What is Edge Gateway
Last Updated on : 2024-06-21 08:08:14download
Tuya Edge Gateway extends cloud capabilities to local edge devices and enables edge devices to quickly respond to local events with local computing services. These services feature low latency, cost efficiency, secure privacy, and local autonomy.
All services are installed from Docker images. This enables easy deployment and efficient management across platforms. On top of that, Edge Gateway provides excellent support for link security, variant scenarios, and cloud development components. Smart devices are compatible with common IoT protocols to extend the types of supported smart devices. You can select a preferred protocol to support third-party hardware devices based on your needs.
Features
Edge Gateway can run on edge gateway hardware by using standard containers. This allows you to control devices and process sub-device data through multiple steps. For example, the data can be collected, parsed, cleansed, aggregated, and then stored. You can achieve multiple purposes, including data security, real-time device control, scene linkage, edge-cloud synergy, and reliable long-term offline operation. In this case, the following features are supported:
- Compatible with network protocols including TCP/IP, UDP, and HTTP.
- Supports multiple functions such as equipment security authentication and access control.
- Comprehensive edge computing minimizes the workload on the platform server.
- Supports online link detection and automatic reconnection.
- Things data models simplify connections to sub-devices over different protocols.
- Allows you to query system status, network connection status, and router status.
- Supports Telnet, web, and SSH configurations.
- Provides remote updates, local system logs, remote logs, and serial output logs.
Advantages
-
Edge-cloud synergy deployment: Deploy cloud configurations to the edge gateway with only a few simple steps to achieve edge-cloud synergy.
-
Standard things data models: Define devices by things data models to provide standard integration solutions for efficient development.
-
Full-link data security: Adopt a variety of data encryption and authentication methods and a complete permission management system to ensure data security.
-
Remote O&M: Provide remote O&M capabilities of secured login to the edge gateway to manage gateway devices.
-
Rule engine: Convenient rule engine configuration and a collection of rule resources simplify rule development.
Supported IoT protocols
A number of common IoT protocols are supported. Protocol drivers are available to enable connections to popular sub-devices. You can use the required toolkits to develop drivers for your proprietary protocol.
- Modbus: an industrial protocol that implements communication between automation devices.
- BACnet: designed to provide mechanisms for communication between building automation and control systems for different applications, such as heating, ventilating, air-conditioning control, refrigeration, lighting control, access control, and fire detection systems.
- OPC Unified Architecture (OPC UA): applies to embedded field devices, such as radio-frequency identification (RFID) readers and protocol converters. This protocol is a machine-to-machine communication protocol for industrial automation developed by the OPC Foundation.
- OPC Data Access (OPC DA): a group of client-server standards that provides specifications for real-time data communication between different applications. These applications can be deployed on programmable logic controllers (PLCs) at workshops, on-premises remote terminal units (RTUs), and desktop computers. OPC DA servers can maintain stable communication with these applications.
- Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP): an internet standard protocol for communication with managed devices on IP networks. Typical SNMP-based devices include servers, workstations, routers, switches, and hubs.
- KNX: built on the European Installation Bus (EIB) communication stack and extended with the beneficial configuration modes of BatiBus and European Home Systems Association (EHSA). This protocol supports comprehensive solutions for home and building automation.
- DALI: an international open standard for network-based products that control lighting.
Device ecosystem
Edge Gateway combines stock-keeping units (SKUs) of smart devices and integrates the no-code development solution over third-party protocols. This allows you to build a leading ecosystem that interconnects diverse smart devices.
Edge Gateway provides software solutions and can run in a standard Linux-based Docker container of version 20.10 or later.
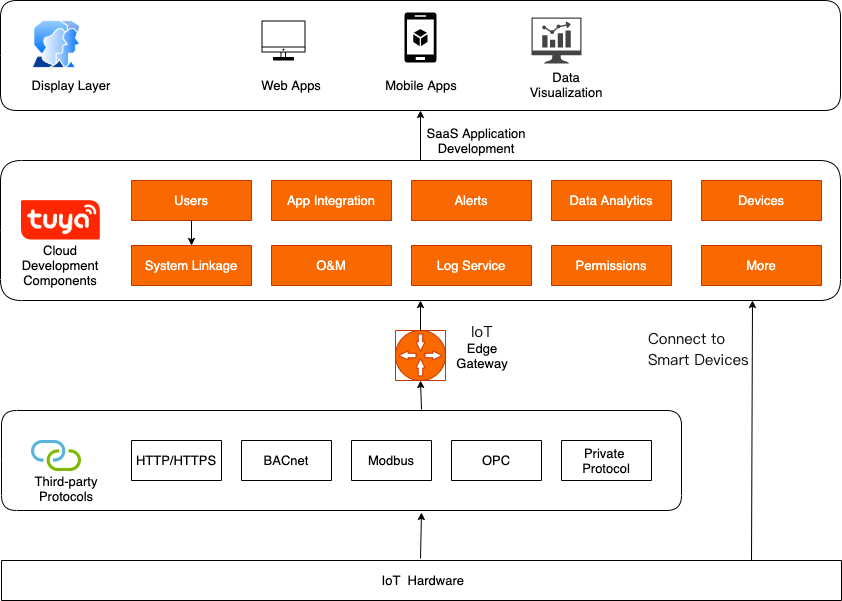
Cloud development components
The Tuya Developer Platform provides centralized management of smart devices or third-party smart devices that are powered to the platform. Cloud development components on the platform are available to these smart devices. These components encapsulate service logic for different industries and provide dedicated capabilities for each industry.
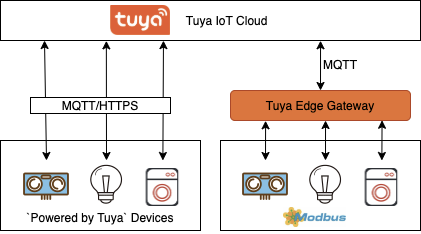
Scenarios
Edge gateways apply to various scenarios in which workloads are migrated from the cloud to the edge. Particularly, edge gateways can optimize the processing of requests from a large number of smart devices in different scenarios. The following scenarios show examples of valuable solutions provided by edge gateways.
- Smart park: provides end-to-end communication over multiple protocols and supports multiple carrier networks that serve office communication, video streaming, and Wi-Fi solutions. Multiple capabilities can be implemented, such as smart data analytics for videos and connected elevators, street lighting control, integrated security protection, and night infrared patrol. This allows you to create a standard integrated smart park system.
- Smart agriculture: provides multiple capabilities, such as sensing, networking, local computing, and device control, and enables interconnection across devices for different purposes, such as water supply, fertilization, and disinsection. This scenario integrates urban water supply devices, information systems, and service processes.
- Industrial manufacturing: encapsulates on-premises devices into edge devices and connects these devices to industrial data platforms in a flat interconnection architecture. This allows these devices to access comprehensive cloud services such as big data and deep learning over industrial wireless and digital software-defined networking (SDN) networks.
Is this page helpful?
YesFeedbackIs this page helpful?
YesFeedback





