Database
Last Updated on : 2025-12-24 02:34:27download
Overview
The database functionality is a structured data management module provided by the Tuya Developer Platform for agents. It enables agents to perform data storage, retrieval, update, and deletion operations during runtime via natural language or system logic.
Using the database functionality, developers can quickly equip agents with the following capabilities:
- Record user behavior and logs.
- Store personalized profiles and preferences.
- Manage data shared among multiple users.
- Construct business knowledge bases and backend data tables.
The platform provides three data modes to cater to different needs, ranging from personal interaction to collaborative sharing:
- Single-user mode: Each user has an independent data space.
- Multi-user mode: Users share or collaborate on the same dataset.
- Developer mode: Backend data is maintained by developers, while users can only query and use it.
Database modes
| Mode | Typical scenario | Data type & read/write logic |
Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-user mode | Designed for personal data recording, companionship, and growth-oriented applications. Suitable for user-specific memories, learning logs, and health records. |
|
|
| Multi-user mode | Designed for sharing and interaction scenarios. Suitable for task boards, collaborative interactions, and social message boards. |
|
|
| Developer mode | Designed for backend knowledge management and centralized data maintenance. Suitable for product information, book Q&A, and FAQ systems. |
|
|
Example
The following section demonstrates typical applications of the three modes in real-world agent scenarios.
Single-user mode
| Example & description | Conversation example |
|---|---|
| AI toy/growth tracker: Creates an independent data table for each user to record daily learning and interactions. |
|
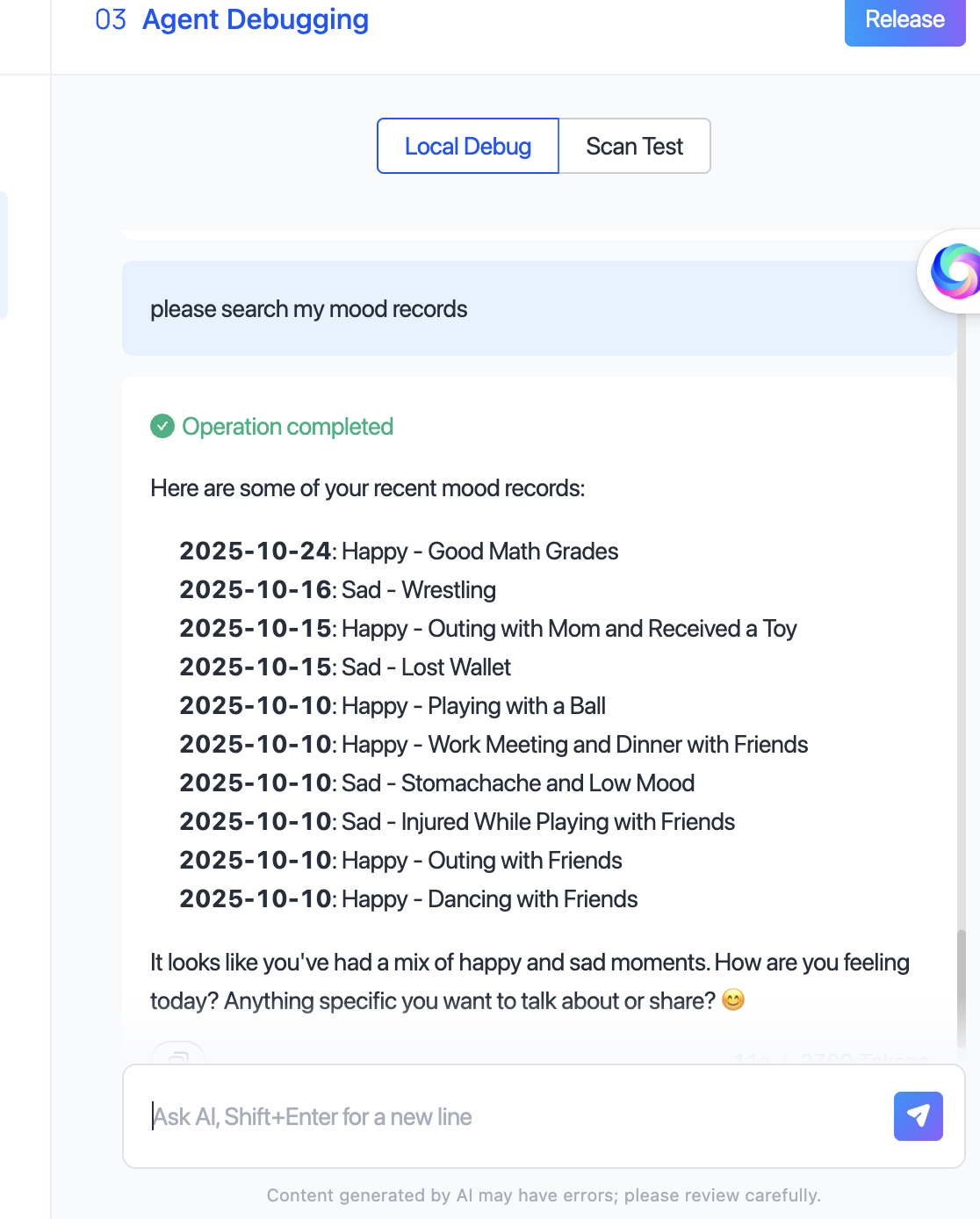
| AI recorder/diary assistant: Users record meetings, to-do lists, or mood logs via voice or text. Data is visible only to the user. |
|
Sample interface of a diary card
Multi-user mode
| Example & description | Conversation example |
|---|---|
| AI task square: Multiple users share a task data table. The system automatically calculates task completion rates and rankings. |
|
| Bottled message/public bulletin board: Users post messages to a public table, which can be randomly viewed or replied to by others. |
|
Developer mode
| Example & description | Conversation example |
|---|---|
| Product Q&A agent: Developers maintain product information (specifications, features, and FAQs) in the backend. The agent queries and returns results during conversations. |
|
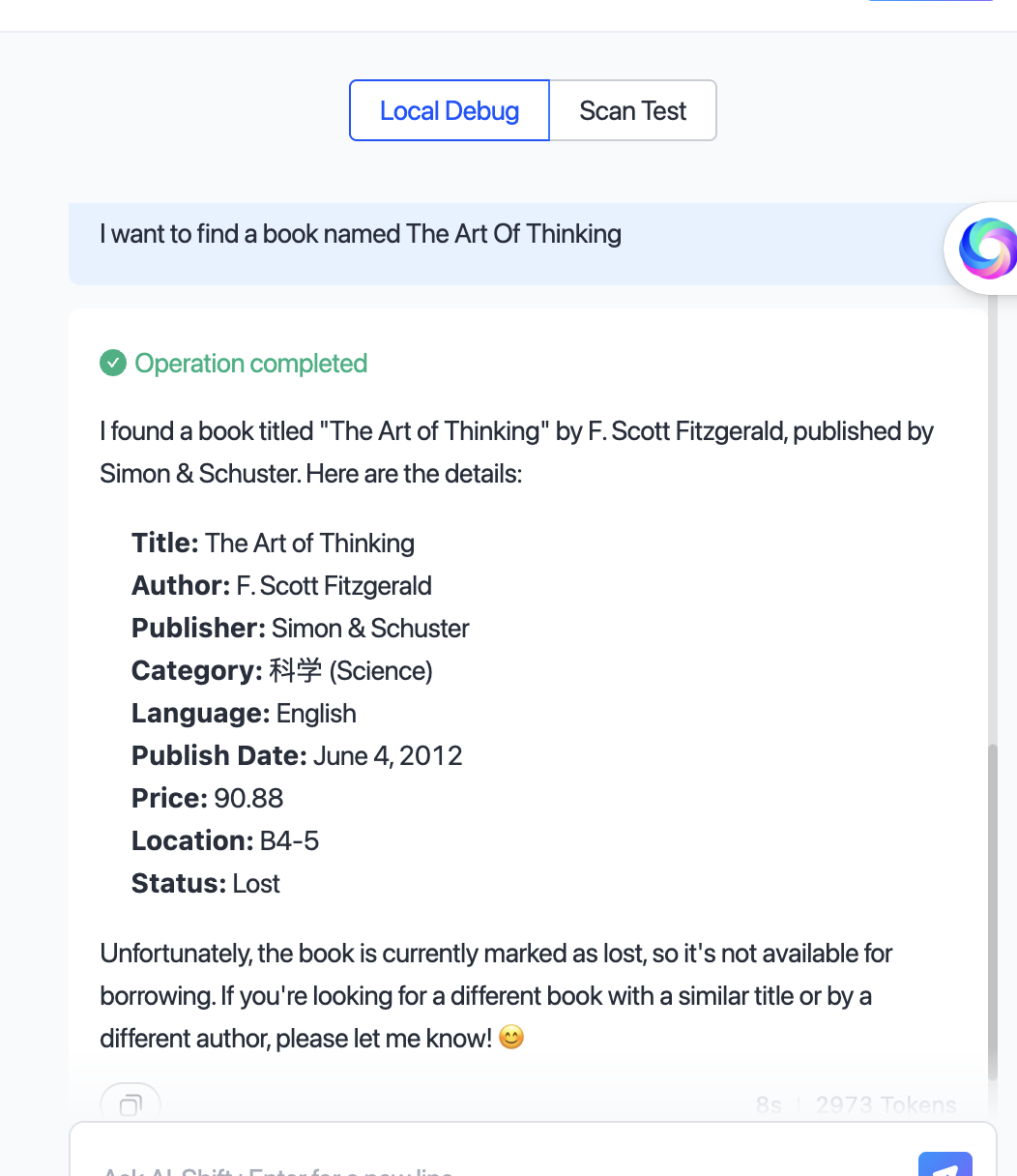
| Library assistant: Book information is maintained in the backend. Users retrieve it via natural language queries. |
|
Sample interface of a library AI assistant:
Data import and testing
| Item | Single-user mode | Multi-user mode | Developer mode |
|---|---|---|---|
| Test data import | Not supported | Not supported | Supported |
| Online data import | Not supported | Not supported | Supported |
Data import functionality is exclusively available in Developer Mode and must be performed by the project administrator.
Procedure
Create database
-
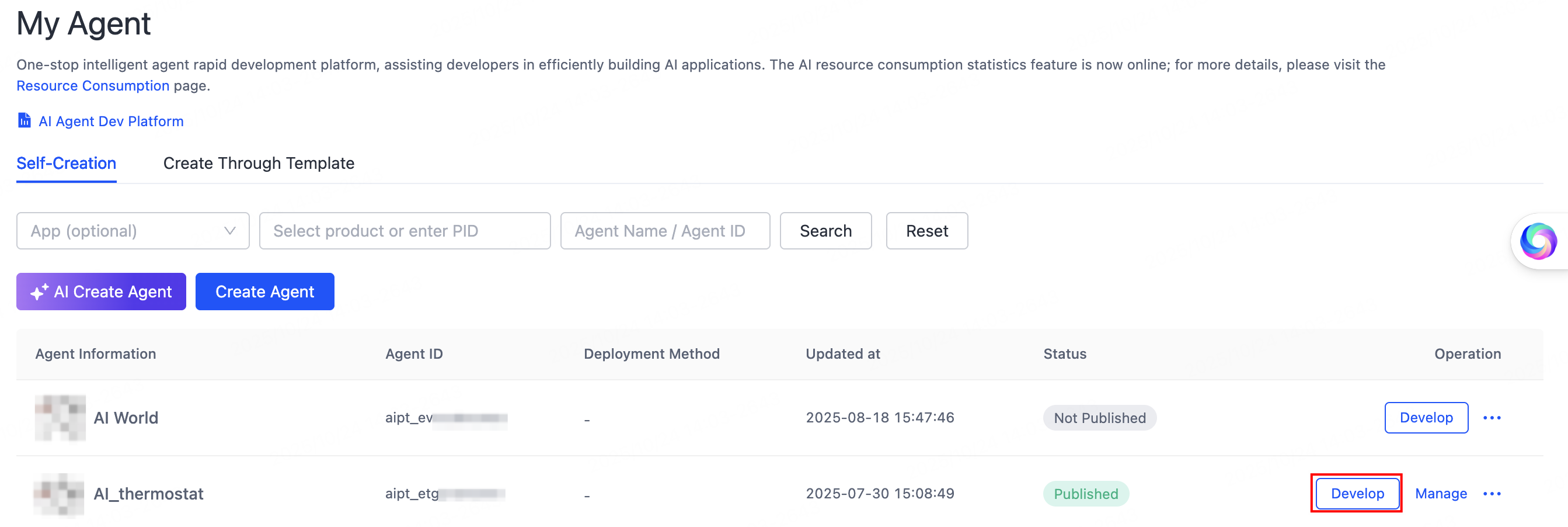
Go to the My Agent page and click Develop in the Operation column of the desired agent.
-
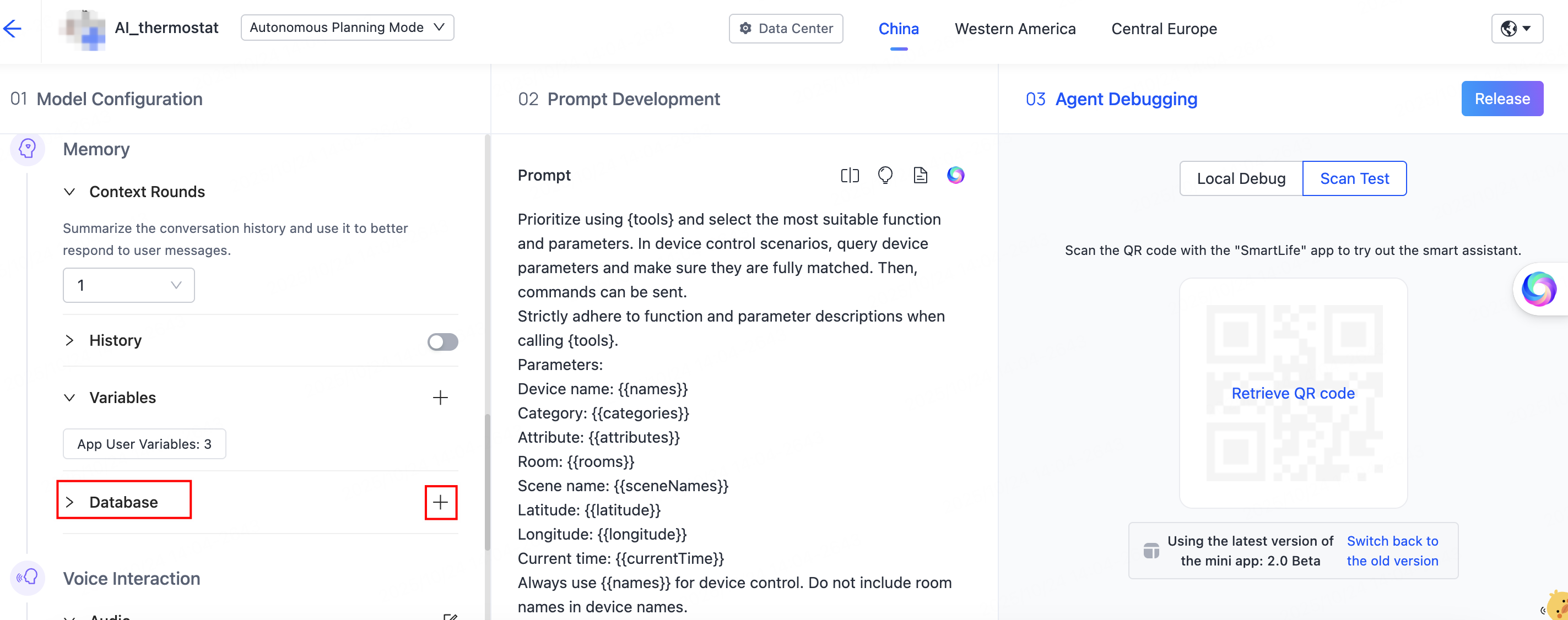
Under Model Configuration > Memory, find Database, then click the Add (+) button on the right.
-
On the Select Database page, click Add database in the top left corner, or bind an existing database from the list on the right.
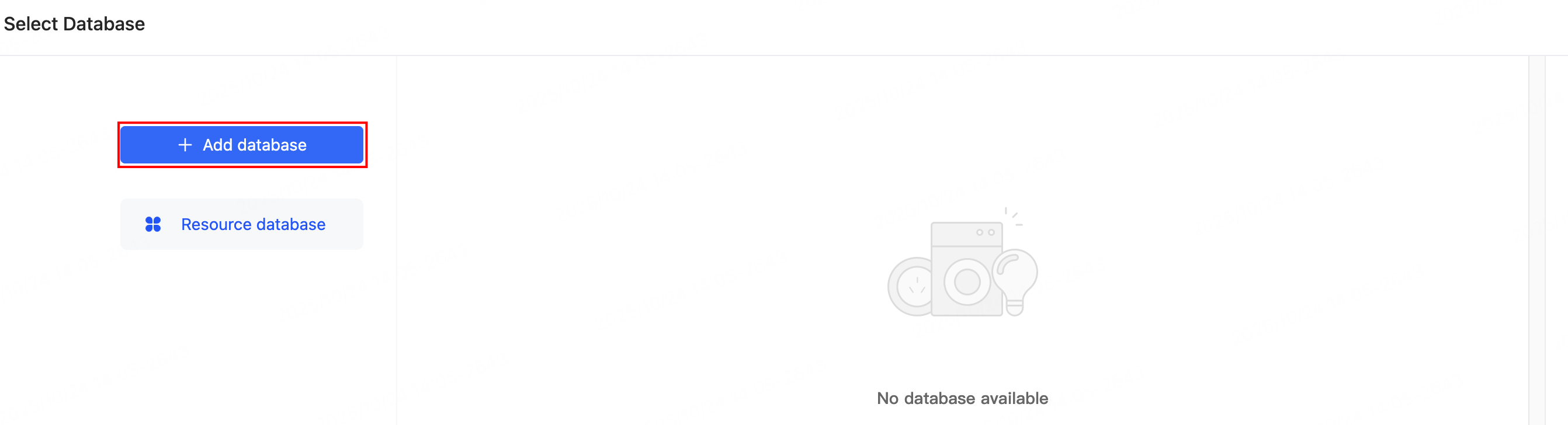
-
Define the data table structure. Refer to the configuration guide below. Based on the agent’s business type, define the table type, description, fields, and other relevant information.
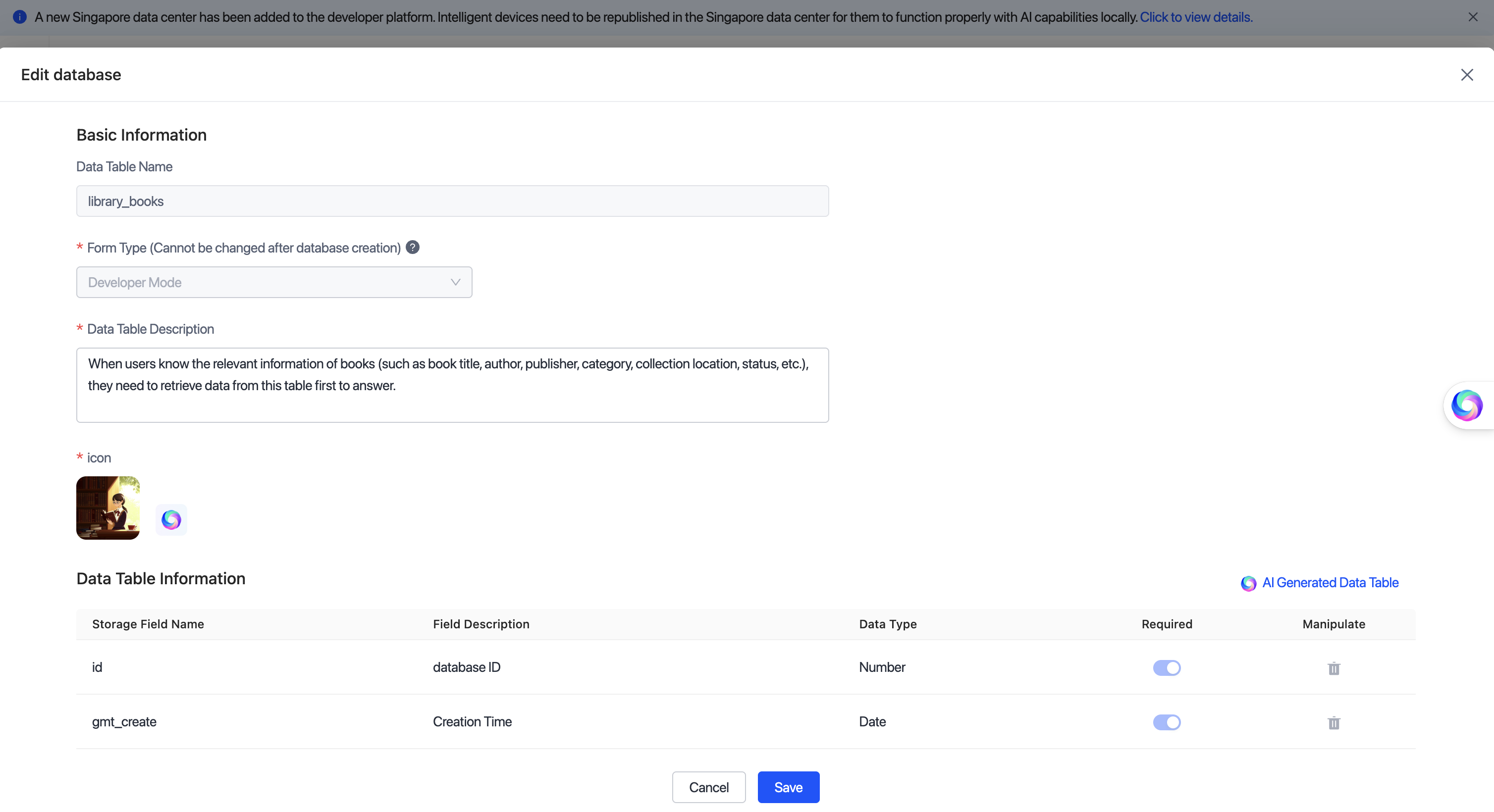
Item Configuration description Table name Use a naming format of lowercase letters and underscores (for example, user_diaryandbook_library).
The name should clearly reflect the business purpose and avoid ambiguous or duplicate names.Table type - Single-user mode: Suitable for independent data management for a single user, like a personal diary, learning records, and spending logs.
- Multi-user mode: Supports multi-user collaboration and data sharing, like task leaderboards, message walls, and family ledger.
- Developer mode: Data tables uniformly managed by the developer, like the knowledge base, product information, and backend FAQs.
Data table description Important: This field directly affects the AI’s understanding of the table’s semantics and its matching accuracy. The description should clearly state the purpose and content scope.
Example: When users inquire about book-related information (such as title, author, publisher, category, location, and status), prioritize retrieving data from this table for answers and recommendations.
This table supports book queries, loan record statistics, reading recommendations, and knowledge retrieval.
Providing a complete, specific, and semantic description for each table significantly improves the accuracy of AI invocations.Icon Select a concise and intuitive icon for each table to facilitate quick identification in the console. Icons that are more relevant to the business theme enhance the front-end display and retrieval experience. Table field Each field must include: - Field Name: Name in English.
- Field Description: Function and purpose.
- Data Type: String, boolean, number, time, and more.
- Required: Yes/no.
Clearer field definitions lead to more accurate AI data retrieval and semantic reasoning. Alternatively, you can generate table fields using AI, then manually adjust or supplement the descriptions in the generated results, as shown in the figure below: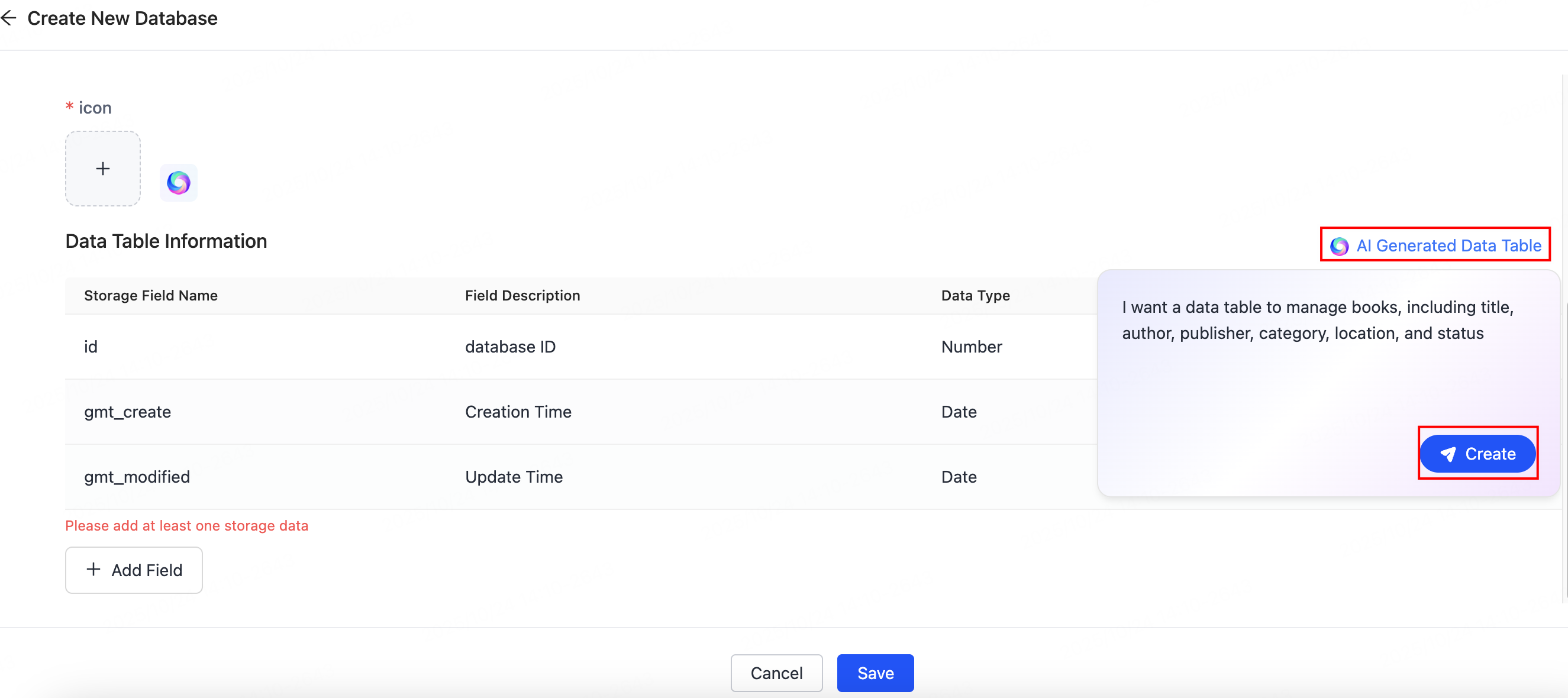
- The AI will intelligently infer the database structure based on the semantics you provide.
- More specific descriptions yield more precise structures, including field names, purposes, and data types.
- Supports multi-turn dialogue for fine-tuning field configurations. The system updates the structure definition in real-time.
-
After completing the form, click Save. The system will automatically initialize the table structure.
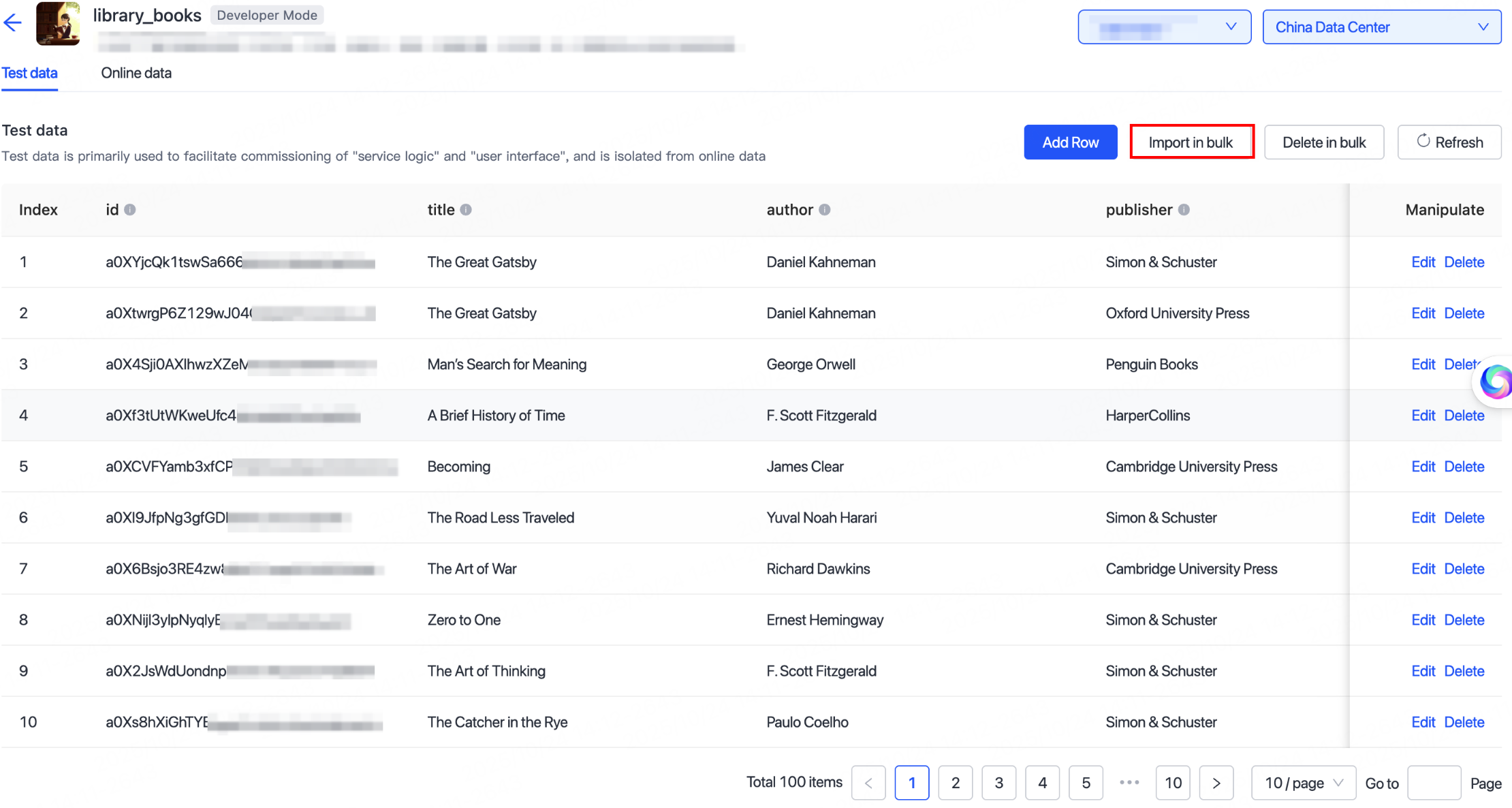
If using Developer Mode, you can click Import in bulk to import sample data for testing.
Testing and debugging
Proceed to the Agent Debugging step. You can choose to debug by scanning a QR code or use online debugging to verify the conversation responses.
Key factors that primarily influence the agent’s accuracy in correctly invoking the database include:
- Completeness of database and field descriptions: Clearer descriptions enable the AI to better understand the data’s purpose and structure.
- Clarity of database usage rules in the agent prompt: Explicitly defining in the prompt which scenarios should trigger queries or writes, supplemented with relevant examples, helps the AI automatically select the correct database behavior.
Is this page helpful?
YesFeedbackIs this page helpful?
YesFeedback





