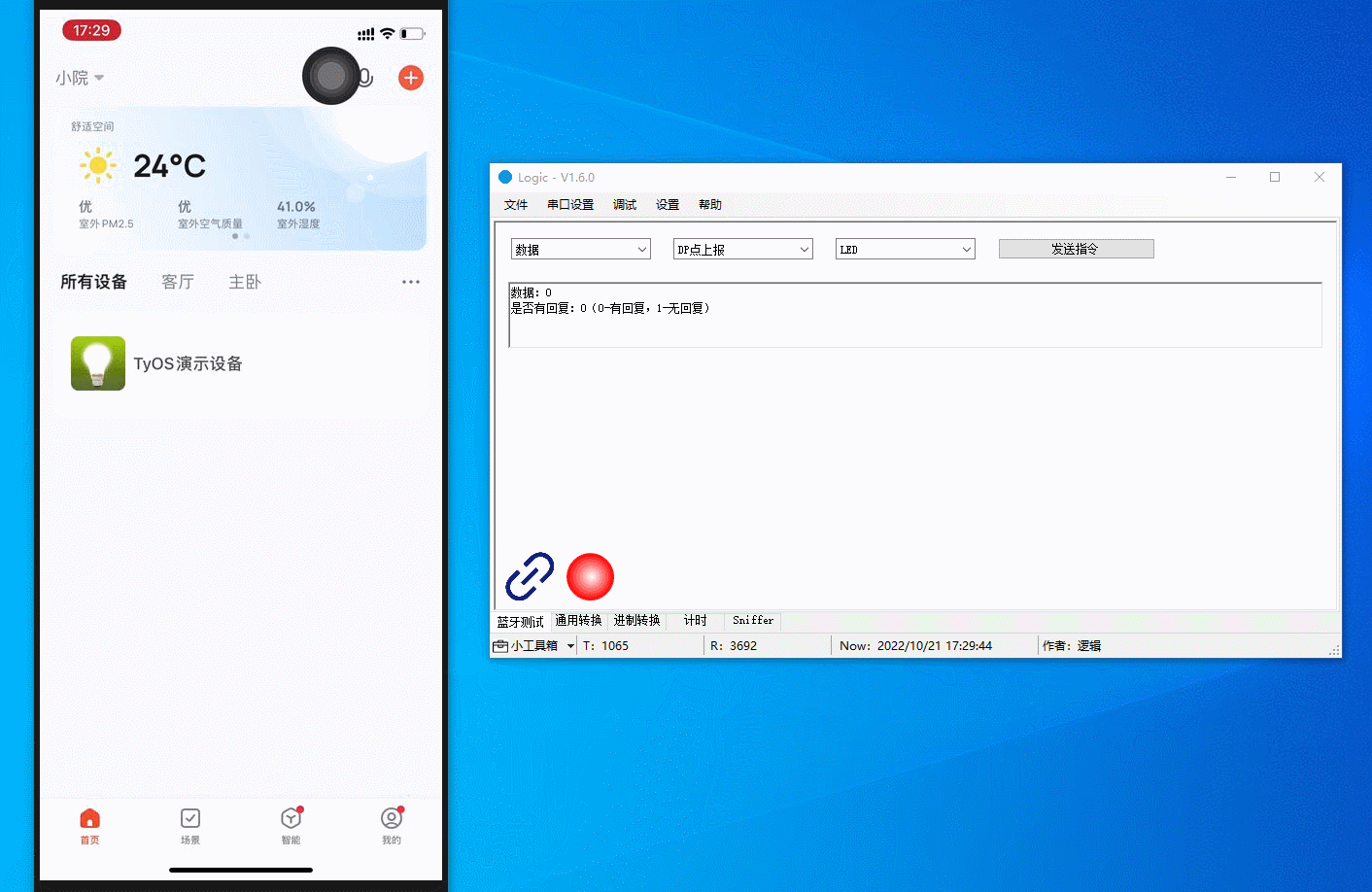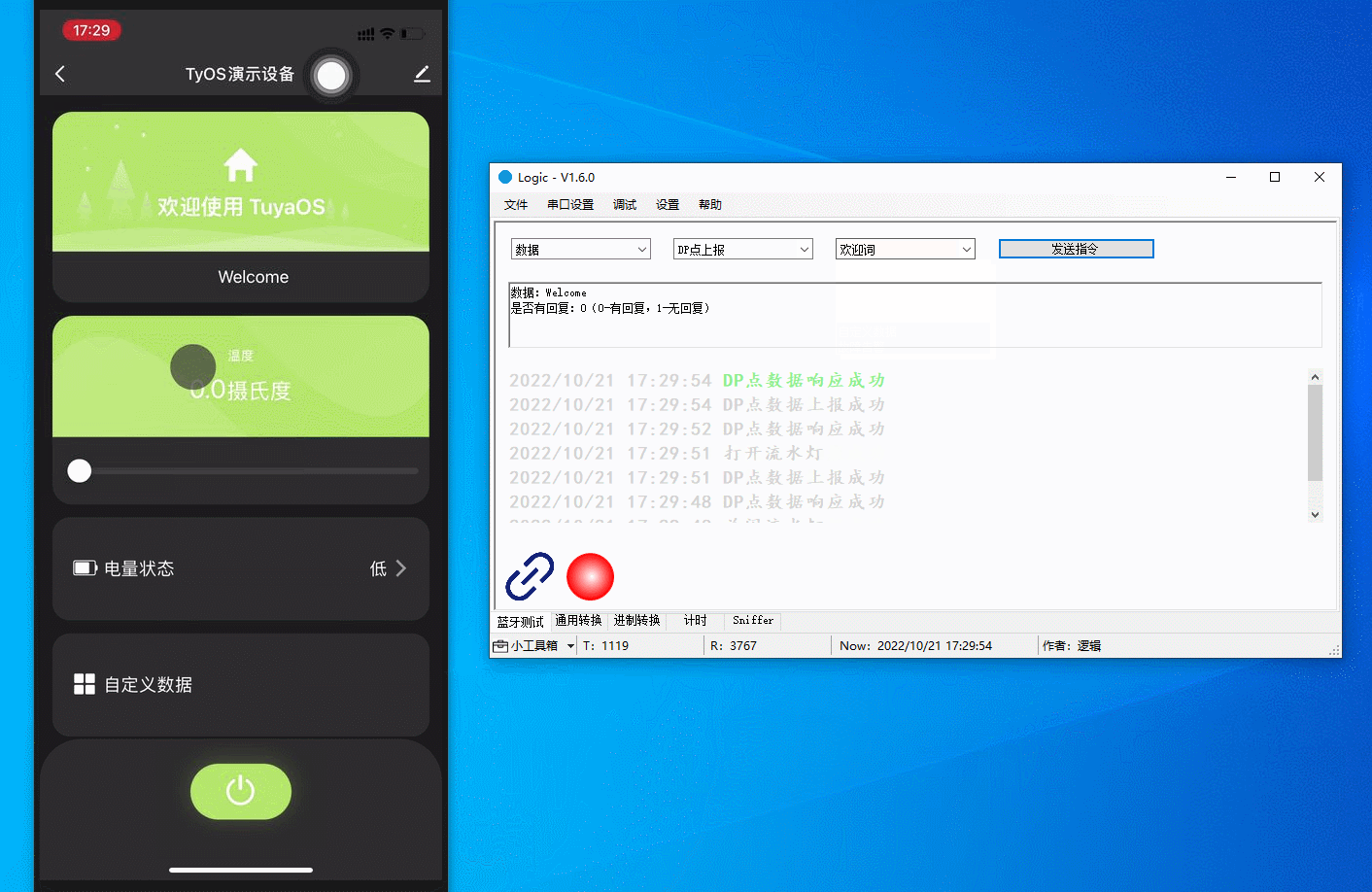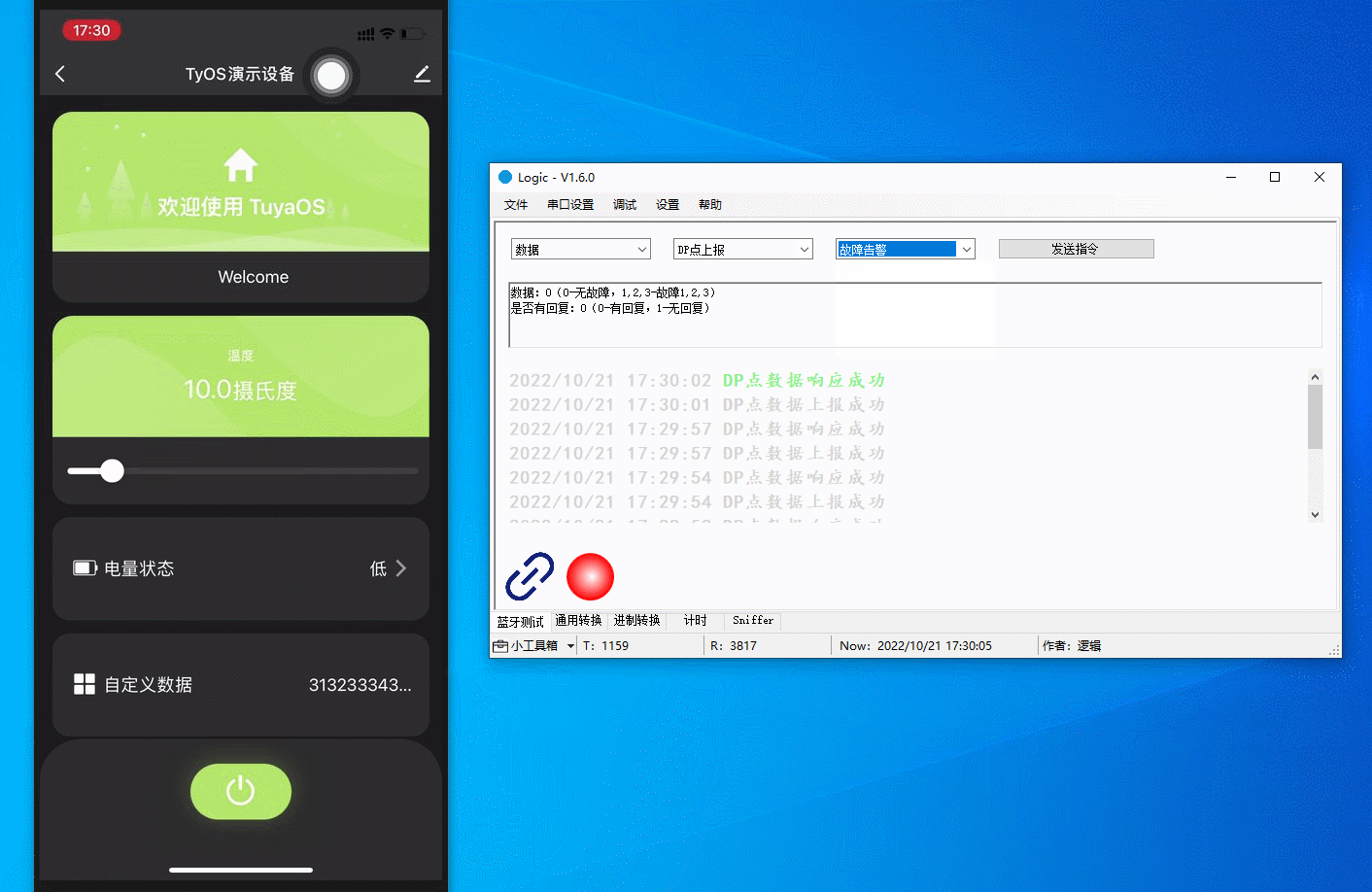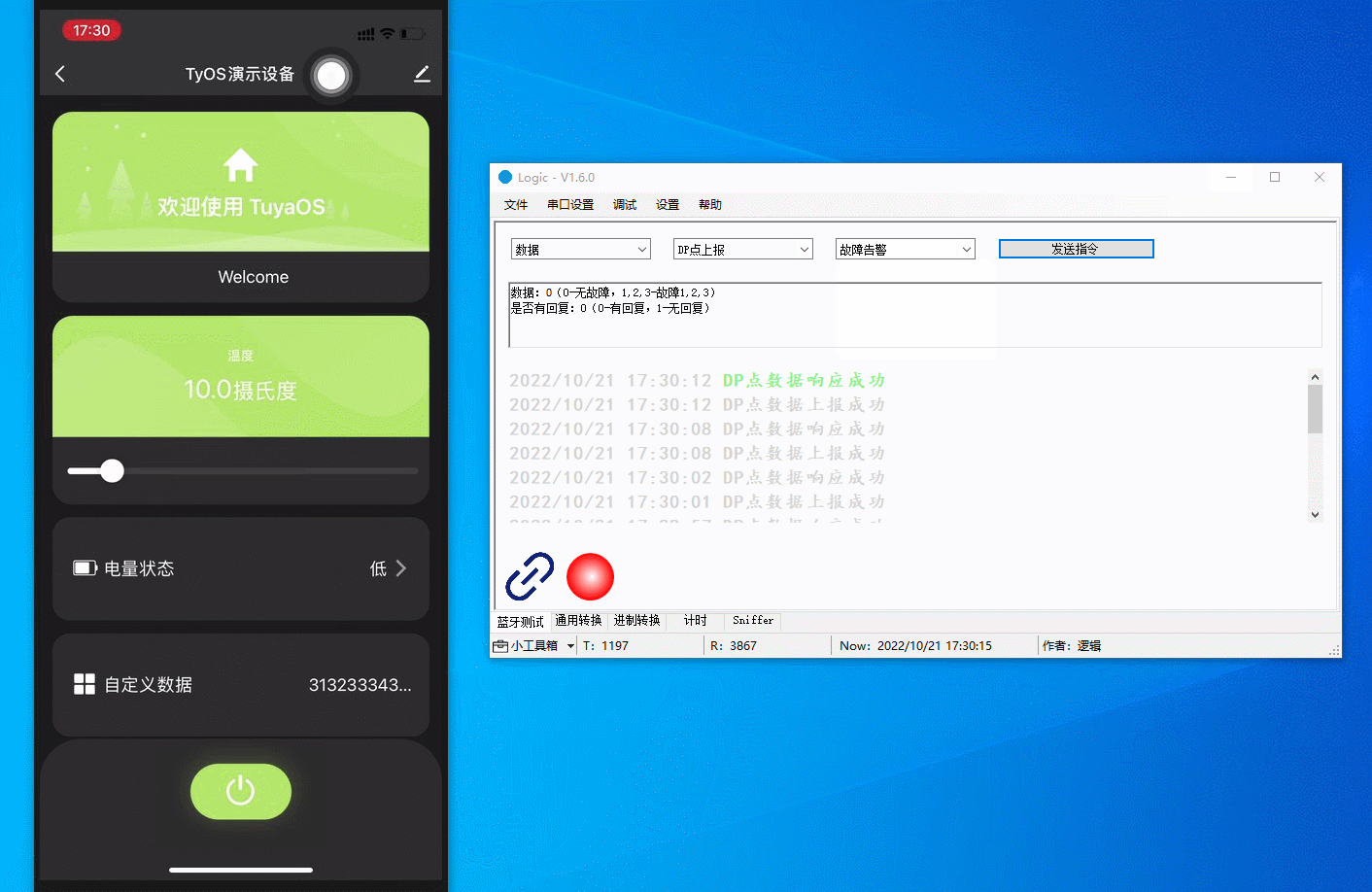
Communicate with the mobile app using the host software that simulates a real device. You can report data, send commands, modify reported data, and present status.
The figure below demonstrates the following actions:
-
Report LED on: The LED on the panel comes on.
-
Report LED off: The LED on the panel comes off.
-
Report welcome message: A welcome message is displayed on the app panel.
-
Report custom data:
123456is displayed on the app panel. -
Report a fault: Fault 2 alert is displayed on the app panel.
-
Report a fault: The alert disappears when no fault is reported.
Debug GPIO
You can implement the following features:
- Control any GPIO to output high level or low level.
- Read the GPIO level.
- Reset the GPIO to its initial state.
- Modify the GPIO serial number directly using the host software.
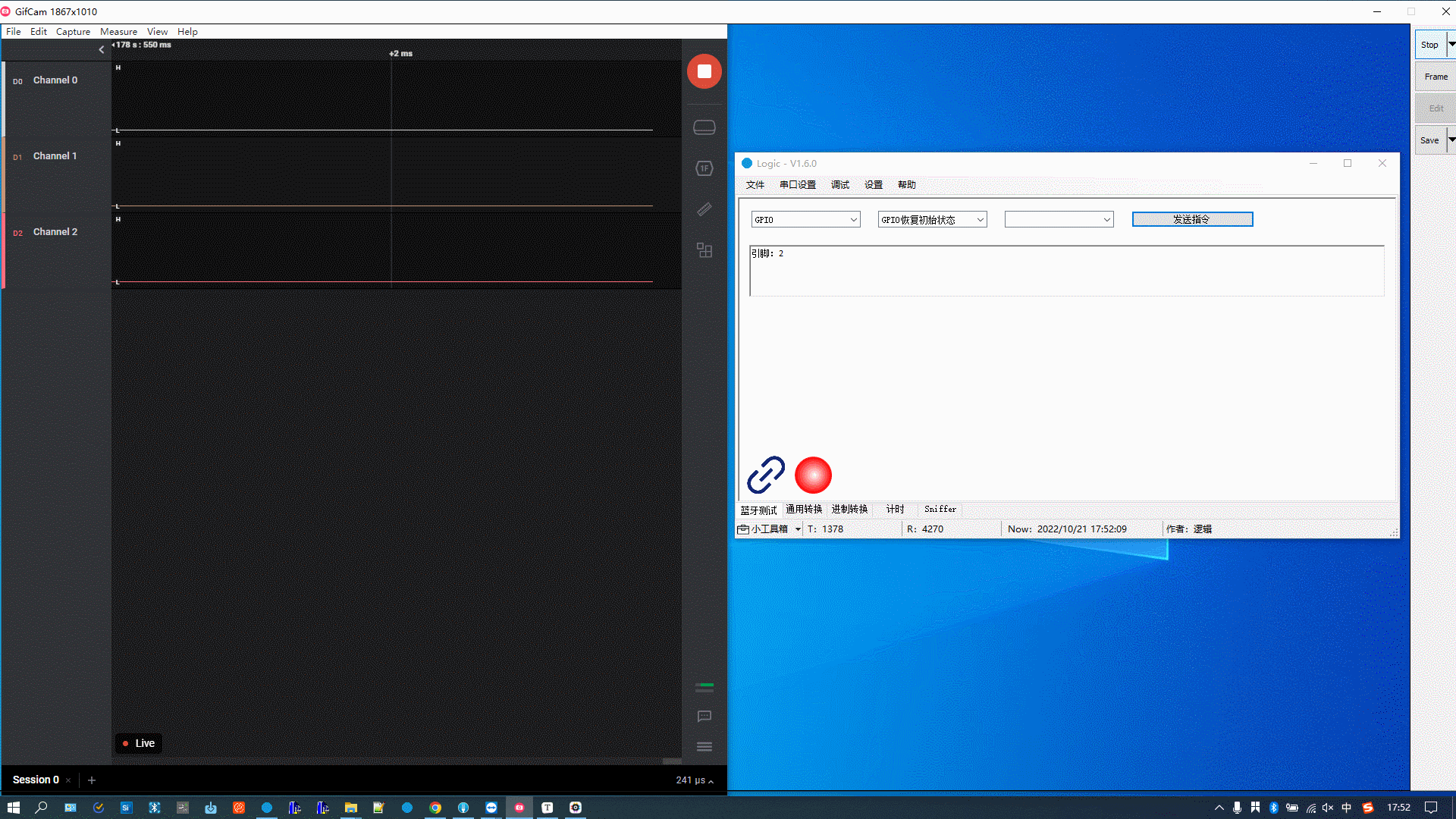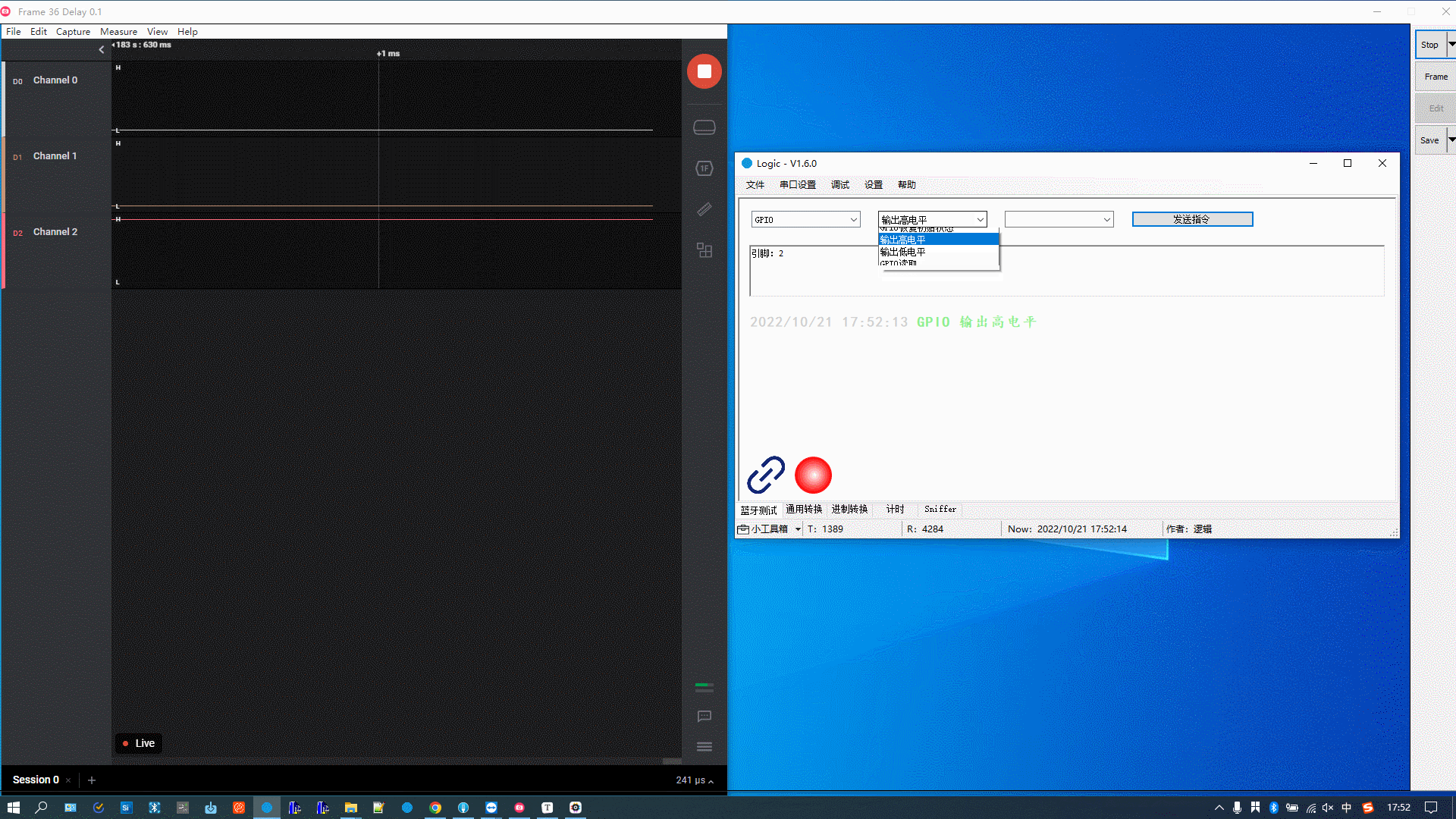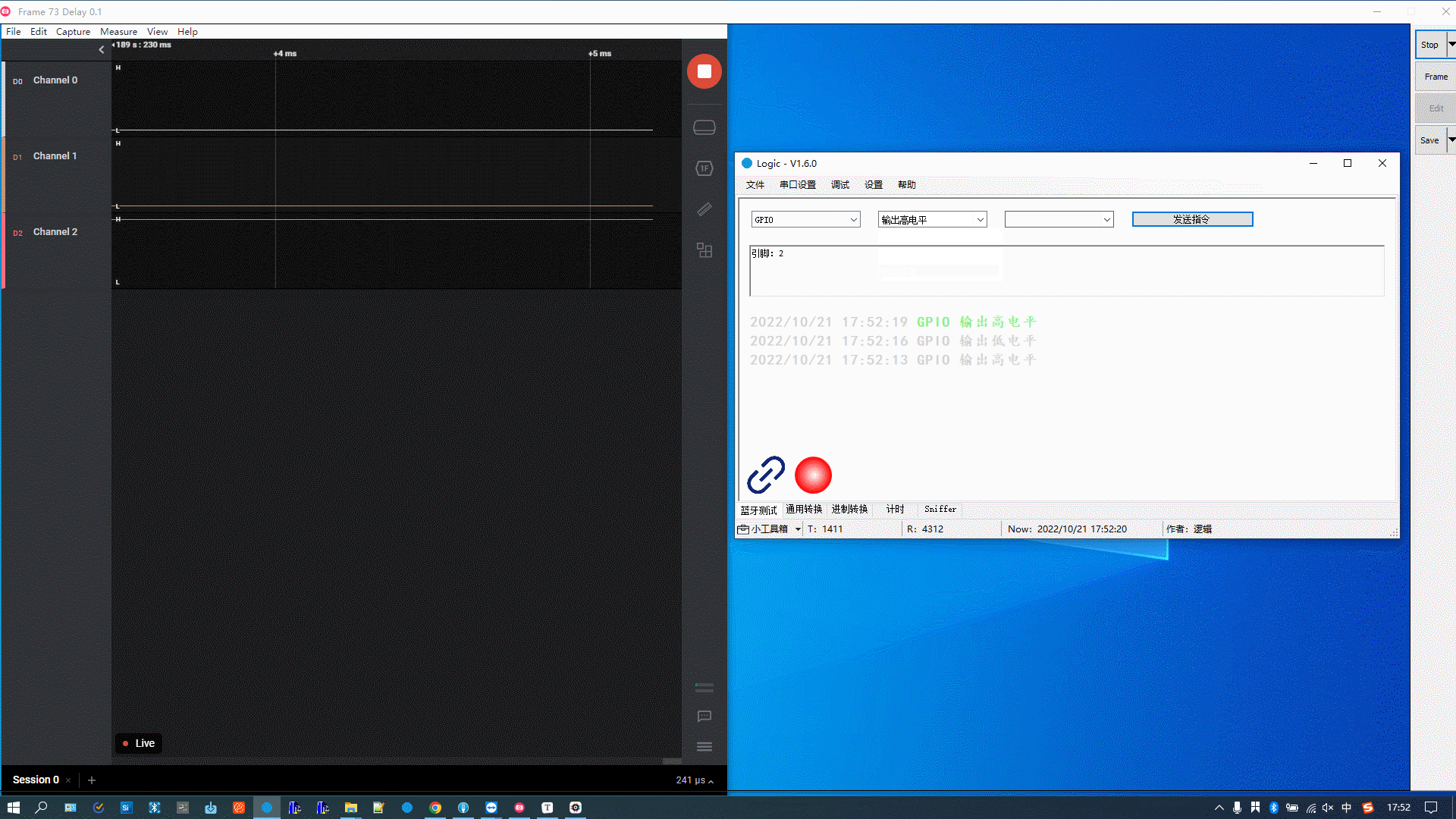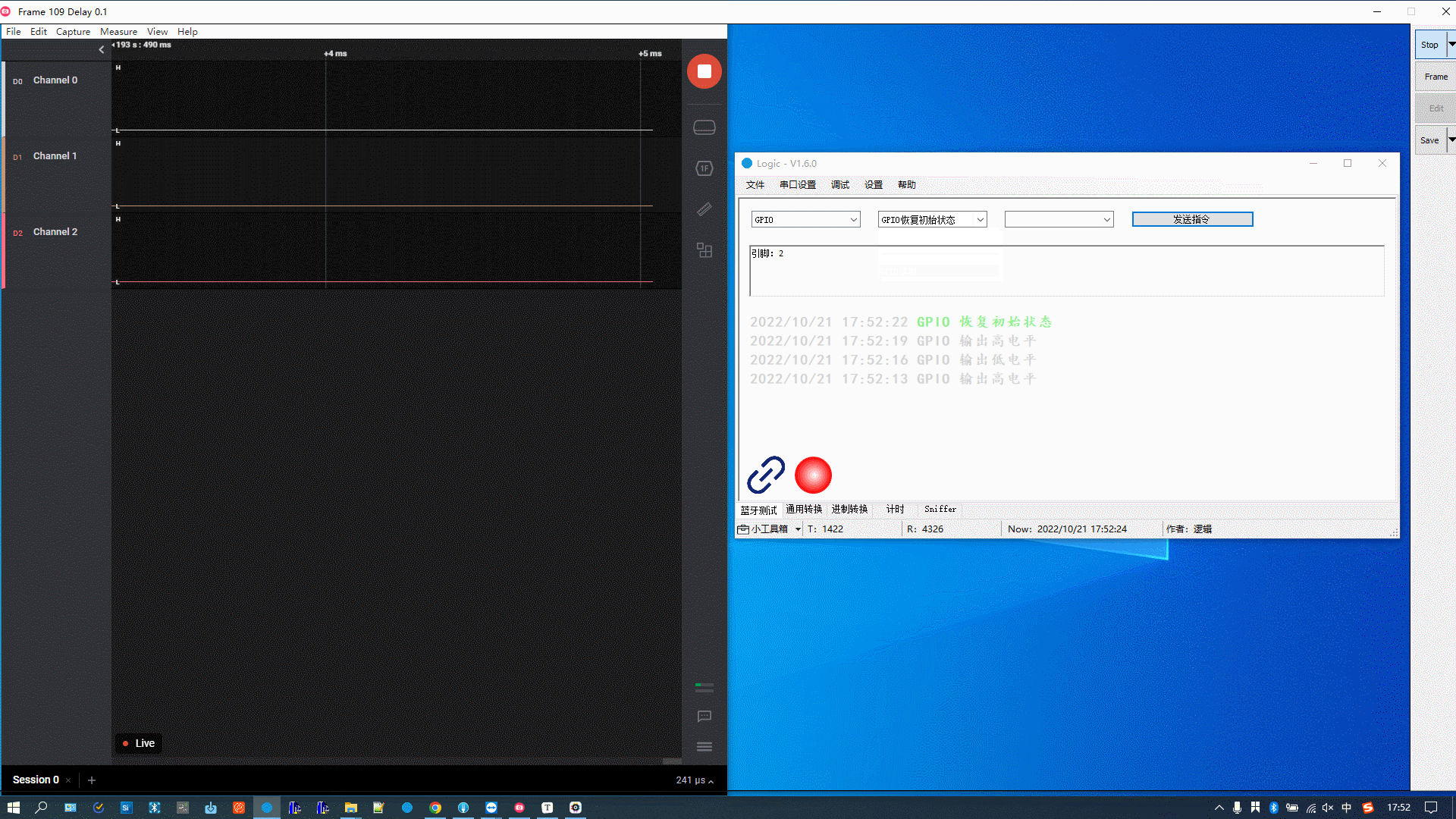
The figure below demonstrates the following actions:
-
GPIO outputs high.
-
GPIO outputs low.
-
GPIO outputs high again.
-
GPIO is reset to its initial state, which has the same effect as output low.
Debug weather service
Location:
-
1: The location where the device is paired. -
2: The location where the mobile phone is.
Weather parameters:
(1 << 0), /**< temperature. */
(1 << 1), /**< high temperature. */
(1 << 2), /**< low temperature. */
(1 << 3), /**< humidity. */
(1 << 4), /**< weather condition. */
(1 << 5), /**< pressure. */
(1 << 6), /**< sensible temperature. */
(1 << 7), /**< uvi. */
(1 << 8), /**< sunrise. */
(1 << 9), /**< sunset. */
(1 << 10), /**< unix time, used with sunrise and sunset. */
(1 << 11), /**< local time, used with sunrise and sunset. */
(1 << 12), /**< wind speed. */
(1 << 13), /**< wind direction. */
(1 << 14), /**< wind speed scale/level. */
(1 << 15), /**< aqi. */
(1 << 16), /**< tips. */
(1 << 17), /**< detailed AQI status and national ranking. */
(1 << 18), /**< pm10. */
(1 << 19), /**< pm2.5. */
(1 << 20), /**< o3. */
(1 << 21), /**< no2. */
(1 << 22), /**< co. */
(1 << 23), /**< so2. */
(1 << 24), /**< weather condition mapping ID. */
A day:
1 to 7: day 1 to day 7.
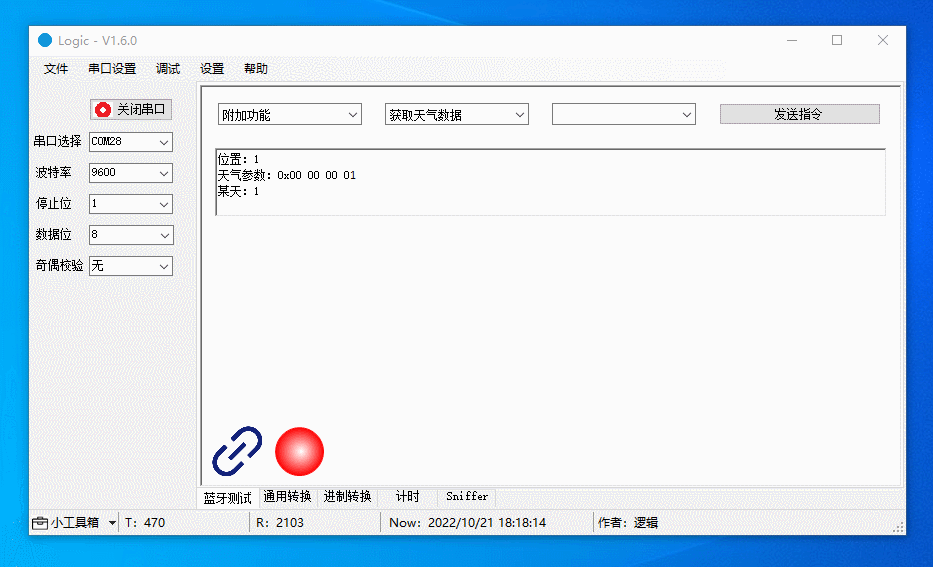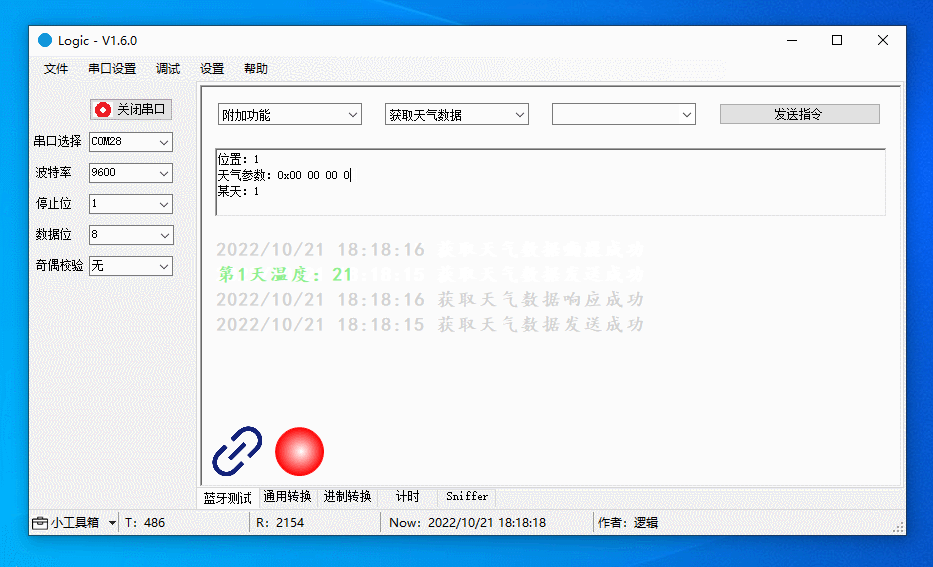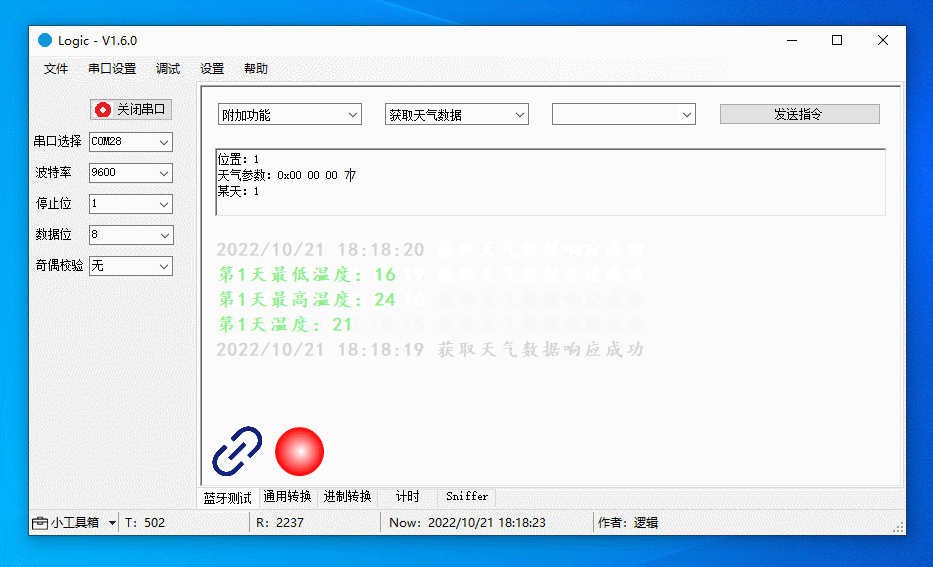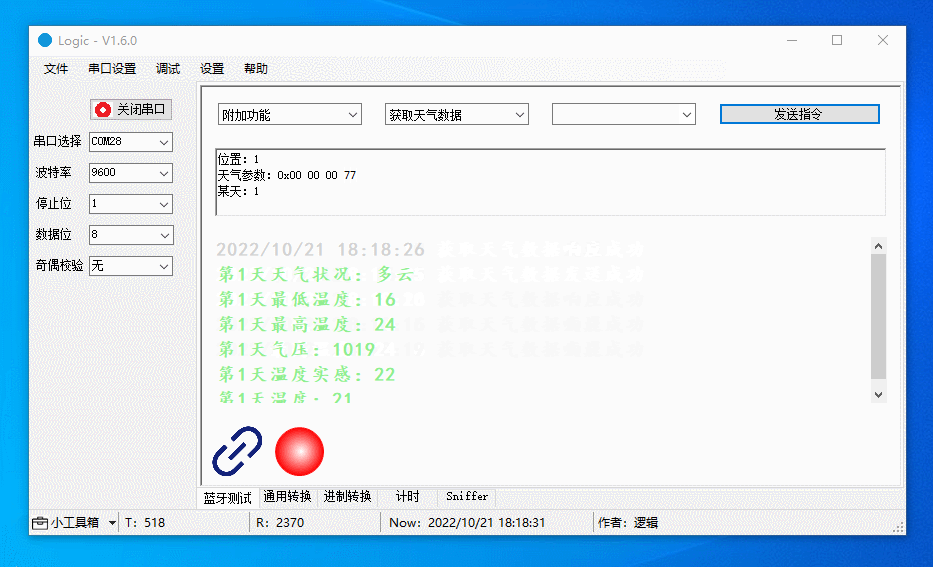
The figure below demonstrates the following actions:
-
Get the current temperature for day 1.
-
Get the current temperature, highest temperature, and lowest temperature for day 1.
-
Get the current temperature, highest temperature, lowest temperature, weather conditions, air pressure, and apparent temperature for day 1.
Debug PWM
Modify the PWM frequency and duty cycle and select a channel. Mappings between channels and pins:
-
Channel 0: the pin P0.28
-
Channel 1: the pin P0.29
-
Channel 2: the pin P0.30
-
Channel 3: the pin P0.31
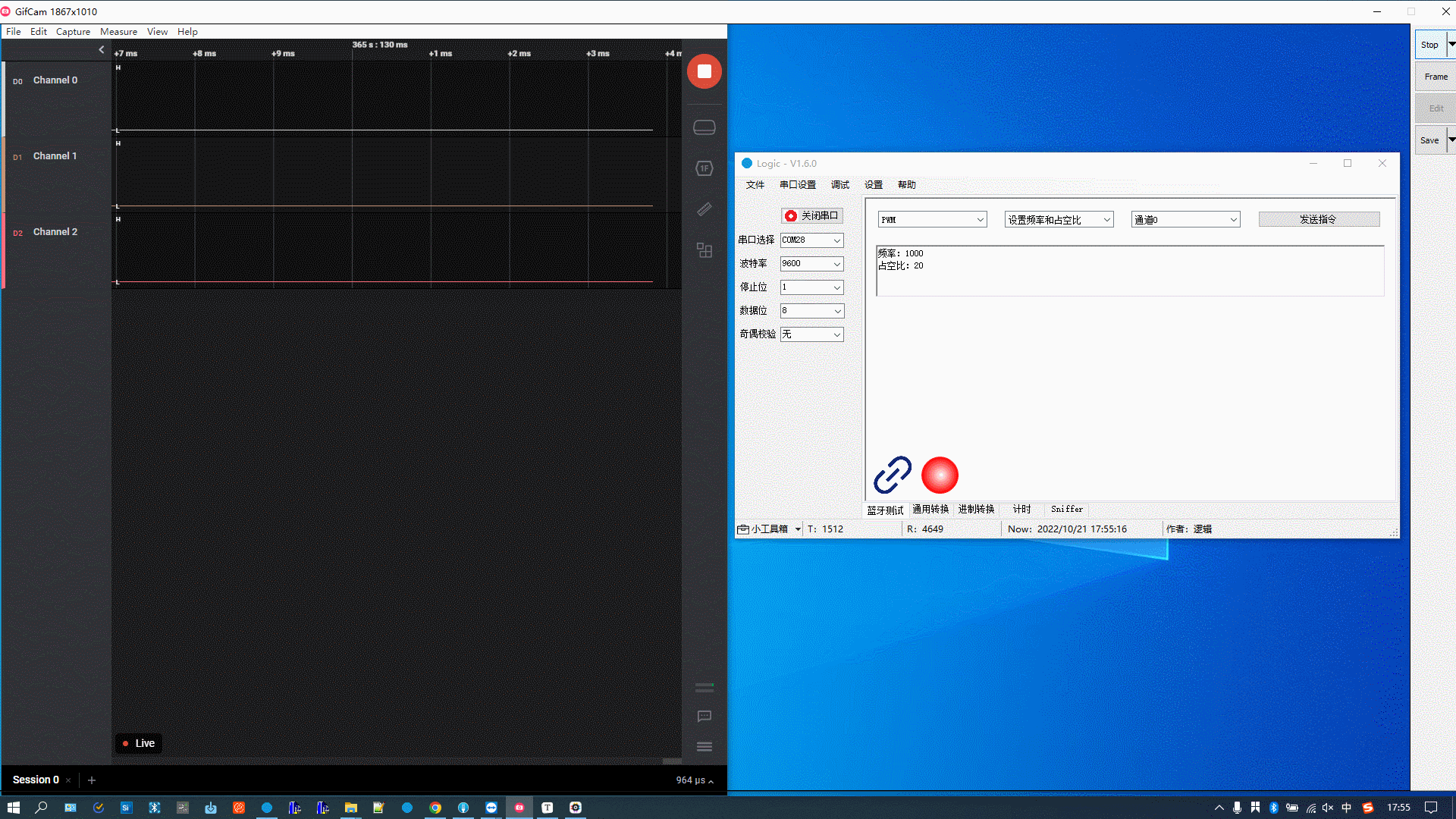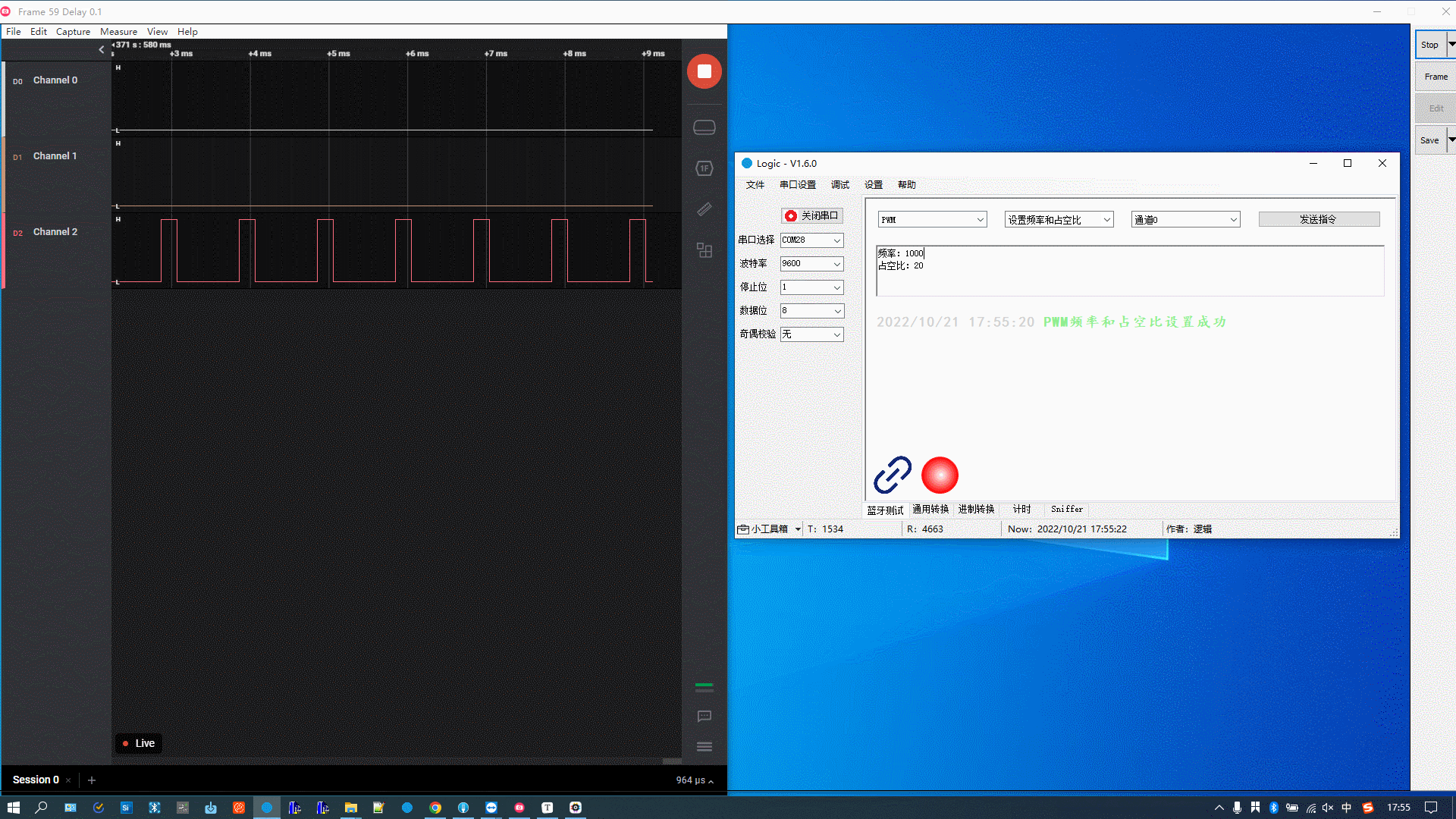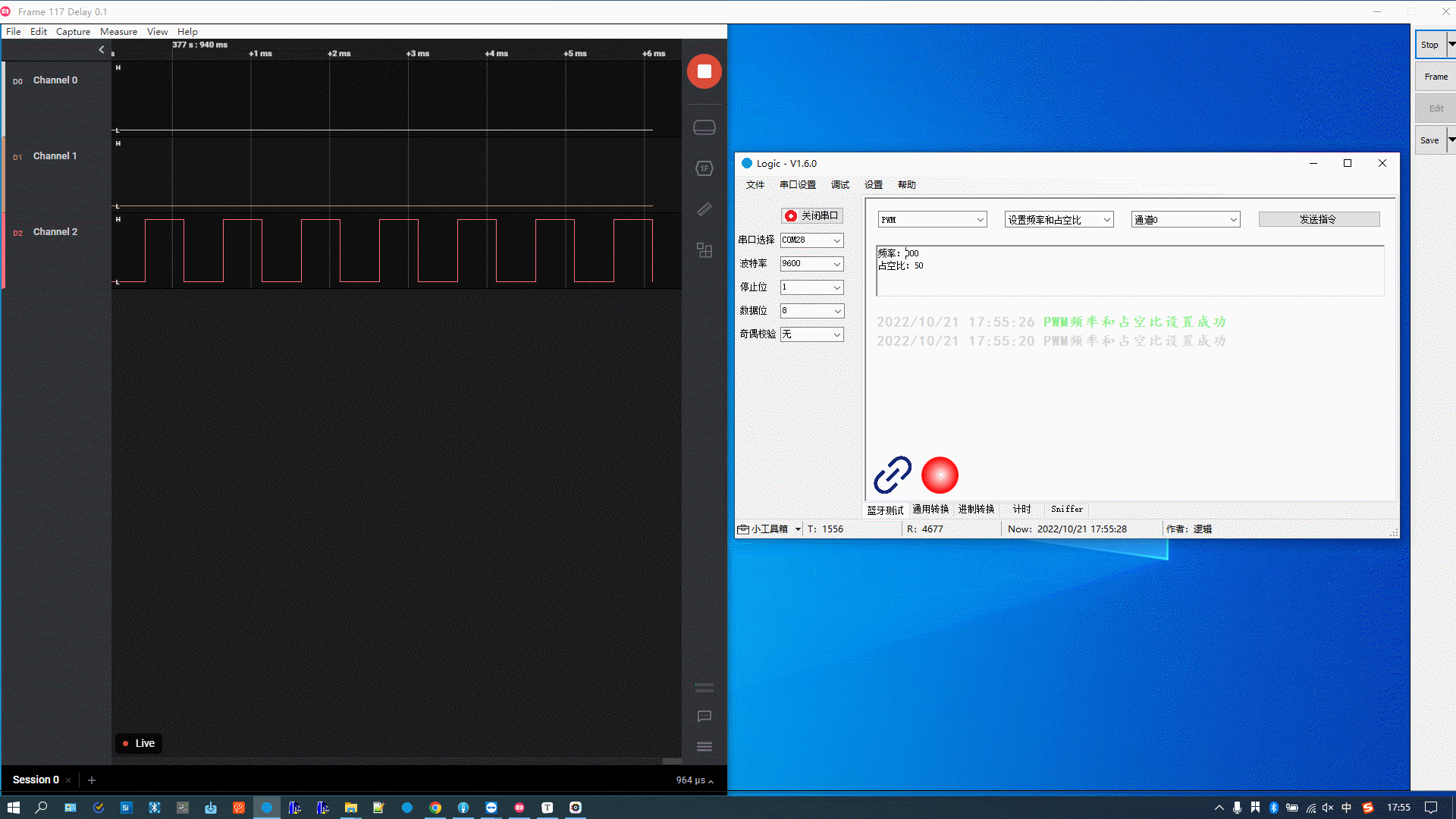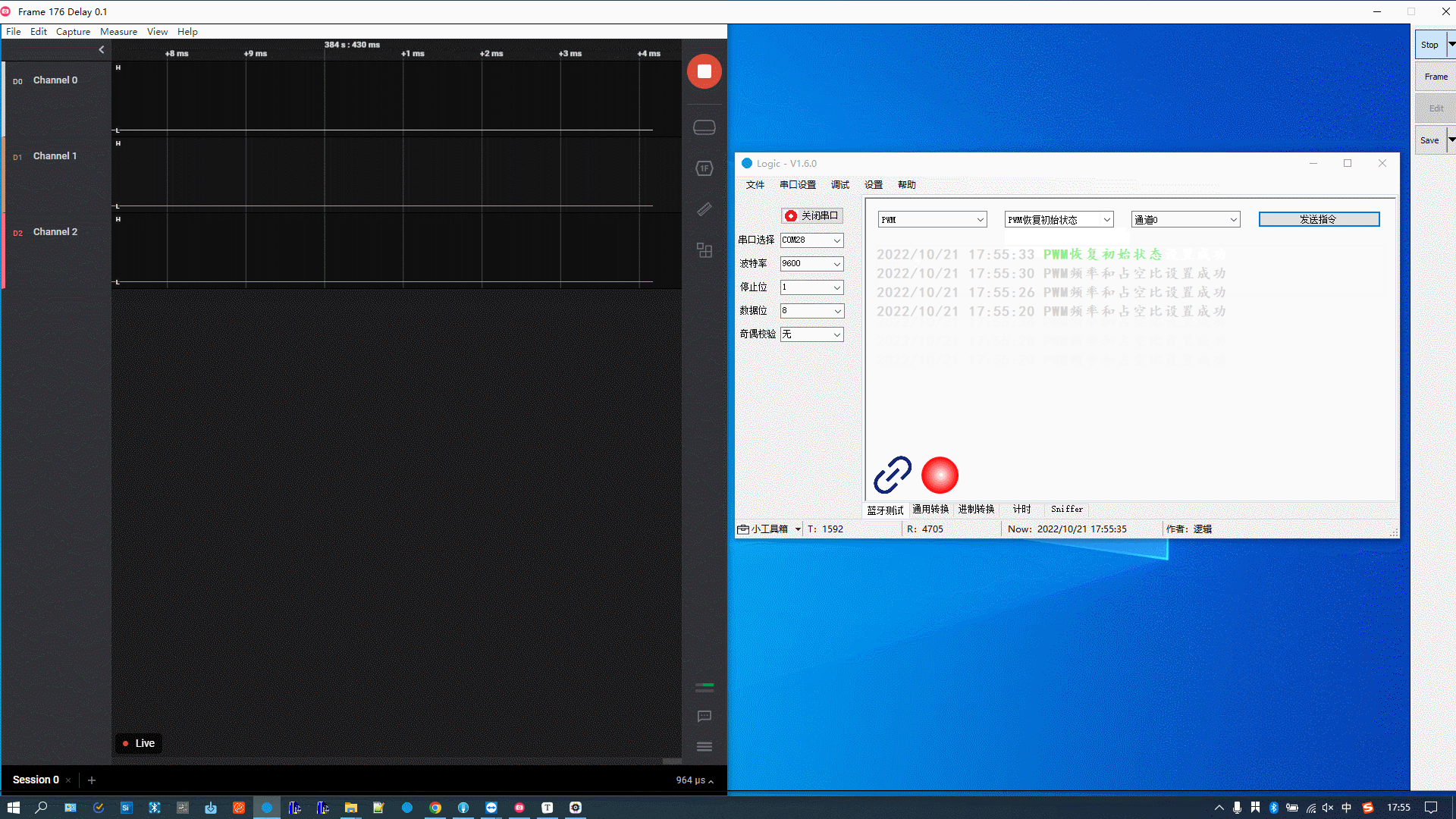
The figure below demonstrates the following actions:
-
Set the PWM frequency to 1000 and the duty cycle to 20%.
-
Set the PWM frequency to 1000 and the duty cycle to 50%.
-
Set the PWM frequency to 2000 and the duty cycle to 50%.
Debug scanning
Support the following features:
- Start and stop scanning.
- Modify scanning interval and window.
- Switch between proactive and passive scanning.
After scanning is started, the device will report the number of discovered devices every second.
The more devices discovered per second, the greater the scanning performance. This metric can be used to determine if the scanning is acceptable.
The figure below demonstrates the following actions:
-
Start passive scanning.
-
Start proactive scanning.
-
Stop scanning.
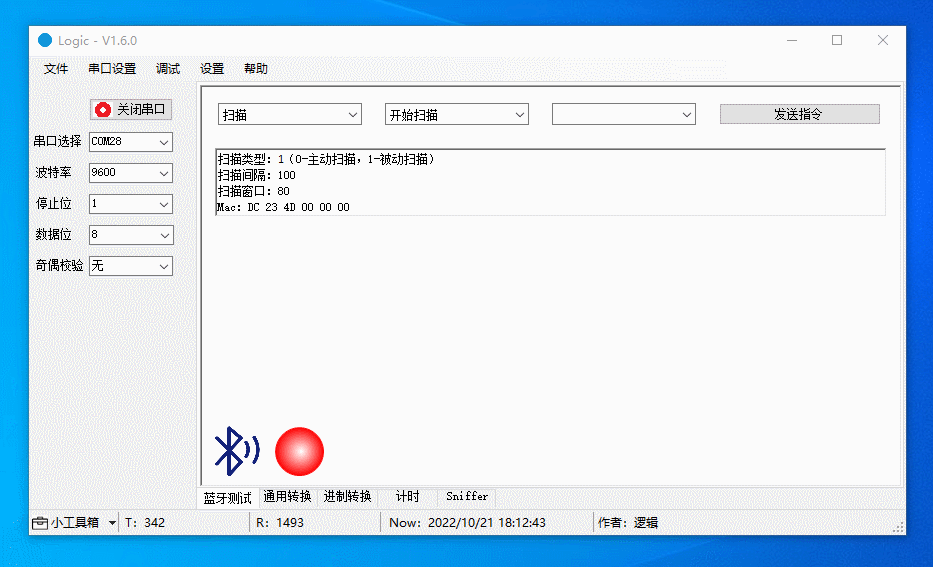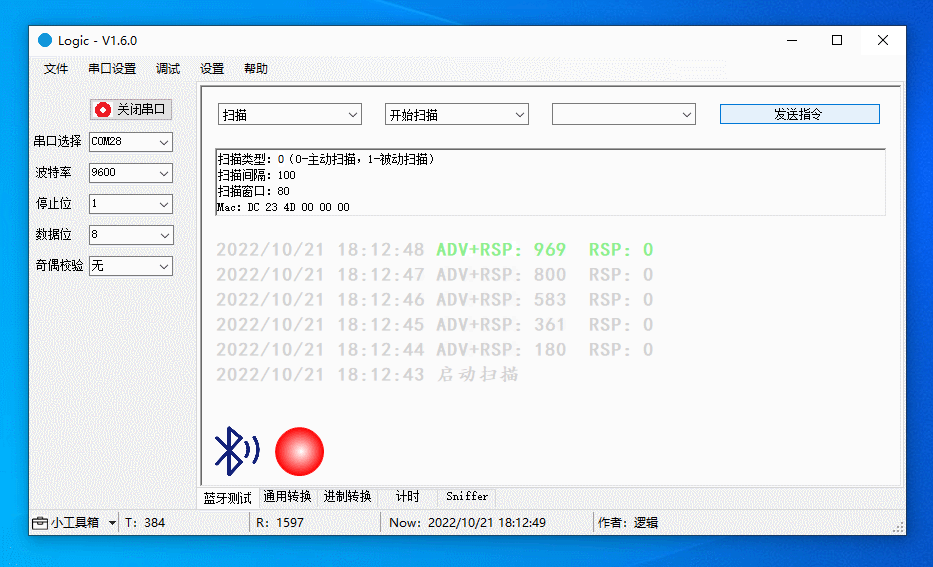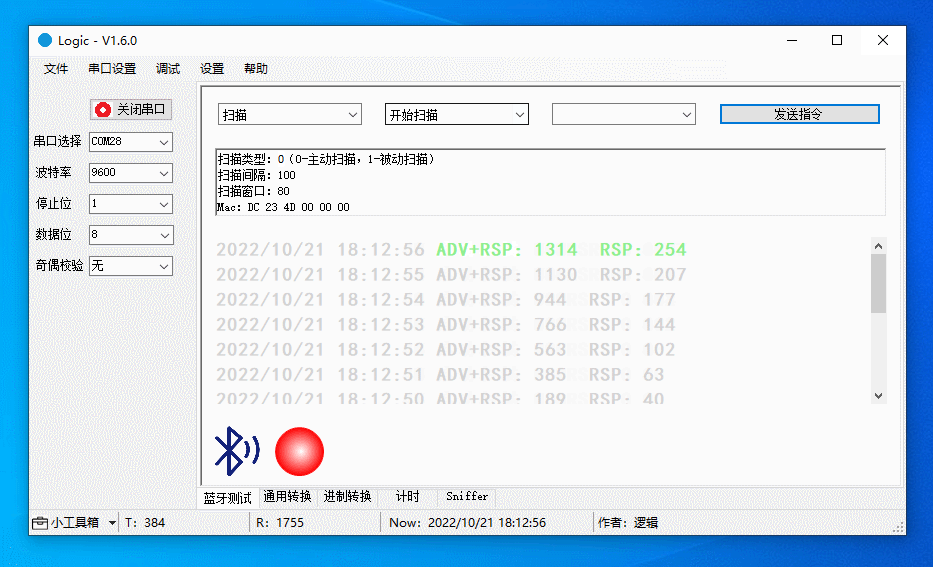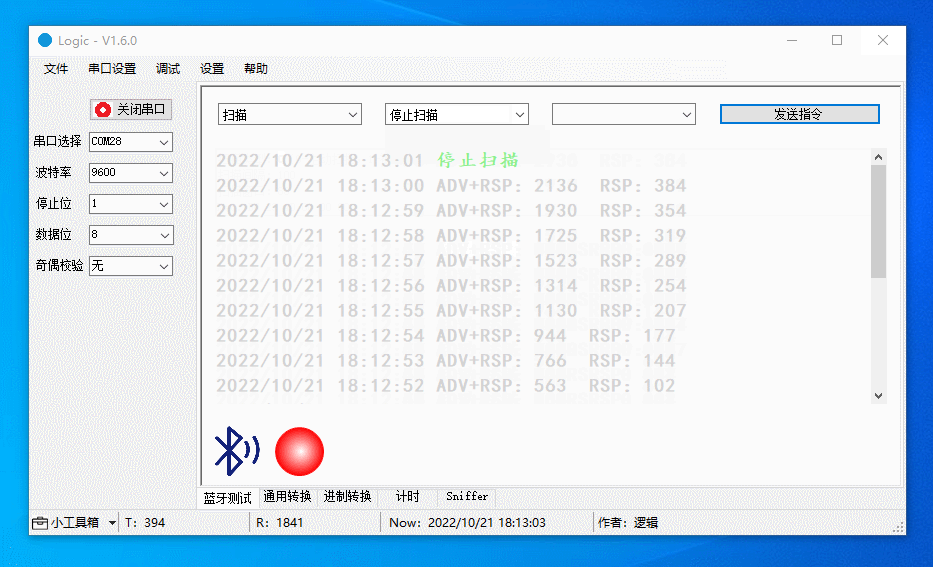
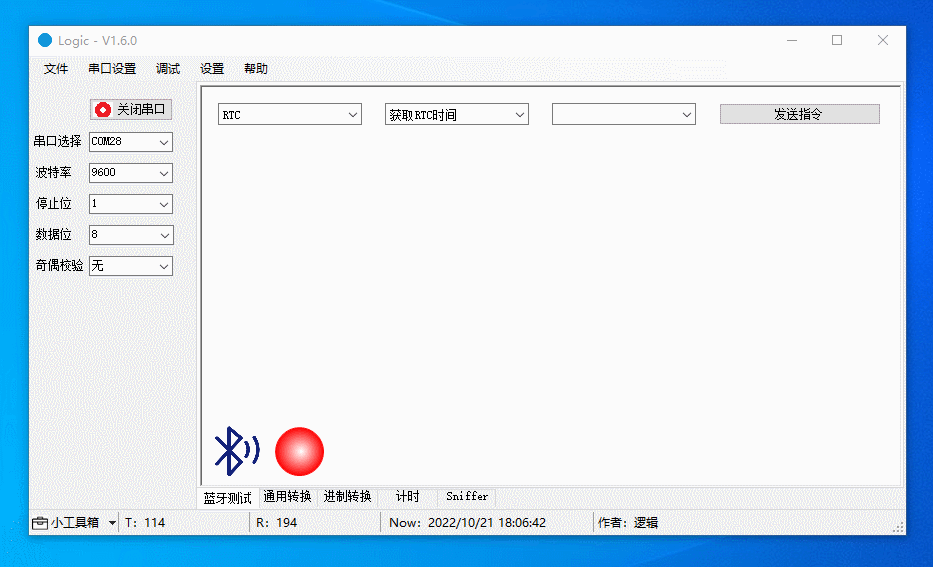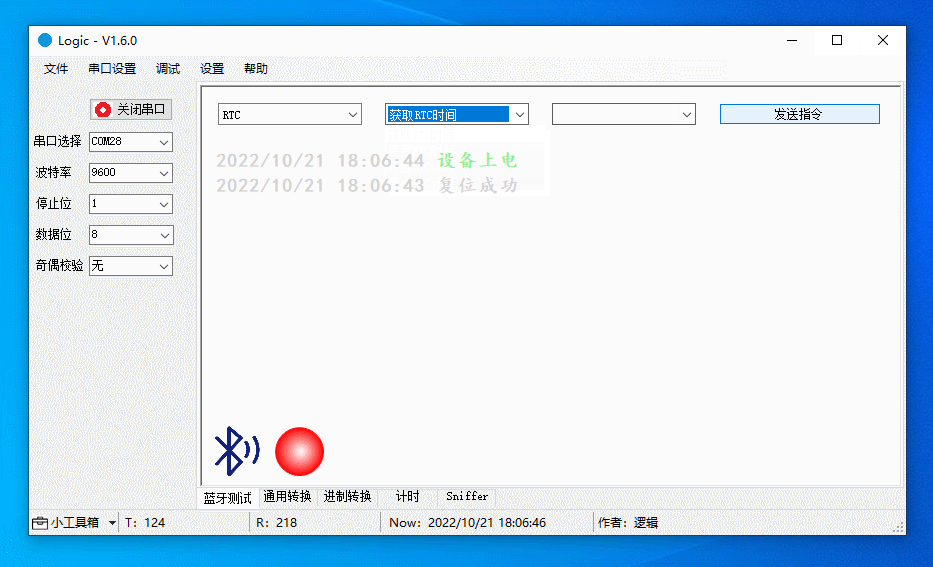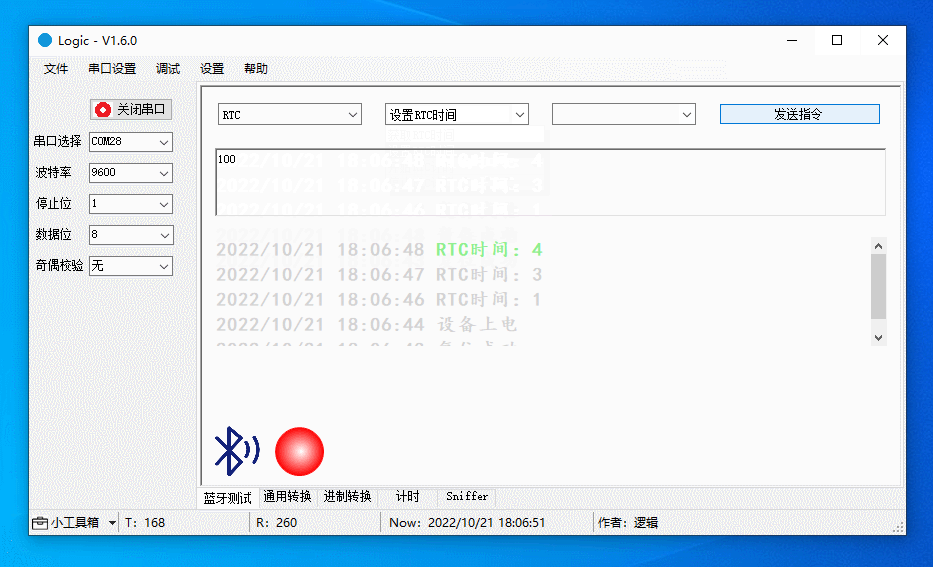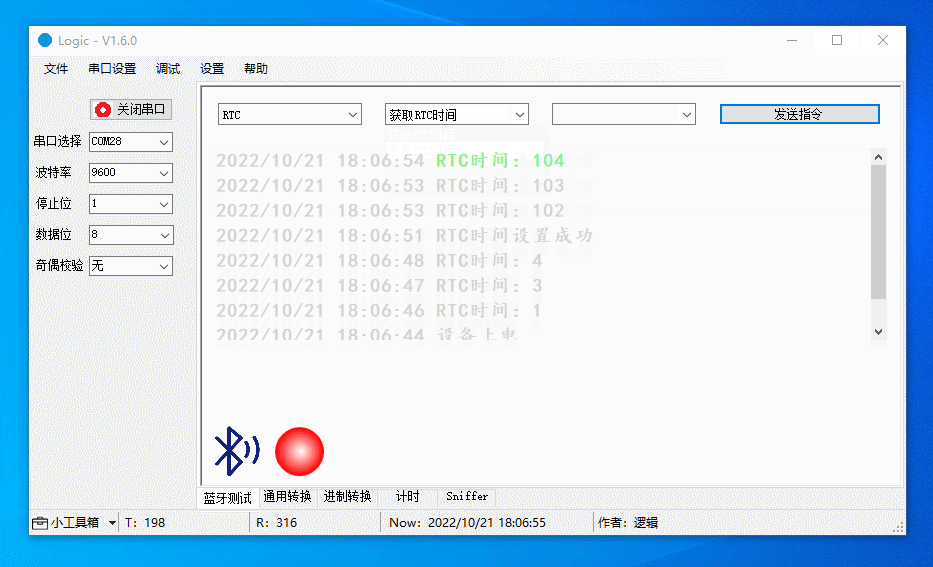
Debug RTC
Get and set RTC and start RTC timer (restart RTC). When the device is powered on, the RTC will start counting from zero.
The figure below demonstrates the following actions:
-
Turn on or off the serial port. Each time the serial port is restarted, a command will be sent to restart the device.
-
Get the RTC, which approaches zero, because the RTC starts counting from zero every time the device is powered on.
-
Set the RTC to 100.
-
Get the RTC again, which approaches 100.
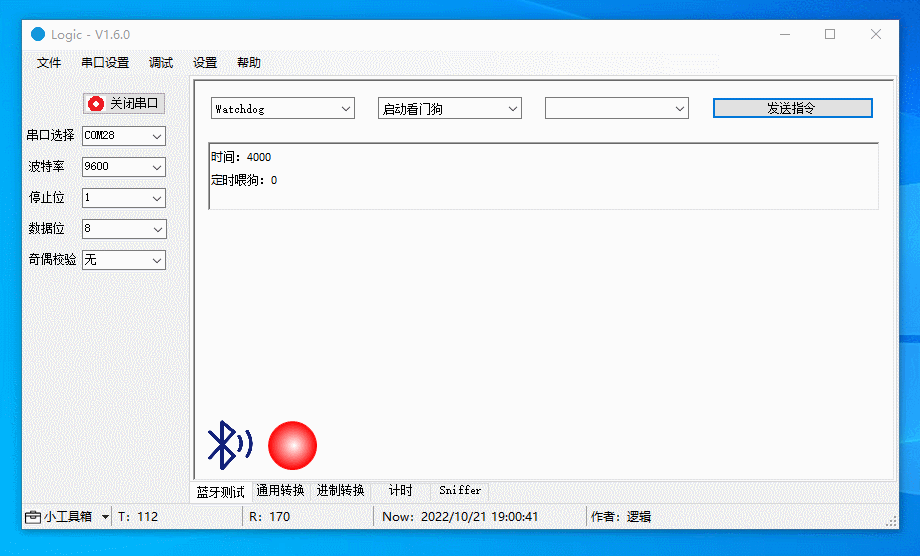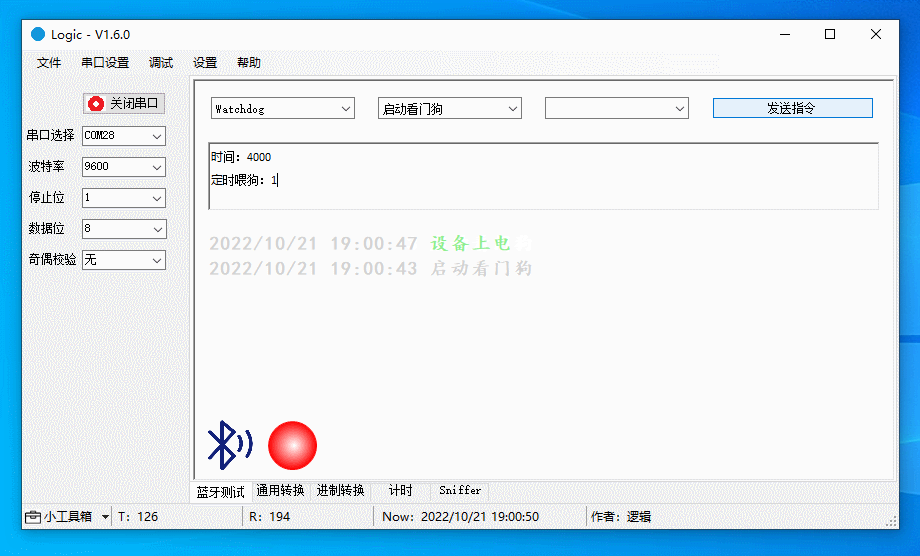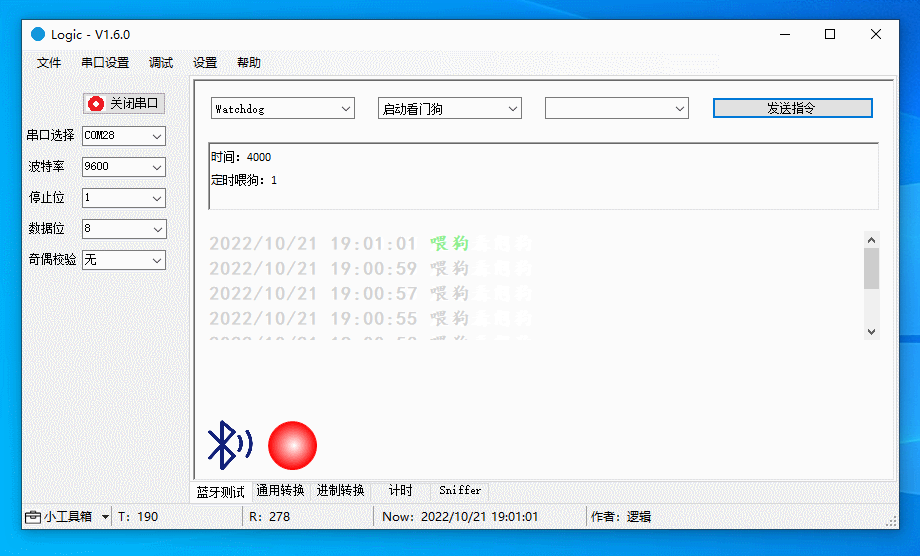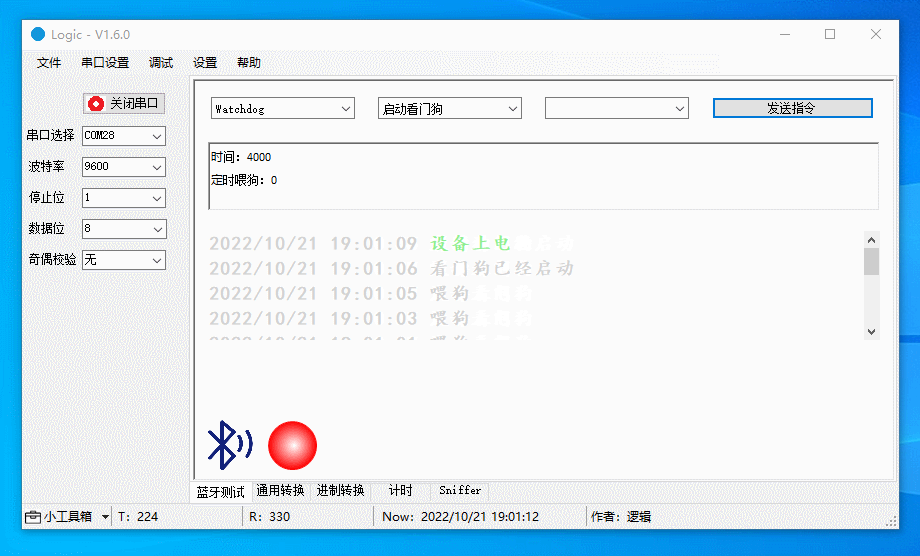
Debug watchdog
Start the watchdog, enable and disable scheduled feeding, and stop the watchdog (if supported by the chip).
The figure below demonstrates the following actions:
-
Start the watchdog, with scheduled feeding disabled. The device will restart in four seconds.
-
Start the watchdog, with scheduled feeding enabled. The watchdog is fed every two seconds, so the device will not restart.
-
Restart the watchdog, with scheduled feeding disabled. You are notified that the watchdog has been activated. The device will restart four seconds after the last feeding.
Debug flash memory
Read, write, and erase the flash memory and modify the start address and operation length.
The figure below demonstrates the following actions:
-
Read the flash memory. The result is all
FF. -
Write
12345678to the flash memory. -
Read
12345678from the flash memory. -
Erase the flash memory.
-
Read the flash memory. The result is all
FFbecause the flash memory has been erased.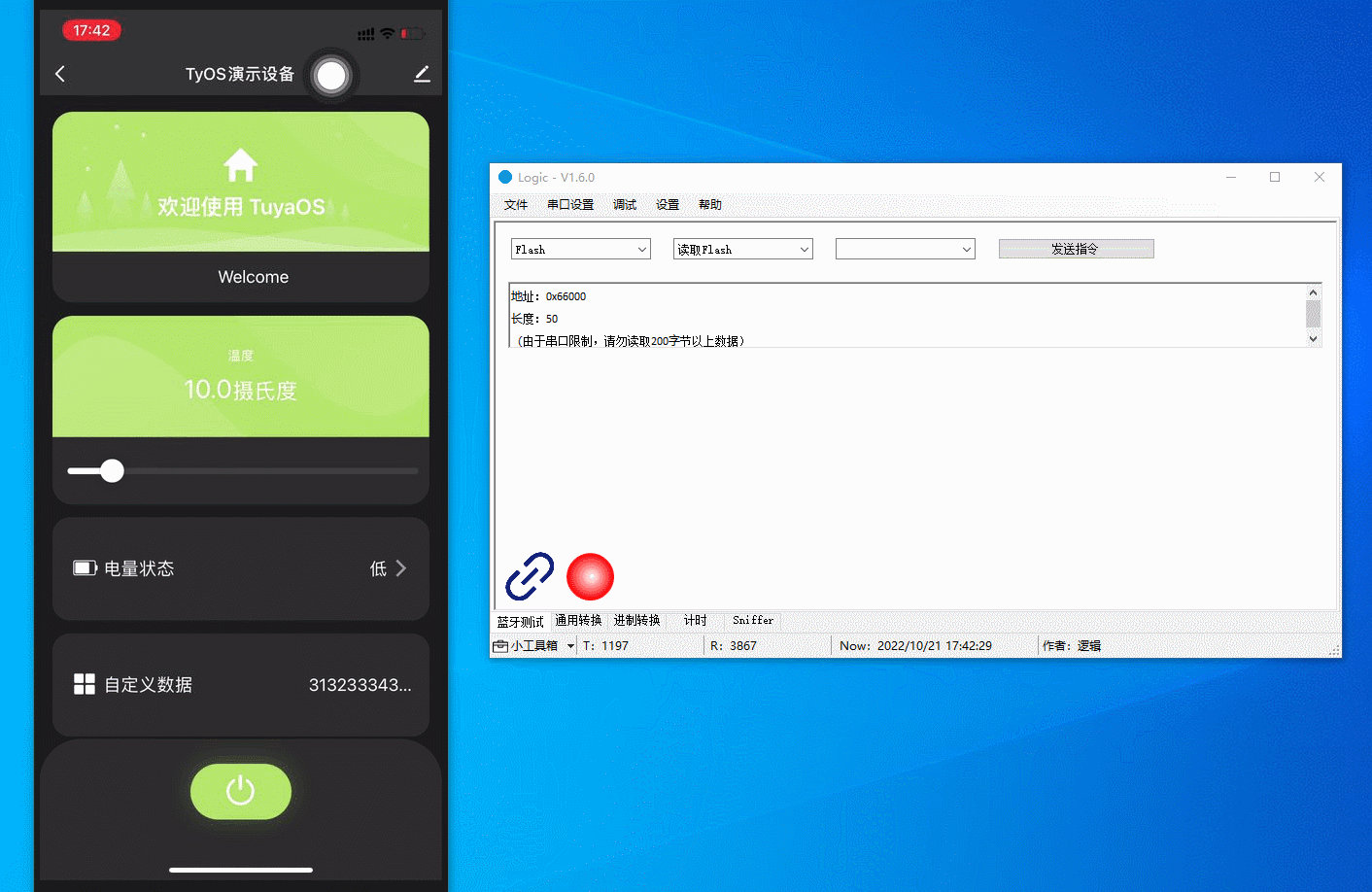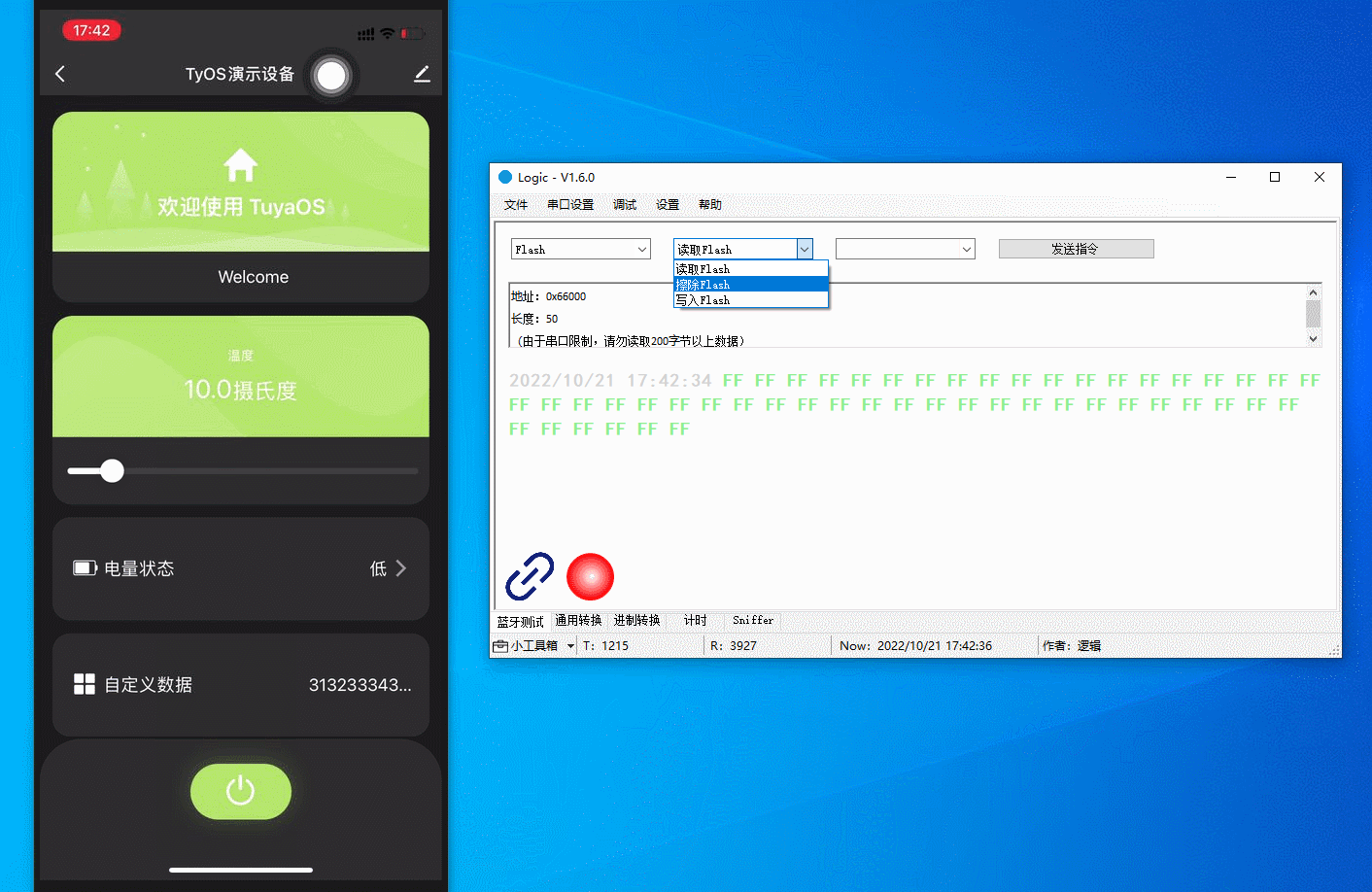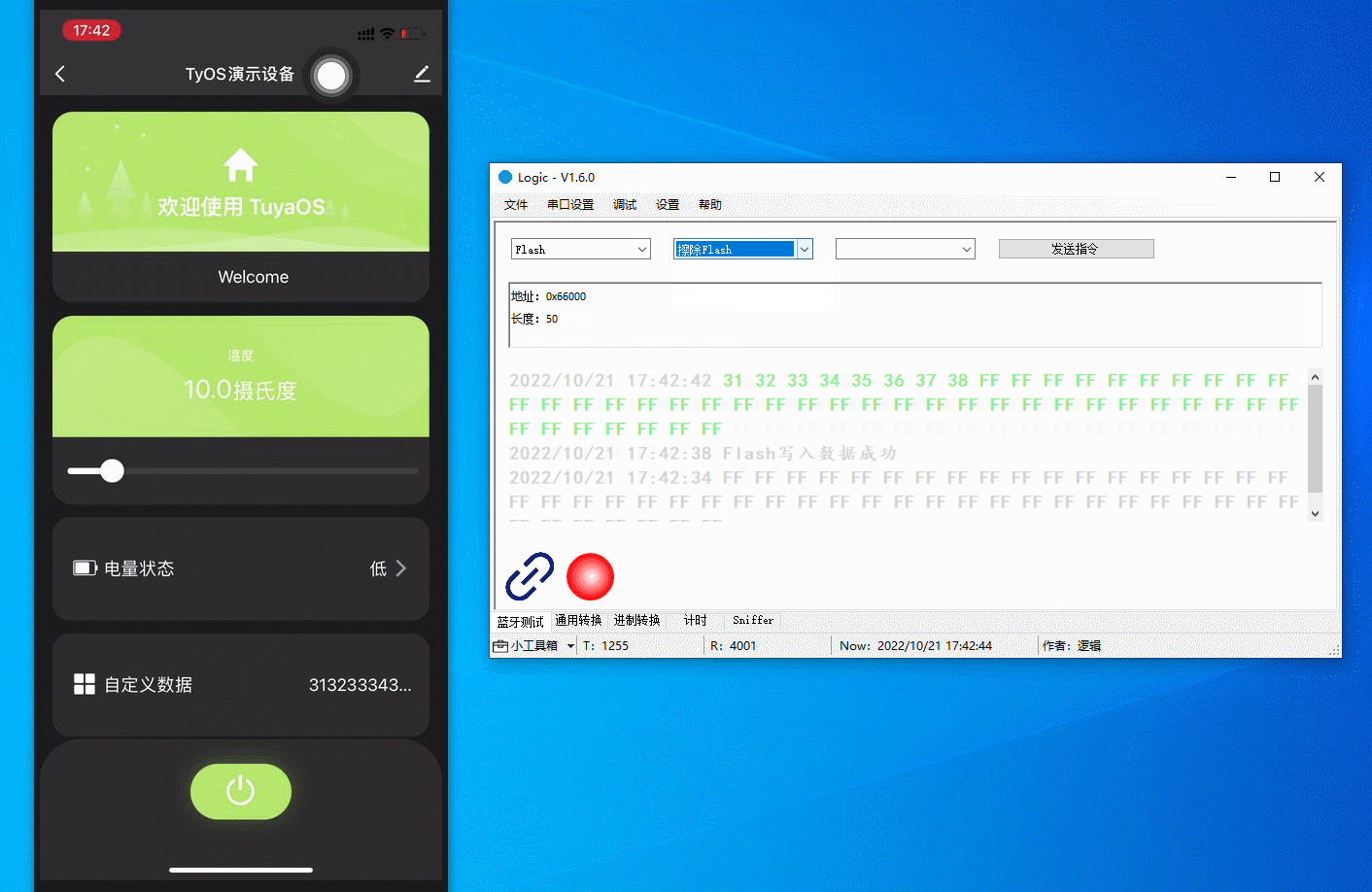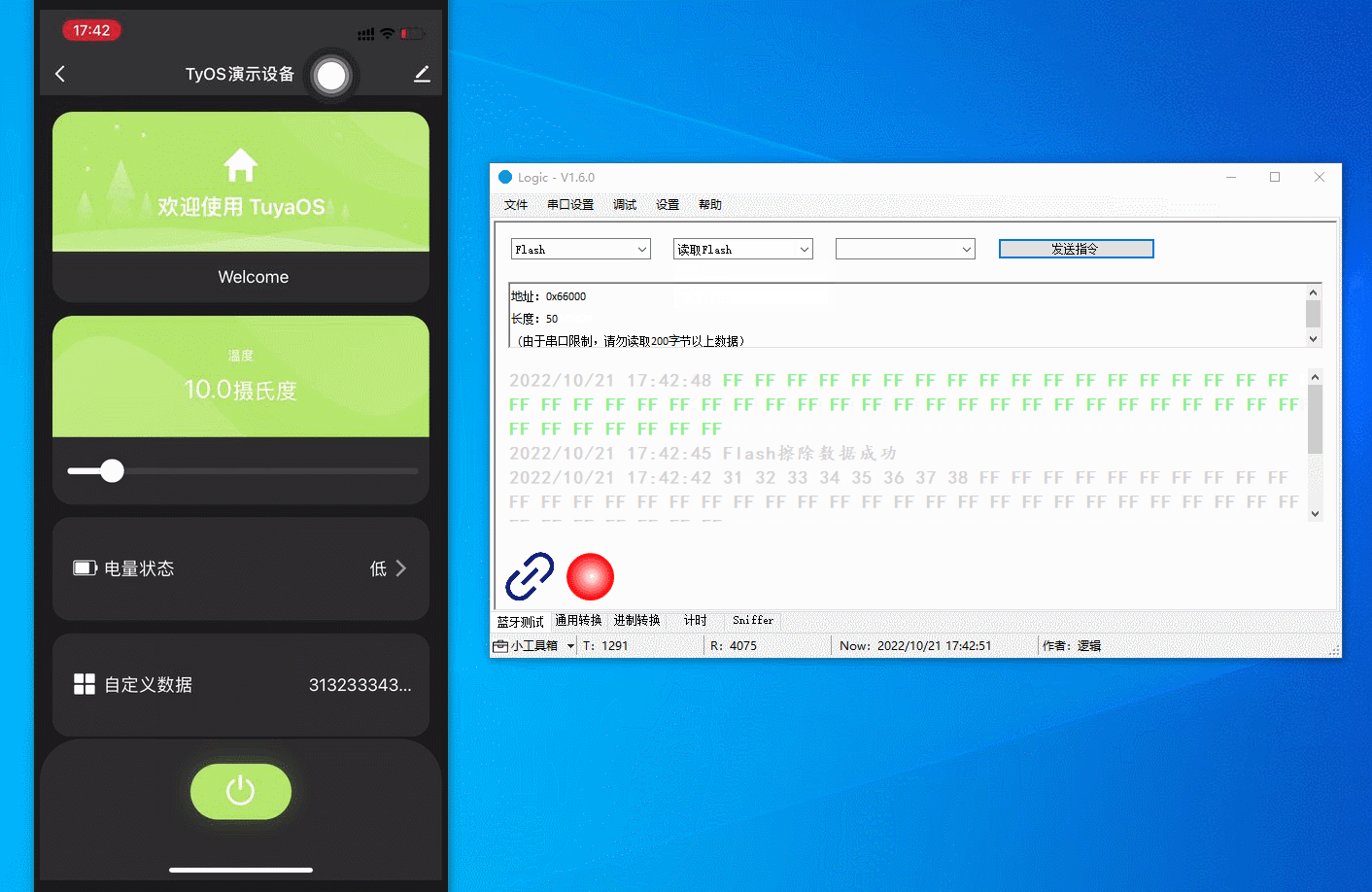
Debugging description
Each macro is a test case. You can debug each test case using the host software and search for a macro to find the code to facilitate your development.
/***********************************************************************
*********************constant (macro and enum)*********************
**********************************************************************/
//GID - Group ID, CID - Command ID
#define TEST_GID_SYSTEM 0x01
#define TEST_GID_DEVICE_INFO 0x02
#define TEST_GID_ADV 0x03
#define TEST_GID_SCAN 0x04
#define TEST_GID_CONN 0x05
#define TEST_GID_DATA 0x06
#define TEST_GID_ELSE 0x07
#define TEST_GID_GPIO 0x10
#define TEST_GID_UART 0x11
#define TEST_GID_PWM 0x12
#define TEST_GID_ADC 0x13
#define TEST_GID_SPI 0x14
#define TEST_GID_IIC 0x15
#define TEST_GID_RTC 0x16
#define TEST_GID_FLASH 0x17
#define TEST_GID_WATCHDOG 0x18
#define TEST_GID_POWERMANGER 0x19
#if (4 == TUYA_SDK_TEST_TYPE)
#define TEST_GID_BREDR_SYSTEM 0x20
#define TEST_GID_BREDR_CONNECT 0x21
#define TEST_GID_BREDR_AVTCP 0x22
#define TEST_GID_BREDR_HFP 0x23
#define TEST_GID_BREDR_EQ 0x24
#endif
// TEST_GID_SYSTEM
#define TEST_CID_SHAKE_HAND 0x00
#define TEST_CID_RESET 0x01
#define TEST_CID_FACTORY_RESET 0x02
#define TEST_CID_GET_TIME 0x03
#define TEST_CID_REQ_TIME 0x04
#define TEST_CID_GET_RAND 0x05
#define TEST_CID_GET_QUEUE_SIZE 0x06
#define TEST_CID_POWER_ON 0x80
// TEST_GID_DEVICE_INFO
#define TEST_CID_SET_MAC 0x00
#define TEST_CID_GET_MAC 0x01
#define TEST_CID_SET_PID 0x02
#define TEST_CID_GET_PID 0x03
#define TEST_CID_SET_VERSION 0x04
#define TEST_CID_GET_VERSION 0x05
// TEST_GID_ADV
#define TEST_CID_ADV_ENABLE 0x00
#define TEST_CID_SET_ADV_INTERVAL 0x01
#define TEST_CID_SET_ADV_PARAM 0x02
#define TEST_CID_SET_ADV_DATA 0x03
#define TEST_CID_CONN_REQUEST 0x04
#define TEST_CID_MESH_FAST_PROV 0x05
// TEST_GID_SCAN
#define TEST_CID_SCAN_START 0x00
#define TEST_CID_SCAN_STOP 0x01
#define TEST_CID_ADV_REPORT 0x80
// TEST_GID_CONN
#define TEST_CID_CONN 0x00
#define TEST_CID_SET_CONN_INTERVAL 0x01
#define TEST_CID_SET_CONN_PARAM 0x02
#define TEST_CID_DISCONN 0x03
#define TEST_CID_NET_STATE 0x04
#define TEST_CID_GET_MESH_ADDR 0x05
#define TEST_CID_UNBIND_MODE 0x80
#define TEST_CID_CONN_PARAM_UPDATE 0x81
#define TEST_CID_MTU_UPDATE 0x82
// TEST_GID_DATA
#define TEST_CID_MASTER_SEND 0x00
#define TEST_CID_SLAVE_SEND 0x01
#define TEST_CID_DP_REPORT 0x02
#define TEST_CID_LONG_DP_REPORT 0x03
#define TEST_CID_DP_REPORT_TIME 0x04
#define TEST_CID_LONG_DP_REPORT_TIME 0x05
#define TEST_CID_DP_PASSTHROUGH 0x06
#define TEST_CID_MESH_DP_REPORT 0x07
#define TEST_CID_DP_REPORT_RSP 0x80
#define TEST_CID_DP_REPORT_TIME_RSP 0x81
#define TEST_CID_DP_WRITE 0x82
#define TEST_CID_LONG_DP_WRITE 0x83
#define TEST_CID_MESH_DP_WRITE 0x84
// TEST_GID_ELSE
#define TEST_CID_GET_WEATHER 0x00
#define TEST_CID_SET_BULK_DATA 0x01
#define TEST_CID_GET_SCENE_LIST 0x02
#define TEST_CID_REQ_SCENE_CTRL 0x03
#define TEST_CID_GET_WEATHER_RSP 0x80
#define TEST_CID_GET_WEATHER_DATA 0x81
#define TEST_CID_GET_REMOTER_DATA 0x82
#define TEST_CID_GET_LOCAL_TIMER 0x83
#define TEST_CID_GET_LOCAL_TIMER_RSP 0x84
#define TEST_CID_GET_LOCAL_TIMER_PARSER 0x85
#define TEST_CID_GET_SCENE_RSP 0x86
// TEST_GID_GPIO
#define TEST_CID_PIN_DEINIT 0x00
#define TEST_CID_OUTPUT_HIGH 0x01
#define TEST_CID_OUTPUT_LOW 0x02
#define TEST_CID_PIN_READ 0x03
// TEST_GID_UART
#define TEST_CID_SET_BAUDRATE 0x00
#define TEST_CID_TX_UART_DATA 0x01
#define TEST_CID_RX_UART_PORT 0x80
#define TEST_CID_RX_UART_DATA 0x81
// TEST_GID_PWM
#define TEST_CID_PWM_DEINIT 0x00
#define TEST_CID_SET_FREQ_DUTY 0x01
// TEST_GID_ADC
#define TEST_CID_ADC_DEINIT 0x00
#define TEST_CID_READ_ADC_DATA 0x01
#define TEST_CID_READ_ADC_DATA_RSP 0x80
#define TEST_CID_READ_VOLTAGE_RSP 0x81
// TEST_GID_SPI
#define TEST_CID_TX_SPI_DATA 0x00
#define TEST_CID_RX_SPI_DATA 0x80
// TEST_GID_IIC
#define TEST_CID_TX_IIC_DATA 0x00
#define TEST_CID_RX_IIC_DATA 0x80
// TEST_GID_RTC
#define TEST_CID_SET_RTC_TIME 0x00
#define TEST_CID_GET_RTC_TIME 0x01
#define TEST_CID_START_RTC 0x02
#define TEST_CID_STOP_RTC 0x03
// TEST_GID_FLASH
#define TEST_CID_READ_FLASH_DATA 0x00
#define TEST_CID_ERASE_FLASH_DATA 0x01
#define TEST_CID_WRITE_FLASH_DATA 0x02
// TEST_GID_WATCHDOG
#define TEST_CID_START_WDG 0x00
#define TEST_CID_FEED_WDG 0x01
#define TEST_CID_STOP_WDG 0x02
// TEST_GID_POWERMANGER
#define TEST_CID_ENTER_SLEEP 0x00
#define TEST_CID_WAKEUP_SRC_SET 0x01
The debugging code can be found in tal_sdk_test.c and tal_sdk_test.h.
You can disable the debugging feature using the macro.
#define TUYA_SDK_TEST 0
Is this page helpful?
YesFeedbackIs this page helpful?
YesFeedback





