Overview
TuyaOS is designed with a modular approach, with capabilities covering basic services, security, networking middleware, and various IoT services. Built on top of TuyaOS capabilities, TuyaOS networked product development framework is a set of SDKs used to build networked products for different specifications and scenarios. Unified APIs and a variety of components allow you to focus on building applications with a consistent development experience, without taking care of specific implementations.
Architecture
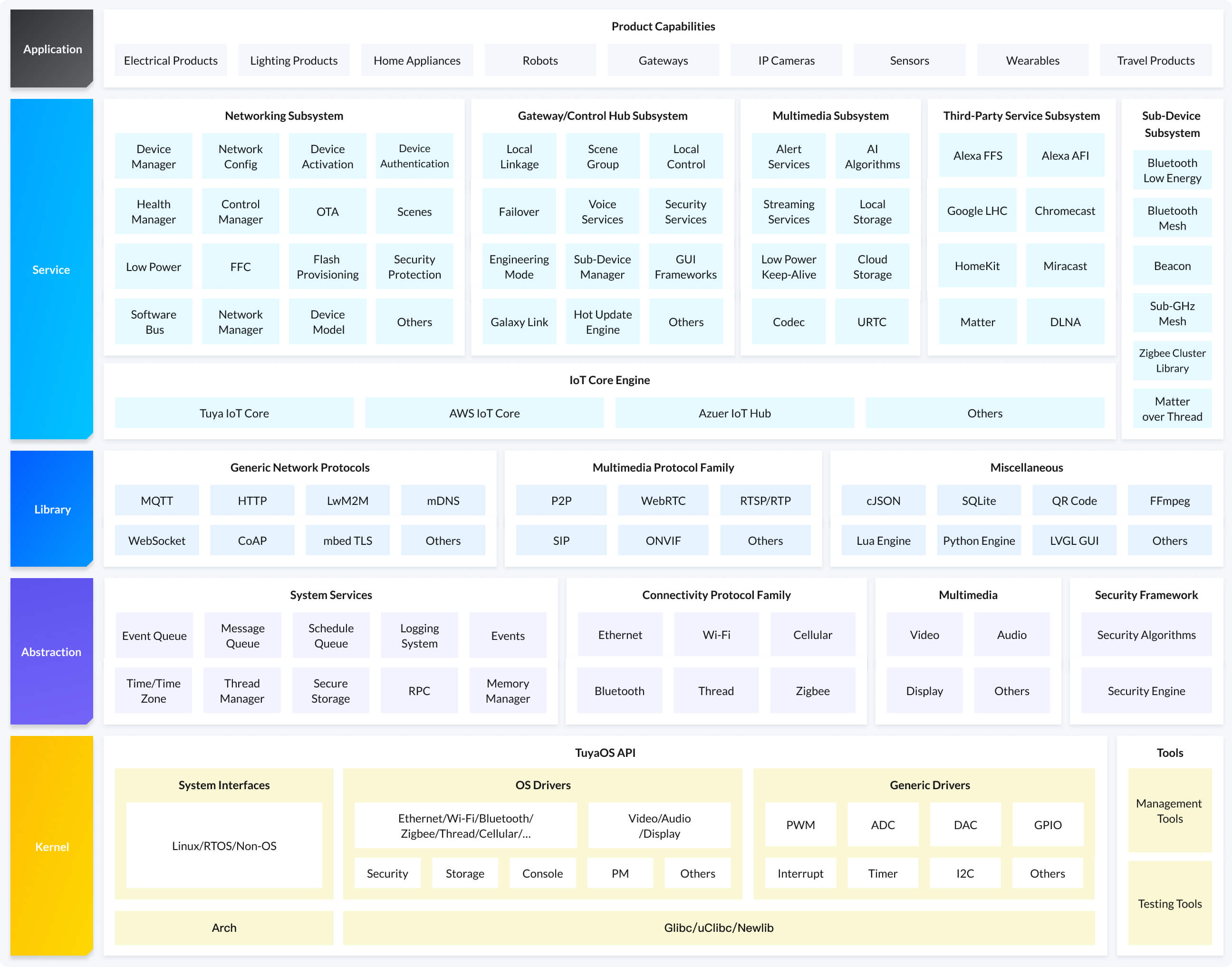
Capability list
Device management
| Capability |
Description |
| Initialization |
After a device is powered on and started, it calls a range of APIs to initialize the hardware environment, TuyaOS software, and applications. On application initialization, you need to provide callback functions as needed to handle internal events including status changes, device controls, and firmware updates. |
| Reset |
A device is restored to the settings that the device had before it was paired and activated. Device reset can be triggered by hardware operation or mobile app operation. In terms of device status after a reset, there are two types of reset: normal reset (device unbound) and factory reset (device unbound with data erased). |
| Authorization |
Authorization is the process of writing the device ID assigned by Tuya to the non-volatile memory on the device for the purpose of authentication. You can perform authorization through code or a tool. The former is for debugging purposes, and the latter is for mass production. |
Pairing and activation
Wi-Fi or Wi-Fi and Bluetooth combo
| Capability |
Description |
| Pairing in AP mode |
A device advertises its Wi-Fi hotspot in access point (AP) mode. After the mobile phone is connected to this hotspot, it sends the device the SSID and password of the router and the activation token over a TLS connection. The device connects to the router with the received SSID and password and then authenticates with the cloud for activation using the authorization information and token. |
| Pegasus pairing |
With the same mobile app, the paired Wi-Fi device (referred to as the server) uses Wi-Fi beacons and probe request/response frames to discover devices ready for pairing (referred to as the client). After discovering a client, the server negotiates a secret key, establishes a connection with the client and sends SSID, password, and activation token to the client. The client connects to the router with the received SSID and password and then authenticates with the cloud for activation using the authorization information and token. |
| Pairing over Bluetooth |
A device sends Bluetooth advertising packets to any listening device. After discovering this device, the mobile app pairs with it, exchanges keys, establishes a connection, and sends it the SSID and password of the router and the activation token. The device connects to the router with the received SSID and password and then authenticates with the cloud for activation using the authorization information and token. |
| Custom pairing |
There are multiple methods to get SSID and password, such as audio, video, and NFC. Tuya provides an API that allows you to pass in the SSID, password, and activation token that are obtained with your preferred method. The device connects to the router with the received SSID and password and then authenticates with the cloud for activation using the authorization information and token. |
| Activation over Bluetooth without internet (plug & play) |
Without an internet connection, the mobile app is connected to the device over Bluetooth to get the device information and then acts as a proxy to this device for activation. In this case, the device uses the point-to-point topology. Note: Cloud-based capabilities are not available on devices that are activated over Bluetooth without an internet connection. |
| Activation in AP mode without internet |
Without an internet connection, the mobile app scans the QR code on the device to get the device information and then acts as a proxy to this device for activation. In this case, the device can work without an internet connection. |
| Device pairing modes |
Tuya defines six device pairing modes to accommodate different scenarios. For example, a device is not paired after it enters pairing mode (anti-misoperation for a short time period and low power mode for a long time period), or a device is reset after it is paired. |
| Backup Wi-Fi |
Set up the SSID and password of a backup Wi-Fi network using the mobile app. When a device is disconnected from the Wi-Fi network, it automatically connects to the backup Wi-Fi with the best signal strength. This can avoid pairing the device again. |
Ethernet
| Capability |
Description |
| Device binding over a LAN |
After a device is connected to a router, it regularly sends user datagram protocol (UDP) packets over a LAN. After the mobile app receives a packet, it negotiates a secret key and then sends the activation token to the device. The device then authenticates with the cloud for activation using the authorization information and token. |
| Device binding via QR code |
After the device is connected to the router, the mobile app scans the QR code on the device body or on the device’s screen to get device information. Then, through the cloud, the mobile app pushes the activation token to the device that has been connected to the server. The device authenticates with the cloud for activation using the authorization information and token. |
Device control
| Capability |
Description |
| Data point (DP) model and device control protocol |
The TuyaOS device model description, which is used to control a physical device. |
| Control over LAN |
When the mobile app and a device are connected to the same LAN, the device can be controlled over a LAN. |
| Control over Bluetooth |
When the mobile app is near an offline device, the device can be controlled over Bluetooth. |
| Channel priority |
You can set the priority of channels over which a device is controlled. By default, the priority order is: Wi-Fi LAN > Wi-Fi WAN > Bluetooth. |
Basic services
| Capability |
Description |
| Secure storage |
Encrypted key-value store as well as file-based data storage in plain text. |
| Health checks |
Regularly check the device memory, wireless signal, and task status. You can customize the metrics. |
| Logging service |
Local logs that record device operations. Exceptions can be recorded, sorted, and reported to the cloud. |
| Event service |
Event subscription and publishing. This allows you to monitor and handle events as needed. |
| Time service (time zone and daylight saving time (DST)) |
Time management and maintenance. UTC time and local time are supported. Local time is determined by UTC time, time zone, and DST. |
| Timer queue |
Software timers. |
| Job queue |
Job queues used to process asynchronous low-priority tasks on which blocking might occur. |
| Connection management |
Device connection management, such as Wi-Fi, Ethernet, and Bluetooth, which is used to maintain the direct connection between devices and the network. |
| Thread management |
Managing threads. |
Device driver
Connection driver
| Capability |
Description |
| Wi-Fi |
Wi-Fi driver |
| Bluetooth |
Bluetooth driver |
Peripheral driver
| Capability |
Description |
| GPIO |
GPIO driver |
| ADC |
ADC driver |
| PWM |
PWM driver |
| I2C |
I2C driver |
| I2S |
I2S driver |
| UART |
UART driver |
| DAC |
DAC driver |
| SPI |
SPI driver |
Third-party ecosystem
| Capability |
Description |
| Matter |
The full features of Matter protocol enable your device to be Matter-compatible and integrated into the Matter ecosystem. |
| HomeKit |
The full features of HomeKit protocol enable your device to be HomeKit-compatible and integrated into the HomeKit ecosystem. |
Power management
| Capability |
Description |
| Low power Wi-Fi |
Low power Wi-Fi management. |
Scheduled task
| Capability |
Description |
| Local schedule |
The scheduled task is downloaded to the device with a timer created accordingly. The device runs the task after the timer expires. |
| Sunrise/sunset-based schedule |
One of the types of local schedule, allowing users to schedule tasks based on local sunrise and sunset. |
| Calendar-based schedule |
One of the types of local schedule, allowing users to schedule tasks with a recurrence pattern. For example, repeat weekly, repeat on odd or even days, or repeat every x day(s) or hour(s). |
Update service
| Capability |
Description |
| Silent update |
The device checks for and installs firmware updates automatically. |
| Update notification/forced update |
The mobile app notifies the device of available firmware updates. |
| Subordinate firmware update |
Update firmware and files on the device. |
Device accessory
| Capability |
Description |
| Remote control over Wi-Fi FFC |
Remote control of devices over a proprietary Wi-Fi mesh protocol. |
| Remote control over Bluetooth beacon |
Remote control of devices over Bluetooth beacon. |
Device security
| Capability |
Description |
| Security system (security level and capability) |
Device authentication, secure storage, secure communication, and privacy and data compliance. |
Network
| Capability |
Description |
| iot-dns |
Domain name configuration, certificate management, and domain name resolution. |
| https |
HTTPS library. |
| mqtt over tls |
MQTT library. |
| mbedTLS |
Mbed TLS library. |
System service
| Capability |
Description |
| Memory management (tuya heap6) |
TuyaOS proprietary heap management. |
| TCP/IP stack (tuya lwip) |
TuyaOS self-maintained lwIP protocol. |
| Bluetooth stack (tuya Bluetooth) |
TuyaOS self-maintained Bluetooth protocol. |
| tuya wpa supplicant |
TuyaOS self-maintained wpa_supplicant component. |
Support and help
If you have any problems with TuyaOS development, you can post your questions in the Tuya Developer Forum.







