T5-AI Box Digital Dual-MIC Voice Solution
Last Updated on : 2025-08-22 06:06:02download
Tuya T5-AI (T5AI-EVB-PRO) digital dual-microphone voice solution is a voice interaction AI box based on the T5-E1, an embedded Wi-Fi and Bluetooth low energy combo module developed by Tuya Smart. The AI box is equipped with two digital microphones (DMIC) and is compatible with one analog microphone, one audio loopback, one speaker, an LCD, and lithium battery charging management. Support major AI models including Doubao, DeepSeek, Qwen, OpenAI, and Gemini, featuring button wake-up, wake-word activation, and free conversation capabilities.
This AI box delivers vivid and engaging AI voice interaction experiences, making it ideally suited for AI smart toys and similar products.
Functional block diagram
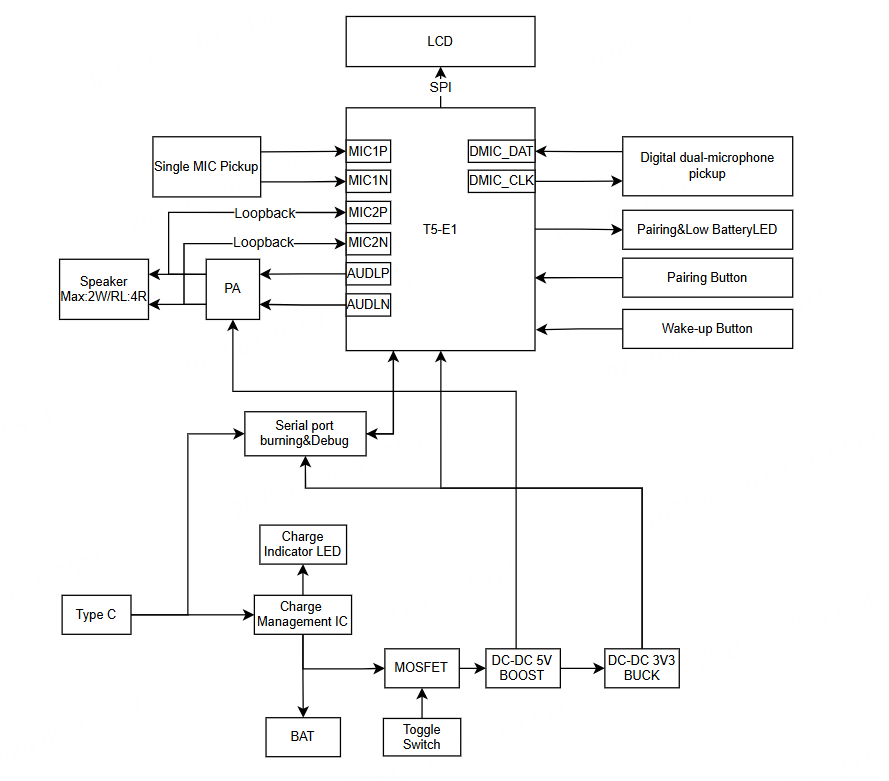
DMIC description
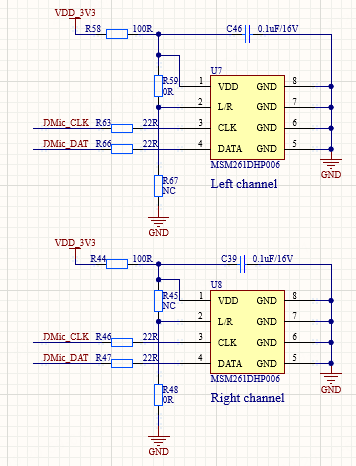
DIMC channel settings
L/R pull-up corresponds to the left channel, and L/R pull-down corresponds to the right channel. It is recommended to maintain a distance of 30 mm between pickup holes of the two digital MEMS microphones.
Peripherals
| Peripheral | Description |
|---|---|
| T5-E1 module | An embedded Wi-Fi and Bluetooth combo module used to control the AI box. With rich peripheral interfaces and powerful signal processing capabilities, this module is suitable for various scenarios in the AIoT field. |
| I/O button | Connected to P6 and P7 of the T5-E1 module, it can be configured as a button. |
| Speaker | The speaker connector has a 1.25 mm pitch and can drive speakers up to 2 W/RL=4Ω. |
| I/O LED | Connected to P25 of the T5-E1 module, it can be configured as an LED indicator. |
| USB type-C | Charging and data port, used for battery charging, T5 firmware flashing, and log reading. |
| BAT | Battery connector with a 1.25 mm pitch. |
| DMIC | Default DMIC. L/R pull-up corresponds to the left channel, and L/R pull-down corresponds to the right channel. |
| Mic1 | (Optional) The microphone connector, with a 1.25 mm pitch, connects to the module’s audio ADC. |
| LCD | The LCD connector, with a 2.54 mm pitch, connects to the module’s SPI0. |
| Power LED | Charging status indicator. |
| Switch | Toggle switch to turn the power on and off. |
Recommended I/O configuration of SPI LCD
| Pin | Definition |
|---|---|
| P44 | SPI0_SCK |
| P46 | SPI0_MOSI |
| P18 | LCD_RST_N |
| P47 | LCD_DC |
| P45 | LCD_CSN |
| P19 | LCD_BL_ON |
| P17 | LCD_PWR_ON |
Considerations
Antenna clearance
- Do not use metal shells or plastic shells with metallic painting or coating in the direction of the antenna radiation. Do not use metal objects such as screws and rivets near the antenna, which might affect the antenna efficiency.
- Try to increase the distance from the top shell to the antenna to minimize the impact on antenna performance.
- Try to increase the distance from the upper and bottom shells to the antenna to minimize the impact on antenna performance.
- Keep the module away from speakers, power switches, cameras, HDMI, USB, and other high-speed signals to avoid interference.
- Avoid metal shielding near the antenna. If co-channel interference occurs, you must evaluate the impact on the antenna performance and ensure isolation from interference.
Antenna placement
- Horizontal placement
We recommend that you place the module at the edge of the backplane with the antenna facing outward, and flush the module’s GND terminal with the backplane’s GND terminal. Both terminals are fully connected. - Embedded placement
Embed the module into the backplane through a slot that is flushed with or deeper than the module’s GND terminal. The side of the slot must be 15 mm or farther from the module’s board edge. A wider slot can help achieve better performance, but it is weaker than that of horizontal placement. - Vertical placement
Insert the module vertically into the backplane slot with the antenna facing upward. The module’s GND terminal and the backplane’s GND terminal must be fully connected. We recommend that you keep a clearance distance of 15 mm or more around the antenna.
Selection and design solutions of the microphone and speaker
-
Microphone selection
- Acoustic technical indicators reference:
- Analog microphone: Sensitivity ≥ -38 dBV, SNR ≥ 62 dB, THD ≤ 1%, and AOP ≥ 120 dB SPL.
- Digital microphone: Sensitivity = -26±2 dBFS, SNR ≥ 62 dB, THD ≤ 1%, and AOP ≥ 120 dB SPL.
- Recommend prioritizing MEMS microphones (superior SNR, consistency, and reliability).
- The frequency response of the microphone should be kept as flat as possible within the range of 100 Hz to 8 KHz, with a fluctuation of ≤ 3 dB.
- Phase consistency shall be ≤ 5° within the 100 Hz to 4 KHz frequency range, and ≤ 10° within the 4 KHz to 8 KHz frequency range.
- Acoustic technical indicators reference:
-
Speaker selection
- Total harmonic distortion (THD) of the speaker:
- 100 Hz to 200 Hz: THD < 8%.
- 200 Hz to 400 Hz: THD < 5%.
- 400 Hz to 8 kHz: THD < 3%.
- Total harmonic distortion (THD) of the speaker:
-
Audio loopback and PA design guidelines
- The echo reference signal should be sampled near the speaker, taken from the power amplifier (PA) output.
- At maximum speaker volume, the echo reference signal input to the microphone must not saturate or distort. PA output THD at maximum volume shall be ≤ 1% within the 100 Hz to 10 kHz range.
- THD of the speaker at maximum volume:
- 100 Hz to 200 Hz: THD < 8%.
- 200 Hz to 400 Hz: THD < 5%.
- 400 Hz to 8 kHz: THD < 3%.
- At maximum volume, the sound pressure level (SPL) at the microphone must not exceed 102 dB @1 kHz.
- During peak playback, the loopback signal level should be between -3 dB and -6 dB.
-
AEC effect verification
- Dump 3 channels of audio (1 channel microphone, AFE loopback, and audio after AEC), then use audio tool software to check whether the audio has saturation, data loss, and other issues.
-
Microphone cavity design
- The inner diameter (ID) of the microphone pickup hole on the housing shall be > 0.8 mm.
- The hole length should be as short as possible, while the diameter should be as large as possible, with an aspect ratio (diameter to depth) ≥ 1:3.
- The microphone must be kept away from interference sources (such as cooling fans) or vibration sources (such as speaker vibrations or structural vibrations). Moreover, the microphone is sealed with a silicone cover and a solid surface to reduce housing vibration and sound transmission.
- Choose the softest possible silicone cover to minimize vibration between the microphone and mold.
- Avoid front cavity designs where both ends are smaller than the middle section to prevent forming resonant chambers.
-
Microphone and speaker layout considerations
- The entire device cavity must maintain proper sealing to ensure microphone recording remains unaffected by internal speaker playback vibrations and echo feedback.
- The speaker must have an independent acoustic chamber, with complete isolation from the microphone chamber. Any structural gaps should be sealed with foam or adhesive.
- The microphone pickup hole and speaker output ports should not face the same plane – ideally oriented at 90° or greater relative to each other.
- Maximize the distance between the speaker output and microphone input. A minimum 100 mm separation is recommended where possible.
- Silicone cover or foam can be applied between the microphone and device housing to enhance sealing and vibration damping.
Flash firmware
- Connect the USB data cable and select the serial port.
- Use serial port A for firmware flashing and serial port B for log reading.
- When a reset prompt appears, you need to reset or power off and restart the device.
- Firmware flashing utilizes the following pins: 3.3 V, GND, TX0, RX0, and RST.
PCB layout
- Ensure power traces are short and wide, with minimal loops, and provide at least two 8 mil (inner diameter) vias or one 12 mil (inner diameter) via for main IC power pins.
- For power traces, use copper pours whenever possible and add sufficient ground vias for heat dissipation. Pay attention to the current-carrying capacity of single traces.
Trace width reference (1 oz copper, outer layer): 20 mil width corresponds to 1A (without considering temperature rise). - The power amplifier IC output lines require differential routing, with coupled traces fully ground-guarded. Trace width should be calculated based on peak output current, and routing should be kept as short as possible.
- The module’s audio output signals
AUDLPandAUDLNmust be routed as differential pairs and fully ground-guarded. - The analog microphone signals must be routed as differential pairs and fully ground-guarded, with a minimum trace width of 8 mil.
Reference
Is this page helpful?
YesFeedbackIs this page helpful?
YesFeedback





