WXU Series Modules
Last Updated on : 2024-06-18 01:42:55download
This topic describes information about implementing serial communication between WX series modules and MCUs.
Overview
WXU is a Wi-Fi and Bluetooth Low Energy (LE) combo module. This module consists of a highly integrated wireless chip T103C-HL with built-in Wi-Fi stacks and various library functions. It comes with a low-energy ARMv8 MCU, WLAN MAC, and 1T1R (1 transmitter/1 receiver) design. It provides output frequency up to 160 MHz, 320 KB on-chip SRAM, 2 MB on-chip flash memory, and configurable GPIOs that can function as digital peripherals for various applications.
Serial protocol
- Wi-Fi generic serial protocol
- Low power Wi-Fi generic serial protocol
- Wi-Fi HomeKit generic serial protocol
Serial communication between module and MCU
-
Connection between a module and a 3.3V MCU
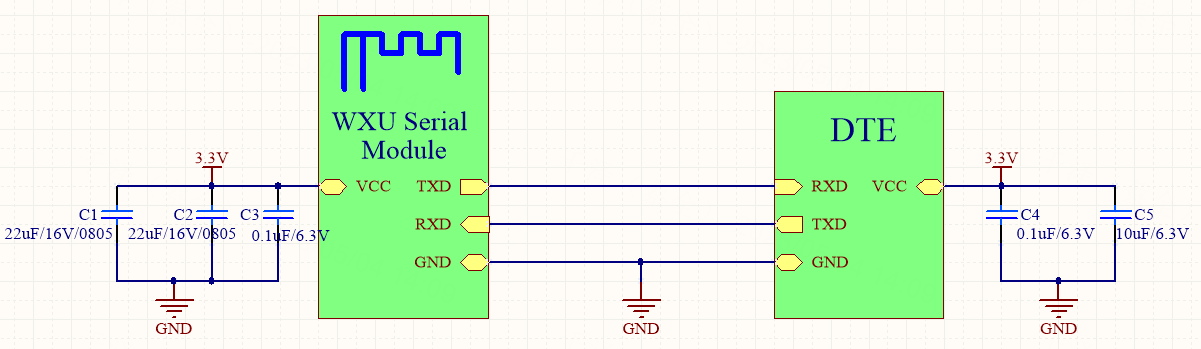
The VCC pin is the power pin of the module. The TXD and RXD pins are used for serial communication.
-
Connection between a module and a 5V MCU
In the following circuit diagram, voltage level translation can be implemented with a bidirectional voltage-level translator, a MOS transistor, or a triode.
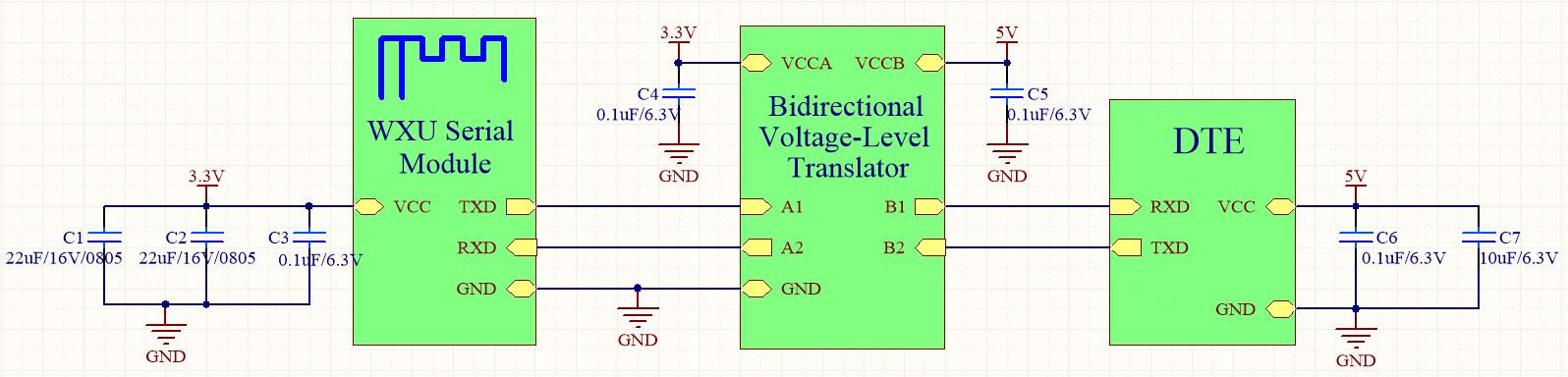
The VCC pin is the power pin of the module. The TXD and RXD pins are used for serial communication.
Level translator reference
-
N-channel MOSFET level translator: An N-channel MOSFET and a built-in body diode are used to implement two-way communication.
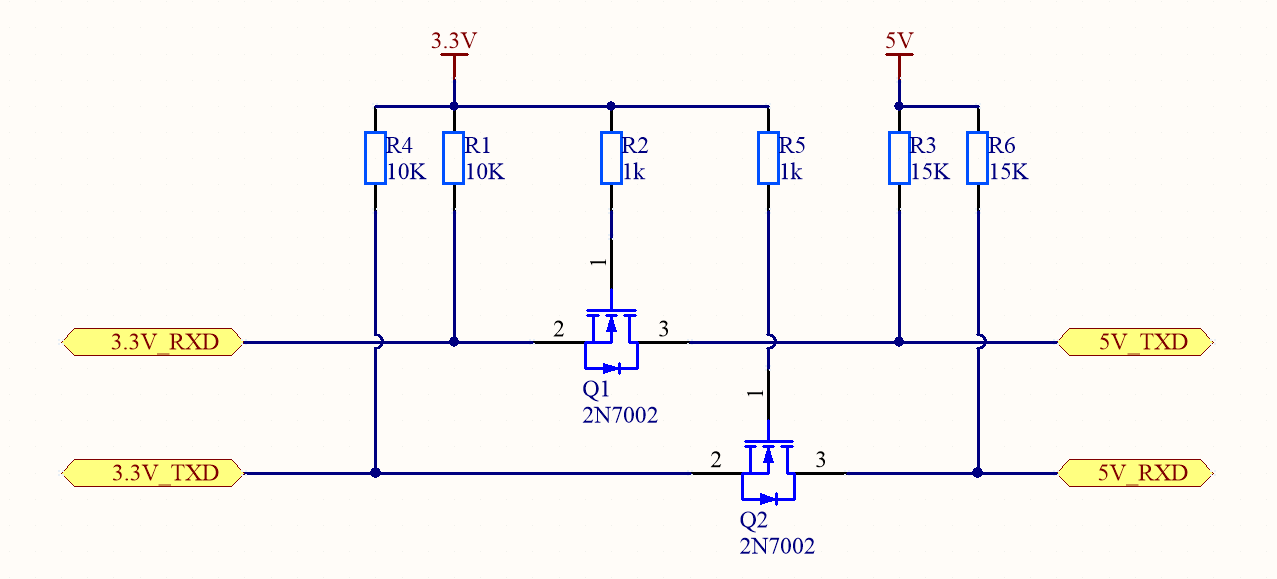
-
NPN triode level translator: An NPN triode is used to implement one-way communication.
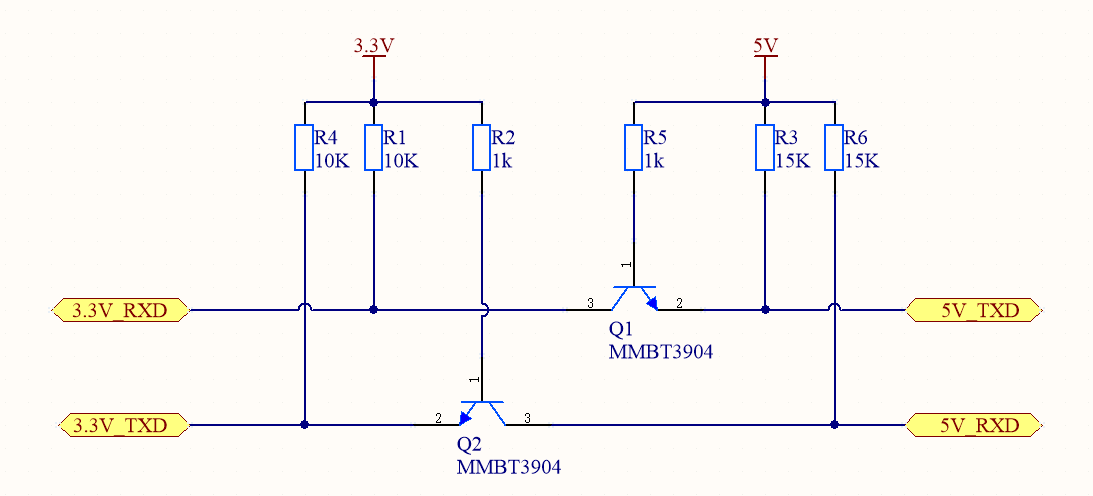
Design specification
Serial port pin
The following table lists the specification and pin information of WXU modules for serial communication with an MCU.
| Module model | Input voltage (TYP) | Input current (MAX) | Power pin | Power pin on silkscreen | TXD pin | TXD on silkscreen | RXD pin | RXD on silkscreen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WYU | 3.3V | 420 mA | 14 | VBAT | 15 | TXD | 16 | RXD |
| WXU-IPEX | 3.3V | 420 mA | 14 | VBAT | 15 | TXD | 16 | RXD |
Power supply
- Given that the supply current for 3.3V modules should be greater than the maximum input current, a supply current of at least 500 mA is recommended.
- The module will have a high peak current when powered on, reset, or paired. To reduce the peak current, it is recommended to add two external 22 μF filter capacitors (16V withstand voltage and 0805 case size) and one 0.1 μF ceramic capacitor.
- Place the filter capacitors C1, C2, and C3 near the power pin of the module.
Pins of the module
- The reset pin or enable pin of the module is a hardware reset pin. The module has internal weak pull-up resistors configured. If the pin is not used, it can float. If a module has been paired, this pin cannot be used to clear pairing information.
- When pin initialization is in progress after a system reboot, the user UART should be in a high impedance state.
- Other unused pins can float.
- For more information about the pin definition, see the datasheet of each module.
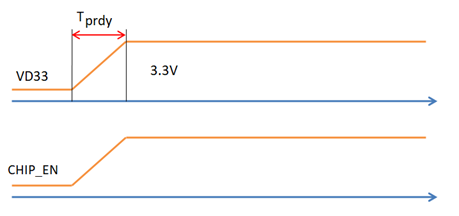
Power-on sequence of the module
Every time a module is powered on, the voltage settling time of the module power pin (tpRDY) is not greater than 5 ms.
Auto-baud detection firmware
To detect the baud rate of the MCU, the program will turn on and off the UART peripheral several times. When UART is turned off, its TX and RX pins will be in a high impedance state. If you plan to use a level translator circuit, make sure the signal lines remain the level in idle state (high level) when the TX and RX pins are high impedance.
Antenna clearance
- Do not use metal shells or plastic shells with metallic paint or coating in the direction of the antenna radiation. Do not use metal objects such as screws and rivets near the antenna, which might affect the antenna efficiency.
- Try to increase the distance from the top shell to the antenna to minimize the impact on antenna performance.

- Try to increase the distance from the upper and bottom shells to the antenna to minimize the impact on antenna performance.
- Keep the module away from speakers, power switches, cameras, HDMI, USB, and other high-speed signals to avoid interference.
- Avoid metal shielding near the antenna. If co-channel interference occurs, you must evaluate the impact on the antenna performance and ensure isolation from interference.
Placement
-
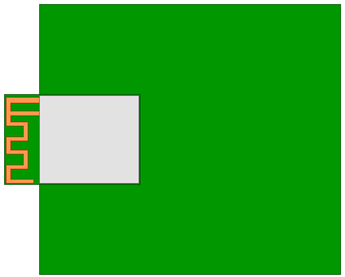
Horizontal placement
We recommend that you place the module at the edge of the backplane with the antenna facing outward, and flush the module’s GND terminal with the backplane’s GND terminal. Both terminals are fully connected.
-
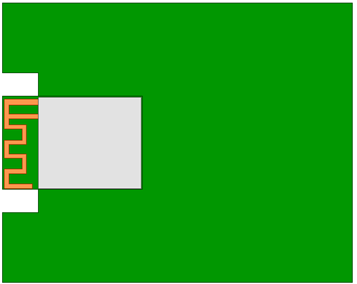
Embedded placement
Embed the module into the backplane through a slot that is flushed with or deeper than the module’s GND terminal. The side of the slot must be 15 mm or farther from the module’s board edge.
A wider slot can achieve better performance that is still weaker than that of horizontal placement.
-
Vertical placement
Insert the module vertically into the backplane slot with the antenna facing upward. The module’s GND terminal and the backplane’s GND terminal must be fully connected. We recommend that you keep a clearance distance of 15 mm or more around the antenna.
Low power design
Option 1: Control module power pin on/off
This circuit design can achieve overall low power consumption.
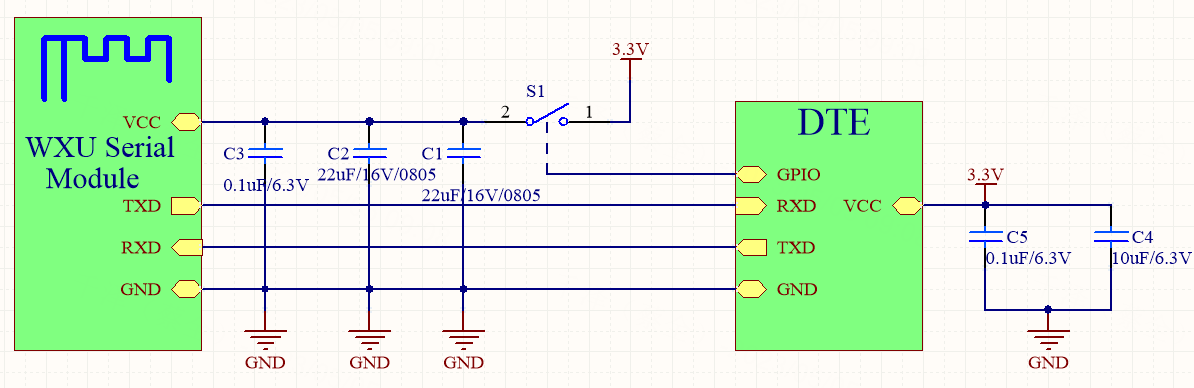
-
How it works: As shown in the circuit diagram, the MCU can control the switch
S1with the GPIO pin to power on/off the module.- When the MCU has data to report to the cloud, it turns the
S1on. Then, the module can receive data from the MCU and report data to the cloud and the mobile app. - When data reporting is completed, the module will be powered off and consume no power.
- When the MCU has data to report to the cloud, it turns the
-
Disadvantages:
- Current sinking occurs. When the switch
S1is turned off, the TXD and RXD pins on the module are still connected to the RXD and TXD pins on the MCU. - Therefore, the current from the MCU can flow into the VCC pin of the module through the UART pin.
- The TXD and RXD pins of the module are high, so the current sinking will increase the consumption of the module.
- As a result, the module might not work properly.
- Current sinking occurs. When the switch
-
Solution 1: Optimize the software of the MCU without hardware modification. When the MCU detects the data reporting is completed, the program proceeds with the following steps.
-
Set the TXD and RXD pins of the MCU as GPIO pins that are configured as the open-drain or weak pull-down mode.
-
Turn the switch
S1off to power off the module. -
This way, when the MCU has data to report, it turns the
S1on firstly. -
Then, it configures the TXD and RXD pins as the UART to establish communication with the module for data transmission.
This solution does not apply to MCUs whose UART pin cannot be configured as the open-drain or weak pull-up mode. If the UART circuit has a pull-up resistor, one terminal of the resistor must be connected to the VCC pin of the module, or you can directly remove this resistor.
-
-
Solution 2: Add a level translator to the circuit without software modification. See the circuit diagram in the preceding sections Level translator reference and Connection between a module and a 3.3V MCU and embed a level translator in the UART circuit.
Option 2: Reduce power usage in idle state
Pull down the module’s clock enable (CEN) pin or reset (RST) pin to reduce idle consumption.
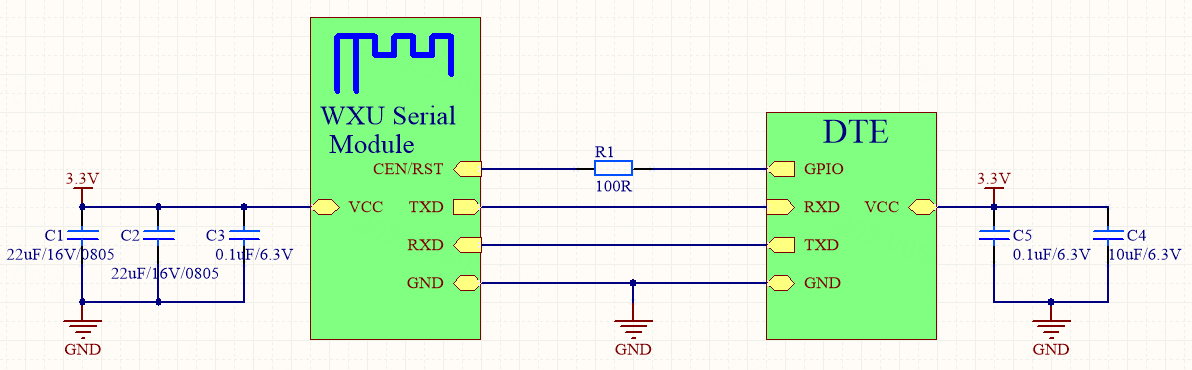
-
How it works: As shown in the circuit diagram, the MCU can control the CEN or RST pin with the GPIO pin to power on/off the module.
- When the MCU has data to report to the cloud, the GPIO outputs high to power on the module. Then, the module can receive data from the MCU and report data to the cloud and the mobile app.
- When data reporting is completed, the GPIO outputs low and the module runs in reset mode with low power consumption.
-
Disadvantage: If the CEN or RST pin has a 10 kΩ internal pull-up resistor, when the module runs in reset mode, this resistor can consume power.
Battery powered
WXU modules support battery-powered low-power persistent connection. You can add a boost converter to extend battery life.
Reference circuit for a boost converter
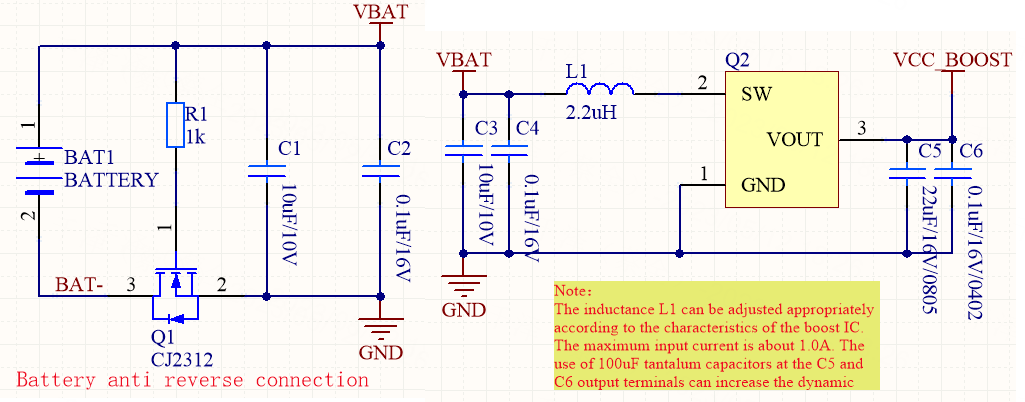
| Symbol | Description | Pin | Package | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Battery | Battery | BAT1 | Battery-5-15.06 mm | 1 |
| 10 μF/10V | Non-polarized capacitor | C1 and C3 | C0404_GRM15 | 2 |
| 0.1 μF/16V | Non-polarized capacitor | C2, C4, and C6 | C0404_GRM15 | 3 |
| 22 μF/16V/0805 | Non-polarized capacitor | C5 | C0603_GRM18 | 1 |
| 2.2 μH | Inductor | L1 | L2520 × 120 | 1 |
| CJ2312 | N-Channel MOSFET | Q1 | SOT23-3 | 1 |
| Boost | Voltage converter | Q2 | - | 1 |
| 1k | Resistor | R1 | R0402 | 1 |
- You select a boost converter based on the WXU datasheet and your needs.
- You can increase the inductance of L1 according to the characteristics of the boost converter. The maximum input current is about 1.0A. Using a 100 μF tantalum capacitor on C5 and C6 output terminals can improve the dynamic response of the boost converter. With the same load, the start voltage will also be reduced.
Radio frequency (RF) test
The antenna is susceptible to the distance from the shell to the surrounding components. We recommend that you test the RF performance after the final test. The RF test items and metrics are listed in the following table.
| Test item | Test metric |
|---|---|
| Increasing indoor distance | ≥ 25 m |
| Increasing outdoor distance | ≥ 75m |
| Total radiated power (TRP) in the signaling mode of end devices (test mode of 11B 11 Mbit/s). | ≥ 10 dBm |
| Total isotropic sensitivity (TIS) in the signaling mode of end devices (test mode of 11B 11 Mbit/s). | ≤ -80 dBm |
- TRP and TIS must be tested in a dark chamber of the antenna manufacturers or certified organizations.
- The test items apply to most Wi-Fi products, excluding certain special products.
Is this page helpful?
YesFeedbackIs this page helpful?
YesFeedback





